Cosmology Unit – FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST
... a. All of the dots should be equally far apart. b. All of the dots should have clustered on one part of the balloon. c. The distance between each dot should have increased by the same amount. d. The distance between faraway dots should have increased more than the distance between nearby dots. 4. Ho ...
... a. All of the dots should be equally far apart. b. All of the dots should have clustered on one part of the balloon. c. The distance between each dot should have increased by the same amount. d. The distance between faraway dots should have increased more than the distance between nearby dots. 4. Ho ...
100 million years after the Big Bang
... monitoring technique (that Jeff Cooke has used to find z 2–4 SLSNe) to search for the SLSNe • SLSNe will rise to peak from 10 – 30 days, stay there for 2 – 20 days, then decline in 20 – 100 days. In the observer frame, this is 75 – 230 day rise, 15 – 150 days near peak, and 150 – 750 day decline for ...
... monitoring technique (that Jeff Cooke has used to find z 2–4 SLSNe) to search for the SLSNe • SLSNe will rise to peak from 10 – 30 days, stay there for 2 – 20 days, then decline in 20 – 100 days. In the observer frame, this is 75 – 230 day rise, 15 – 150 days near peak, and 150 – 750 day decline for ...
EM Spectrum notes - Biloxi Public Schools
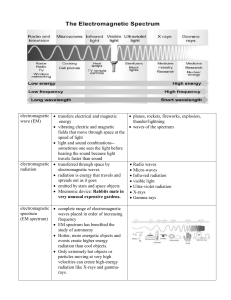
... energy/frequency Used to sterilize medical equipment by killing any germs produced by stars Nuclear energy Cancer treatment ...
... energy/frequency Used to sterilize medical equipment by killing any germs produced by stars Nuclear energy Cancer treatment ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Berkeley Center for Cosmological Physics
... Fisher estimates give a N-dimension ellipsoid. Marginalize (integrate over the probability distribution) over parameters not of immediate interest by crossing out their row/column in F-1. Fix a parameter by crossing out row/column in F. 1 (68.3% probability enclosed) joint contours have 2=2.30 in ...
... Fisher estimates give a N-dimension ellipsoid. Marginalize (integrate over the probability distribution) over parameters not of immediate interest by crossing out their row/column in F-1. Fix a parameter by crossing out row/column in F. 1 (68.3% probability enclosed) joint contours have 2=2.30 in ...
EM Spectrum Notes - Biloxi Public Schools
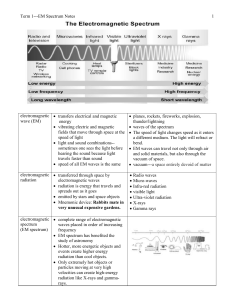
... Term 1---EM Spectrum Notes blue shift objects moving towards Earth shorter wavelength ...
... Term 1---EM Spectrum Notes blue shift objects moving towards Earth shorter wavelength ...
EM Spectrum Notes 2015-2016
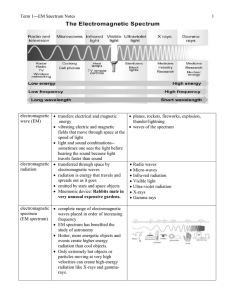
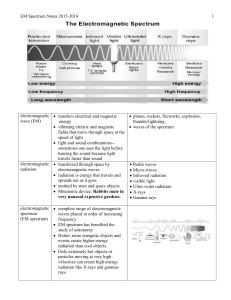
... EM Spectrum Notes 2015-2016 blue shift objects moving towards Earth shorter wavelength ...
... EM Spectrum Notes 2015-2016 blue shift objects moving towards Earth shorter wavelength ...
ASTRO 1050 Distant Galaxies and the Expanding Universe
... object is zero, the shift in wavelength will also be zero. For an object which is moving at high speed, v will be large, and the shift in wavelength will also be large. 4. Use the Doppler formula to determine the speeds of the galaxies. (Write your answer below each spectrum on the last page.) ...
... object is zero, the shift in wavelength will also be zero. For an object which is moving at high speed, v will be large, and the shift in wavelength will also be large. 4. Use the Doppler formula to determine the speeds of the galaxies. (Write your answer below each spectrum on the last page.) ...
Astro 3303 - Cornell Astronomy
... GM/R sin θ where θ is the azimuthal angle in the disk measured from the BH, R is the radial distance from the BH, M is the mass of the BH. Close to l.o.s., sin θ ~ b/R, where b is the impact parameter, so Vz ~ b GM/R3 ...
... GM/R sin θ where θ is the azimuthal angle in the disk measured from the BH, R is the radial distance from the BH, M is the mass of the BH. Close to l.o.s., sin θ ~ b/R, where b is the impact parameter, so Vz ~ b GM/R3 ...
galaxy.
... • van Maanen must have made errors in his measurements of M101, and it wasn’t rotating. • The zone of avoidance must be an artifact of something in our galaxyperhaps dust extinction- blocking our view of galaxies in the Milky Way. • S Andromeda was not a normal nova. It was something else, something ...
... • van Maanen must have made errors in his measurements of M101, and it wasn’t rotating. • The zone of avoidance must be an artifact of something in our galaxyperhaps dust extinction- blocking our view of galaxies in the Milky Way. • S Andromeda was not a normal nova. It was something else, something ...
Probing the Early Universe with Distant Galaxies
... possibility of discovering galaxies in the first billion years of the universe's history. Some of these galaxies have been followed up with observations undertaken from the ground to obtain their spectra and infer further clues about the universe during its infancy. In particular, a lot of effort ha ...
... possibility of discovering galaxies in the first billion years of the universe's history. Some of these galaxies have been followed up with observations undertaken from the ground to obtain their spectra and infer further clues about the universe during its infancy. In particular, a lot of effort ha ...
Lecture
... away from us, or Universe as a whole is expanding But if universe is steadily increasing in size, implies that at some time in the past, Universe was a single point. `Start of the Universe’ ...
... away from us, or Universe as a whole is expanding But if universe is steadily increasing in size, implies that at some time in the past, Universe was a single point. `Start of the Universe’ ...
Document
... 28.3 Doppler Shift Doppler shift also occurs with electromagnetic waves, such as visible light, X-rays, and microwaves. This phenomenon is an important tool used by astronomers to study the motion of objects in space. ...
... 28.3 Doppler Shift Doppler shift also occurs with electromagnetic waves, such as visible light, X-rays, and microwaves. This phenomenon is an important tool used by astronomers to study the motion of objects in space. ...
Redshift
In physics, redshift happens when light or other electromagnetic radiation from an object is increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum. In general, whether or not the radiation is within the visible spectrum, ""redder"" means an increase in wavelength – equivalent to a lower frequency and a lower photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, the wave and quantum theories of light.Some redshifts are an example of the Doppler effect, familiar in the change of apparent pitches of sirens and frequency of the sound waves emitted by speeding vehicles. A redshift occurs whenever a light source moves away from an observer. Another kind of redshift is cosmological redshift, which is due to the expansion of the universe, and sufficiently distant light sources (generally more than a few million light years away) show redshift corresponding to the rate of increase in their distance from Earth. Finally, gravitational redshift is a relativistic effect observed in electromagnetic radiation moving out of gravitational fields. Conversely, a decrease in wavelength is called blueshift and is generally seen when a light-emitting object moves toward an observer or when electromagnetic radiation moves into a gravitational field. However, redshift is a more common term and sometimes blueshift is referred to as negative redshift.Knowledge of redshifts and blueshifts has been applied to develop several terrestrial technologies such as Doppler radar and radar guns. Redshifts are also seen in the spectroscopic observations of astronomical objects. Its value is represented by the letter z.A special relativistic redshift formula (and its classical approximation) can be used to calculate the redshift of a nearby object when spacetime is flat. However, in many contexts, such as black holes and Big Bang cosmology, redshifts must be calculated using general relativity. Special relativistic, gravitational, and cosmological redshifts can be understood under the umbrella of frame transformation laws. There exist other physical processes that can lead to a shift in the frequency of electromagnetic radiation, including scattering and optical effects; however, the resulting changes are distinguishable from true redshift and are not generally referred to as such (see section on physical optics and radiative transfer).