Origins of the Universe
... • If a star is moving away from us its waves are stretched and it appears more RED (RED SHIFT) • If a star is moving towards us its waves are squished and it appears more BLUE (BLUE SHIFT) ...
... • If a star is moving away from us its waves are stretched and it appears more RED (RED SHIFT) • If a star is moving towards us its waves are squished and it appears more BLUE (BLUE SHIFT) ...
Dust Clouds at the Center of Milky Way
... • In our Milky Way and in external galaxies, the space between the stars is filled with an interstellar medium consisting of gas and dust ...
... • In our Milky Way and in external galaxies, the space between the stars is filled with an interstellar medium consisting of gas and dust ...
Evidence for the Big Bang
... In 14 billion years, stars have not burned hot enough, or long enough to make this much helium The oldest stars (11 billion years) also have ~ 24% He so this He cannot have been made in stars! Big Bang - in early history the whole universe was the same temp as the inside of a star! Fusion in the ...
... In 14 billion years, stars have not burned hot enough, or long enough to make this much helium The oldest stars (11 billion years) also have ~ 24% He so this He cannot have been made in stars! Big Bang - in early history the whole universe was the same temp as the inside of a star! Fusion in the ...
understanding-the
... c. The blue shift indicates that distant galaxies are moving away from each other. d. The blue shift indicates that distant galaxies are moving towards each other. ...
... c. The blue shift indicates that distant galaxies are moving away from each other. d. The blue shift indicates that distant galaxies are moving towards each other. ...
Structure of the Universe
... Spectroscopic Parallax -- Have to be able to resolve star and it must be bright enough to get a spectrum ...
... Spectroscopic Parallax -- Have to be able to resolve star and it must be bright enough to get a spectrum ...
The initial conditions and the large
... – The Universe in its globality can be treated as a physical system – Science can deal with times and places we cannot experience (the observable Universe is a strict subset of the Universe) ...
... – The Universe in its globality can be treated as a physical system – Science can deal with times and places we cannot experience (the observable Universe is a strict subset of the Universe) ...
Bayesian Spectral Line Fitting
... Go to https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.08278 to read the paper and get the code ...
... Go to https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.08278 to read the paper and get the code ...
ppt
... Many aspects of the physics that govern galaxy formation depend simply on galaxy and dark matter properties as indicated by observed scaling relations. ...
... Many aspects of the physics that govern galaxy formation depend simply on galaxy and dark matter properties as indicated by observed scaling relations. ...
Stellar Masses
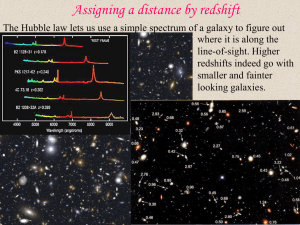
... Hubble’s Law • The prelude to Hubble’s Law was the establishment of measurements of galactic distances and also measurements of their Doppler shifts. • Vesto Slipher [Lowell Observatory] measured the redshifts of many galaxies[nebulae] in the early decades of the 20thC. They were expected to be ran ...
... Hubble’s Law • The prelude to Hubble’s Law was the establishment of measurements of galactic distances and also measurements of their Doppler shifts. • Vesto Slipher [Lowell Observatory] measured the redshifts of many galaxies[nebulae] in the early decades of the 20thC. They were expected to be ran ...
How does light tell us the temperatures of planets and stars
... Very Large Array (VLA), New Mexico ...
... Very Large Array (VLA), New Mexico ...
Two prevailing theories on how the universe was created
... was stealing a million dollars from his vault. He caught the thief and turned him into the police, then when the owner found out he thanked the guard and fired him. Why? ...
... was stealing a million dollars from his vault. He caught the thief and turned him into the police, then when the owner found out he thanked the guard and fired him. Why? ...
Class 8 (Ch 5b) Feb3
... 26 April 2007, L-3 Communications, Waco Texas: SOFIA takes to the air for its first test flight after completion of modifications ...
... 26 April 2007, L-3 Communications, Waco Texas: SOFIA takes to the air for its first test flight after completion of modifications ...
Redshift
In physics, redshift happens when light or other electromagnetic radiation from an object is increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum. In general, whether or not the radiation is within the visible spectrum, ""redder"" means an increase in wavelength – equivalent to a lower frequency and a lower photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, the wave and quantum theories of light.Some redshifts are an example of the Doppler effect, familiar in the change of apparent pitches of sirens and frequency of the sound waves emitted by speeding vehicles. A redshift occurs whenever a light source moves away from an observer. Another kind of redshift is cosmological redshift, which is due to the expansion of the universe, and sufficiently distant light sources (generally more than a few million light years away) show redshift corresponding to the rate of increase in their distance from Earth. Finally, gravitational redshift is a relativistic effect observed in electromagnetic radiation moving out of gravitational fields. Conversely, a decrease in wavelength is called blueshift and is generally seen when a light-emitting object moves toward an observer or when electromagnetic radiation moves into a gravitational field. However, redshift is a more common term and sometimes blueshift is referred to as negative redshift.Knowledge of redshifts and blueshifts has been applied to develop several terrestrial technologies such as Doppler radar and radar guns. Redshifts are also seen in the spectroscopic observations of astronomical objects. Its value is represented by the letter z.A special relativistic redshift formula (and its classical approximation) can be used to calculate the redshift of a nearby object when spacetime is flat. However, in many contexts, such as black holes and Big Bang cosmology, redshifts must be calculated using general relativity. Special relativistic, gravitational, and cosmological redshifts can be understood under the umbrella of frame transformation laws. There exist other physical processes that can lead to a shift in the frequency of electromagnetic radiation, including scattering and optical effects; however, the resulting changes are distinguishable from true redshift and are not generally referred to as such (see section on physical optics and radiative transfer).