EOC Review Part 3
... Make sure you understand how I figured out how to label the genotype of each individual. Remember that if the parents are normal and the child has the disease then the parents must be heterozygous. ...
... Make sure you understand how I figured out how to label the genotype of each individual. Remember that if the parents are normal and the child has the disease then the parents must be heterozygous. ...
the Note
... The plants of the F1 grow and mature. When they are ready to reproduce, they produce gametes for tallness (T) and shortness (t) because the gametes segregate (T + T + t + t) during meiosis. One half of the gametes will contain the characteristic of one of the parents - for tallness and the other hal ...
... The plants of the F1 grow and mature. When they are ready to reproduce, they produce gametes for tallness (T) and shortness (t) because the gametes segregate (T + T + t + t) during meiosis. One half of the gametes will contain the characteristic of one of the parents - for tallness and the other hal ...
Food Inc.
... Potential human health impacts, including allergens, transfer of antibiotic resistance markers, unknown effects Potential environmental impacts, including: unintended transfer of transgenes through crosspollination, unknown effects on other organisms (e.g., soil microbes), and loss of flora and faun ...
... Potential human health impacts, including allergens, transfer of antibiotic resistance markers, unknown effects Potential environmental impacts, including: unintended transfer of transgenes through crosspollination, unknown effects on other organisms (e.g., soil microbes), and loss of flora and faun ...
Mendel and Gen terms BIO
... 5) Can control breeding because of access to male and female sex parts ...
... 5) Can control breeding because of access to male and female sex parts ...
File
... • There are over eight million combinations possible from the 23 chromosomes you inherit from your mom and 23 you inherit from your dad. • The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called heredity. ...
... • There are over eight million combinations possible from the 23 chromosomes you inherit from your mom and 23 you inherit from your dad. • The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called heredity. ...
Chapter 16: Population Genetics &Speciation
... random events or chance. • Genetic drift refers to the expected population dynamics of neutral alleles (those defined as having no positive or negative impact on fitness) (Natural selection describes the tendency of beneficial alleles to become more common over time (and detrimental ones less common ...
... random events or chance. • Genetic drift refers to the expected population dynamics of neutral alleles (those defined as having no positive or negative impact on fitness) (Natural selection describes the tendency of beneficial alleles to become more common over time (and detrimental ones less common ...
Chapter 7 and Chapter 8
... How can two individuals with different genotypes for a particular trait be identical in phenotype? ...
... How can two individuals with different genotypes for a particular trait be identical in phenotype? ...
Review Questions
... compare the genes of affected individuals with the genes of those who did not inherit the disorder to identify the specific genes responsible. In other studies the disease-causing gene is known, and researchers study the gene mutation (s). A pedigree can help identify which family members should be ...
... compare the genes of affected individuals with the genes of those who did not inherit the disorder to identify the specific genes responsible. In other studies the disease-causing gene is known, and researchers study the gene mutation (s). A pedigree can help identify which family members should be ...
No Slide Title
... Out of Africa • Neanderthal mT DNA: – Very different from modern humans – Hard to reconcile difference with possible presence of some Neanderthal ancestry in modern ...
... Out of Africa • Neanderthal mT DNA: – Very different from modern humans – Hard to reconcile difference with possible presence of some Neanderthal ancestry in modern ...
Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... thigh bone, are involved in walking. In whales, the pelvis and femur shown in Figure 16–1 are a. examples of fossils. b. vestigial structures. c. acquired traits. d. examples of natural variation. ...
... thigh bone, are involved in walking. In whales, the pelvis and femur shown in Figure 16–1 are a. examples of fossils. b. vestigial structures. c. acquired traits. d. examples of natural variation. ...
modification of gene expression
... Review and Questions • What is gene expression? • What is gene regulation? • What is the general role of proteins in cells and organisms? • How do DNA and proteins contribute to cell differentiation? • What are the factors that regulate the expression of a gene? • What is epigenetics? How does it r ...
... Review and Questions • What is gene expression? • What is gene regulation? • What is the general role of proteins in cells and organisms? • How do DNA and proteins contribute to cell differentiation? • What are the factors that regulate the expression of a gene? • What is epigenetics? How does it r ...
Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 7.3: Human Genetics and Biotechnology
... many possible combinations of alleles, especially if each gene has multiple alleles. Therefore, a whole continuum of phenotypes is possible. An example of a human polygenic trait is adult height. Several genes, each with more than one allele, contribute to this trait, so there are many possible adul ...
... many possible combinations of alleles, especially if each gene has multiple alleles. Therefore, a whole continuum of phenotypes is possible. An example of a human polygenic trait is adult height. Several genes, each with more than one allele, contribute to this trait, so there are many possible adul ...
HCLSIG_BioRDF_Subgroup$$QueryFederation2
... al. A journey to semantic web query federation in the life sciences. BMC Bioinformatics. 10(Suppl 10):S10, 2009) ...
... al. A journey to semantic web query federation in the life sciences. BMC Bioinformatics. 10(Suppl 10):S10, 2009) ...
Chapter 23 - Cloudfront.net
... • A. _________genetics is the study of the genetic variation within a population and how it changes over time. – 1.A _________ is a localized group of individuals that belong to the same species. – 2A ______ is a group of populations which can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. ...
... • A. _________genetics is the study of the genetic variation within a population and how it changes over time. – 1.A _________ is a localized group of individuals that belong to the same species. – 2A ______ is a group of populations which can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 3. The different forms of a gene are called _______________________________. 4. What is a hybrid? ______________________________________________________________ 5. What does the notation TT mean to geneticists? What are the two types of alleles? 6. What does the notation tt mean to geneticists? What ...
... 3. The different forms of a gene are called _______________________________. 4. What is a hybrid? ______________________________________________________________ 5. What does the notation TT mean to geneticists? What are the two types of alleles? 6. What does the notation tt mean to geneticists? What ...
genetics test study guide
... 31. A genetic pedigree showing that only males are affected by a certain disorder is evidence of what type of inheritance? _____________ 32. In mice, the gray fur gene (G) is dominant and the gene for black fur (g) is recessive. If 50% of a mouse litter is black, what parental cross probably produce ...
... 31. A genetic pedigree showing that only males are affected by a certain disorder is evidence of what type of inheritance? _____________ 32. In mice, the gray fur gene (G) is dominant and the gene for black fur (g) is recessive. If 50% of a mouse litter is black, what parental cross probably produce ...
Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 3: Human Genetics and Biotechnology
... many possible combinations of alleles, especially if each gene has multiple alleles. Therefore, a whole continuum of phenotypes is possible. An example of a human polygenic trait is adult height. Several genes, each with more than one allele, contribute to this trait, so there are many possible adul ...
... many possible combinations of alleles, especially if each gene has multiple alleles. Therefore, a whole continuum of phenotypes is possible. An example of a human polygenic trait is adult height. Several genes, each with more than one allele, contribute to this trait, so there are many possible adul ...
1 h pi The ul30 (DNA polymerase) gene reaches
... 2 h pi Similarly as at 1 h pi, the ul30 gene has the highest R2 h value (70.5%) among the protein-encoding genes (Additional file 4a). Intriguingly, the net increase of the ul30 transcripts is also the highest (R(2 h-1 h) = 24.1%) between 1 and 2 h (Additional file 4b). The ul30 transcripts are high ...
... 2 h pi Similarly as at 1 h pi, the ul30 gene has the highest R2 h value (70.5%) among the protein-encoding genes (Additional file 4a). Intriguingly, the net increase of the ul30 transcripts is also the highest (R(2 h-1 h) = 24.1%) between 1 and 2 h (Additional file 4b). The ul30 transcripts are high ...
File
... 1. LRRK2: leucine-rich repeat kinase gene (from humans) 2. LRRK2-G2019S: mutant form of the normal LRRK2 gene that leads to Parkinson symptoms. The G2019S notation means that a normal G (glycine) amino acid is mutated to a S (serine) at the 2019 amino acid in the polypeptide chain. 3. CG5483: the or ...
... 1. LRRK2: leucine-rich repeat kinase gene (from humans) 2. LRRK2-G2019S: mutant form of the normal LRRK2 gene that leads to Parkinson symptoms. The G2019S notation means that a normal G (glycine) amino acid is mutated to a S (serine) at the 2019 amino acid in the polypeptide chain. 3. CG5483: the or ...
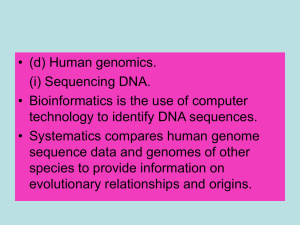
Higher Human Biology unit 1 section 3 BIOINFORMATI
... 2. Should genetic testing be performed when no treatment is available? 3. Should parents have the right to have their minor ...
... 2. Should genetic testing be performed when no treatment is available? 3. Should parents have the right to have their minor ...
eofad
... The doctor swabbed the inside of Suzanne’s cheek to obtain some cells. The was extracted from these cells and tested for the gene. Suzanne’s test came back positive—she had inherited the gene mutation from her father. When they got the news, Suzanne reacted with tearful stoicism, David with ...
... The doctor swabbed the inside of Suzanne’s cheek to obtain some cells. The was extracted from these cells and tested for the gene. Suzanne’s test came back positive—she had inherited the gene mutation from her father. When they got the news, Suzanne reacted with tearful stoicism, David with ...
Ch. 23 - ltcconline.net
... 9. Explain why the majority of point mutations are harmless. 10. Explain the following statement: “Only natural selection leads to the adaptation of organisms to their environment.” 11. Explain the role of population size in genetic drift. 12. Distinguish between the bottleneck effect and the founde ...
... 9. Explain why the majority of point mutations are harmless. 10. Explain the following statement: “Only natural selection leads to the adaptation of organisms to their environment.” 11. Explain the role of population size in genetic drift. 12. Distinguish between the bottleneck effect and the founde ...