PowerPoint presentation file for this
... • These foam cells are then deposited into the lining of the artery wall. • This process, known as atherosclerosis, causes plaque deposits to enlarge, artery walls to lose elasticity, and the passage through the artery to narrow. ...
... • These foam cells are then deposited into the lining of the artery wall. • This process, known as atherosclerosis, causes plaque deposits to enlarge, artery walls to lose elasticity, and the passage through the artery to narrow. ...
Lipids
... • Recent decreases in the trans content of the diet have been observed, presumably due to modifications of commercially available fats or changes in consumer choices. • Today, most margarines in the European market have a lower content of trans fatty acids than 5 to 10 years ago and in most cases th ...
... • Recent decreases in the trans content of the diet have been observed, presumably due to modifications of commercially available fats or changes in consumer choices. • Today, most margarines in the European market have a lower content of trans fatty acids than 5 to 10 years ago and in most cases th ...
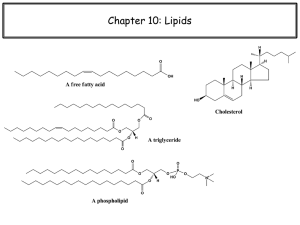
Chapter 19: Lipids
... when high dietary fat intake does not translate into high risks for cardiovascular disease, obesity, and certain types of cancers. These exceptions, which include some Mediterranean; countries and the Inuit people of Greenland, suggest that relationships between direct triglyceride intake and risk f ...
... when high dietary fat intake does not translate into high risks for cardiovascular disease, obesity, and certain types of cancers. These exceptions, which include some Mediterranean; countries and the Inuit people of Greenland, suggest that relationships between direct triglyceride intake and risk f ...
Fats and Nutrition - Canon
... Cholesterol is a fat-like substance found in the body that helps make up skin tissue, aids in transportation of fatty acids in the body, and helps the body produce hormones. High cholesterol diets lead to clogged arteries and heart disease. Monounsaturated fats and Omega 3 fatty acids are show ...
... Cholesterol is a fat-like substance found in the body that helps make up skin tissue, aids in transportation of fatty acids in the body, and helps the body produce hormones. High cholesterol diets lead to clogged arteries and heart disease. Monounsaturated fats and Omega 3 fatty acids are show ...
O–CH 2 - IS MU
... COX-2 inhibitors They are proposed to act as potent anti-inflammatory agents by inhibiting COX-2 activity, without the gastrointestinal (stomach ulcer) and antiplatelet side effects associated with NSAIDs Examples: celecoxib, rofecoxib However further studies indicated that specific COX-2 inhibitor ...
... COX-2 inhibitors They are proposed to act as potent anti-inflammatory agents by inhibiting COX-2 activity, without the gastrointestinal (stomach ulcer) and antiplatelet side effects associated with NSAIDs Examples: celecoxib, rofecoxib However further studies indicated that specific COX-2 inhibitor ...
Summary of Chapter 4 – Lipids
... health effects similar to those of saturated fatty acids. Linoleic acid and linolenic acid are essential nutrients. In addition to serving as structural parts of cell membranes, they make powerful substances that help regulate blood pressure, blood clot formation, and the immune response. Phospholip ...
... health effects similar to those of saturated fatty acids. Linoleic acid and linolenic acid are essential nutrients. In addition to serving as structural parts of cell membranes, they make powerful substances that help regulate blood pressure, blood clot formation, and the immune response. Phospholip ...
Is water a polar or nonpolar molecule
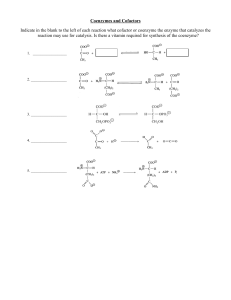
... 1. Which of the following lipids contains phosphate? A. cholesterol B. cerebroside C. diacylglycerol D. sphingomyelin 2. Fatty acids are stored in mammals as A. free fatty acids B. triacylglycerols C. phosphatidylcholine D. cholesterol 4. Which of the following is not a major component of biological ...
... 1. Which of the following lipids contains phosphate? A. cholesterol B. cerebroside C. diacylglycerol D. sphingomyelin 2. Fatty acids are stored in mammals as A. free fatty acids B. triacylglycerols C. phosphatidylcholine D. cholesterol 4. Which of the following is not a major component of biological ...
Lipoprotein structure
... The dynamic properties of the lipid monolayers depend largely on the nature of the constituent lipids. For example, the surface lipids of LDL are more condensed and rigid than those of HDL due to the presence of more saturated fatty acids in the phospholipids of LDL, a higher sphingomyelin-to-PC rat ...
... The dynamic properties of the lipid monolayers depend largely on the nature of the constituent lipids. For example, the surface lipids of LDL are more condensed and rigid than those of HDL due to the presence of more saturated fatty acids in the phospholipids of LDL, a higher sphingomyelin-to-PC rat ...
AP Biology
... can self-assemble into “bubbles” bubble = “micelle” can also form a phospholipid bilayer early evolutionary stage of cell? ...
... can self-assemble into “bubbles” bubble = “micelle” can also form a phospholipid bilayer early evolutionary stage of cell? ...
Lipids - University of Winnipeg
... * Phospholipids: They are esters of phosphoric acids.There are two main types of phospholipids in cellular membranes: Phosphoglecerides: They are also known as Phosphaitdyl choline (lecithin). They are built from long chain fatty acid, glycerol and phosphoric acids. sphingomyelins: They do not conta ...
... * Phospholipids: They are esters of phosphoric acids.There are two main types of phospholipids in cellular membranes: Phosphoglecerides: They are also known as Phosphaitdyl choline (lecithin). They are built from long chain fatty acid, glycerol and phosphoric acids. sphingomyelins: They do not conta ...
Slides
... • Of the classes of biological molecules that we have covered in this class (proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and now lipids), lipids are the most structurally diverse…yet in some ways (i.e., they all contain nonpolar moieties), they are also quite ...
... • Of the classes of biological molecules that we have covered in this class (proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and now lipids), lipids are the most structurally diverse…yet in some ways (i.e., they all contain nonpolar moieties), they are also quite ...
4. Essential fatty acid
... • 22. Cholesterol is the precursor for the biosynthesis of • (A) essential fatty acids • (B) prostaglandins • (C) bile acids • (D) sphingmyelin ...
... • 22. Cholesterol is the precursor for the biosynthesis of • (A) essential fatty acids • (B) prostaglandins • (C) bile acids • (D) sphingmyelin ...
Chapter 24 – Lipids_Summary
... -Among other substances, glucose passes into many cells by facilitated diffusion. In active transport, substances can pass against a concentration gradient. -Active transport requires a supply of energy (often ATP) to overcome the concentration gradient. • The relatively high ratio of K+/Na+ between ...
... -Among other substances, glucose passes into many cells by facilitated diffusion. In active transport, substances can pass against a concentration gradient. -Active transport requires a supply of energy (often ATP) to overcome the concentration gradient. • The relatively high ratio of K+/Na+ between ...
chapter_6_ppt
... • Once used for emulsification, can go through 1 of 2 routes: – Reabsorbed in small intestine and recycled – Binds to fiber in large intestine and excreted • This is how fiber (in particular soluble fiber) helps lower blood cholesterol levels ...
... • Once used for emulsification, can go through 1 of 2 routes: – Reabsorbed in small intestine and recycled – Binds to fiber in large intestine and excreted • This is how fiber (in particular soluble fiber) helps lower blood cholesterol levels ...
5.6. membrane lipids
... Platelet activating factor: major mediator of hypersensivity, acute inflammatory reactions, allergic responses and anaphylactic shock. ...
... Platelet activating factor: major mediator of hypersensivity, acute inflammatory reactions, allergic responses and anaphylactic shock. ...
Fats and Lipids
... Lipids are insoluble in water. This is very important as most proteins and carbohydrates are water soluble. The long alkyl chain in the fatty acid makes makes them insoluble. Lipids are therefore ‘hydrophobic’. 3. Chemical Messenger lipids. Ex: Steroid hormones, prostaglandins ...
... Lipids are insoluble in water. This is very important as most proteins and carbohydrates are water soluble. The long alkyl chain in the fatty acid makes makes them insoluble. Lipids are therefore ‘hydrophobic’. 3. Chemical Messenger lipids. Ex: Steroid hormones, prostaglandins ...
Lh6Ch10Lipids
... Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. Fatty acid properties and system of names. 2. Structures of Triacylglycerols. 3. Structures of Glycerol-Phospho-lipids. 4. Structures of Sphingolipids. 5. Progenitor of prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and ...
... Things to Know and Do Before Class 1. Fatty acid properties and system of names. 2. Structures of Triacylglycerols. 3. Structures of Glycerol-Phospho-lipids. 4. Structures of Sphingolipids. 5. Progenitor of prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and ...
Lecture 27
... food products that could contribute to high cholesterol levels. Not only do these foods have high cholesterol, they also contain high amounts of saturated fats and trans-fats--both of which contribute to high cholesterol levels and atherosclerosis. Given these studies and the fact that eggs are an e ...
... food products that could contribute to high cholesterol levels. Not only do these foods have high cholesterol, they also contain high amounts of saturated fats and trans-fats--both of which contribute to high cholesterol levels and atherosclerosis. Given these studies and the fact that eggs are an e ...
Ch5LIPIDS
... The triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and protein carriers form LIPOPROTEIN Once these lipoproteins leave the cell, they become CHYLOMICRONS and enter the lymph system • MCTs, short-chain fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed directly into bloodstream. They do not enter the lymph system. ...
... The triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and protein carriers form LIPOPROTEIN Once these lipoproteins leave the cell, they become CHYLOMICRONS and enter the lymph system • MCTs, short-chain fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed directly into bloodstream. They do not enter the lymph system. ...
group “head” dehydration synthesis H 2 O enzyme AP
... Hydrophobic or hydrophilic? fatty acid tails = hydrophobic PO4 head = hydrophillic “attracted to water” split “personality” ...
... Hydrophobic or hydrophilic? fatty acid tails = hydrophobic PO4 head = hydrophillic “attracted to water” split “personality” ...
Lipid Metabolism
... Monoglyceride, cholesterol and f.fas and bile salts form amphipathic micelles. These micelles keep the insoluble lipid components in soluble aggregates from which small amounts are released and absorbed by epithelial cells via diffusion. - Free fatty acids and monoglycerides then recombine into tria ...
... Monoglyceride, cholesterol and f.fas and bile salts form amphipathic micelles. These micelles keep the insoluble lipid components in soluble aggregates from which small amounts are released and absorbed by epithelial cells via diffusion. - Free fatty acids and monoglycerides then recombine into tria ...
Review session for exam-I
... Q25. What distinguishes eicosanoids from other potent biological signaling molecules such as ...
... Q25. What distinguishes eicosanoids from other potent biological signaling molecules such as ...
High-density lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80-100 proteins/particle (organized by one, two or three ApoA; more as the particles enlarge picking up and carrying more fat molecules) and transporting none to hundreds of fat molecules/particle. Unlike the larger lipoprotein particles which deliver fat molecules to cells, HDL particles remove fat molecules from cells which want to export fat molecules. The fats carried include cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides; amounts of each quite variable.Lipoproteins, in order of molecular size, largest to smallest, are chylomicrons, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and HDL. Lipoprotein molecules (all particles far smaller than human cells), enable the transportation of all lipids, such as cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides, within the water around cells (extracellular fluid), including the bloodstream. For perspective on particle size; see: Cell Size and Scale,.. HDL particles, unlike the larger particles, transfer fats away from cells, artery walls and tissues (around the body, body wide) through the bloodstream, back to both (a) LDL particles and (b) back to the liver for other disposition.Increasing concentrations of HDL particles are strongly associated with decreasing accumulation of atherosclerosis within the walls of arteries[4] over weeks, years, decades. This is important because atherosclerosis, eventually, results in sudden plaque ruptures triggering clots within the artery opening, narrowing/closing the opening(s), i.e. cardiovascular disease, stroke(s) and other vascular disease complications body wide.HDL particles (though vastly different from just cholesterol and other fat molecules per-se) are sometimes referred to as good cholesterol because they can transport fat molecules (including cholesterol, triglycerides, etc.) out of artery walls, reduce macrophage accumulation, and thus help prevent, even regress atherosclerosis over weeks, years, decades, thereby helping prevent cardiovascular disease, stroke(s) and other vascular disease complications body wide. In contrast, LDL particles (also far different from cholesterol per-se) are often called bad cholesterol or unhealthy cholesterol, because they deliver fat molecules to macrophages in the wall of arteries.[5]