Discovering genotypes underlying human phenotypes: past successes for mendelian disease, future approaches for complex disease.
... Initially, LD mapping methods depend on allelic associations between single markers (typically microsatellites) and disease, which are compared between affected subjects and suitable controls from the same population. Recessive diseases are straightforward for such analyses, because both chromosomes ...
... Initially, LD mapping methods depend on allelic associations between single markers (typically microsatellites) and disease, which are compared between affected subjects and suitable controls from the same population. Recessive diseases are straightforward for such analyses, because both chromosomes ...
Document
... 50 and Mutations *the information from the gene on DNA that was inherited from parents is the genotype. It is transcribed onto mRNA, and eventually translated into a protein. The protein is the phenotype (expression of the genotype) ...
... 50 and Mutations *the information from the gene on DNA that was inherited from parents is the genotype. It is transcribed onto mRNA, and eventually translated into a protein. The protein is the phenotype (expression of the genotype) ...
Nonisotopic method for accurate detection of (CAG
... Fig. 2 shows PGR products from 3 HD patients. Both normal and expanded alleles are clearly visible and no background bands are present. Fig. 3 illustrates the separation of different normal (non-HD) alleles in three unaffected individuals, both homozygotes and heterozygotes. Differences of only one ...
... Fig. 2 shows PGR products from 3 HD patients. Both normal and expanded alleles are clearly visible and no background bands are present. Fig. 3 illustrates the separation of different normal (non-HD) alleles in three unaffected individuals, both homozygotes and heterozygotes. Differences of only one ...
Surrogate Genetics and Metabolic Profiling for Characterization of
... high concentration of serum total homocysteine, the sum of free, oxidized, and protein-bound forms. CBS catalyzes a committed step in the pathway that produces cysteine and ultimately glutathione, the major endogenous intracellular antioxidant. Upstream of CBS, homocysteine is an intermediate in the ...
... high concentration of serum total homocysteine, the sum of free, oxidized, and protein-bound forms. CBS catalyzes a committed step in the pathway that produces cysteine and ultimately glutathione, the major endogenous intracellular antioxidant. Upstream of CBS, homocysteine is an intermediate in the ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... • The female cats have white fur; and black (b) or orange fur (B) alleles on their X Chromosomes- these will be expressed ...
... • The female cats have white fur; and black (b) or orange fur (B) alleles on their X Chromosomes- these will be expressed ...
Probability of Inheritance Lesson 2
... plant (tt) with a homozygous Short pea plant (tt)? 3. What would be the result of crossing a heterozygous Tall (Tt) pea plant with a homozygous Short pea plant? 4. What would be the result of crossing a heterozygous tall pea plant with a heterozygous tall pea plant? ...
... plant (tt) with a homozygous Short pea plant (tt)? 3. What would be the result of crossing a heterozygous Tall (Tt) pea plant with a homozygous Short pea plant? 4. What would be the result of crossing a heterozygous tall pea plant with a heterozygous tall pea plant? ...
Chromosomal Basis
... Because males have only one X chromosome (hemizygous), any male receiving the recessive allele from his mother will express the recessive trait. ...
... Because males have only one X chromosome (hemizygous), any male receiving the recessive allele from his mother will express the recessive trait. ...
BSc in Applied Biotechnology 3 BO0048 ‑ GENETICS PROGRAM
... • The frequencies of two alleles of a single locus was studied. In which When two individuals heterozygous for the same gene Aa are crossed (Aa x Aa), they segregate in a ratio 1 AA : 2Aa : 1aa. • This ratio can be obtained by simple expansion of binomial theorem (A + a)2 = 1 AA : 2Aa : 1aa. • In th ...
... • The frequencies of two alleles of a single locus was studied. In which When two individuals heterozygous for the same gene Aa are crossed (Aa x Aa), they segregate in a ratio 1 AA : 2Aa : 1aa. • This ratio can be obtained by simple expansion of binomial theorem (A + a)2 = 1 AA : 2Aa : 1aa. • In th ...
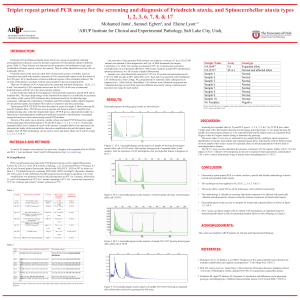
Triplet repeat primed PCR assay for the screening and diagnosis of
... There are 28 subtypes of SCA characterized by autosomal dominant inheritance. SCA1, 2, 3, 6 and 7 are caused by CAG expansion and account for 50–65% of all cases of autosomal dominant ataxia, with SCA3 as the most common subtype. Current molecular methods for the diagnosis of trinucleotide expansion ...
... There are 28 subtypes of SCA characterized by autosomal dominant inheritance. SCA1, 2, 3, 6 and 7 are caused by CAG expansion and account for 50–65% of all cases of autosomal dominant ataxia, with SCA3 as the most common subtype. Current molecular methods for the diagnosis of trinucleotide expansion ...
MCDB 1041 Activity 4 Complex Patterns and Errors in Meiosis
... (approximately 10-20% of all human fertilized eggs contain chromosome abnormalities!); however, this is still a relatively rare event. Usually, during meiosis, chromosomes separate to produce gametes with 23 chromosomes (one of each kind of chromosome). Nondisjunction can happen to any chromosome; i ...
... (approximately 10-20% of all human fertilized eggs contain chromosome abnormalities!); however, this is still a relatively rare event. Usually, during meiosis, chromosomes separate to produce gametes with 23 chromosomes (one of each kind of chromosome). Nondisjunction can happen to any chromosome; i ...
Chase, B. A., and Baker, B. S.
... was obtained from KATHRYNANDERSON (University of California, Berkeley), shnm5-' and shnTD5,2( =shn3) are (possibly identical) alleles generated by hybrid dysgenesis obtained from PETERGERGEN (SUNY, Stony Brook, N Y ) . The P-strains 7r-2, Y8b51, 8-31-15, 78.16 and ZnbredCage 3 were obtained from WIL ...
... was obtained from KATHRYNANDERSON (University of California, Berkeley), shnm5-' and shnTD5,2( =shn3) are (possibly identical) alleles generated by hybrid dysgenesis obtained from PETERGERGEN (SUNY, Stony Brook, N Y ) . The P-strains 7r-2, Y8b51, 8-31-15, 78.16 and ZnbredCage 3 were obtained from WIL ...
23_Lecture_Presentation
... a locus is the total number of individuals times 2 The total number of dominant alleles at a locus is two alleles for each homozygous dominant individual plus one allele for each heterozygous individual; the same logic applies for recessive alleles ...
... a locus is the total number of individuals times 2 The total number of dominant alleles at a locus is two alleles for each homozygous dominant individual plus one allele for each heterozygous individual; the same logic applies for recessive alleles ...
D. Jewish or Middle Eastern
... __________________ cell mutations happen in sperm or eggs and can be passed on to the offspring. A. body B. somatic C. germ D. allele ____________________ mutations cause death, often before birth. A. Somatic cell B. X-linked C. Germ cell D. Lethal __________________ cell mutations happen in body ce ...
... __________________ cell mutations happen in sperm or eggs and can be passed on to the offspring. A. body B. somatic C. germ D. allele ____________________ mutations cause death, often before birth. A. Somatic cell B. X-linked C. Germ cell D. Lethal __________________ cell mutations happen in body ce ...
C. African American
... __________________ cell mutations happen in sperm or eggs and can be passed on to the offspring. A. B. somatic C. germ D. allele ____________________ mutations cause death, often before birth. A. B. X-linked C. Germ cell D. Lethal __________________ cell mutations happen in body cells so they affect ...
... __________________ cell mutations happen in sperm or eggs and can be passed on to the offspring. A. B. somatic C. germ D. allele ____________________ mutations cause death, often before birth. A. B. X-linked C. Germ cell D. Lethal __________________ cell mutations happen in body cells so they affect ...
ppt
... graft onto it a random genetic drift. Just imagine that each individual harbours two alleles without consequential phenotypic effect, which in the reproductive process are reassorted according to Mendel’s laws. ...
... graft onto it a random genetic drift. Just imagine that each individual harbours two alleles without consequential phenotypic effect, which in the reproductive process are reassorted according to Mendel’s laws. ...
ID_3183_Organism as a level of life or_English_sem_1
... 46,XY 47,XXY 46,XX 45,X0 A boy, 9 years of age, is admitted to the pediatric ward with hemophilia A. He inherited this condition through a ___________ trait. X-linked dominant Y-linked Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive X-linked recessive Consider the cross Aa x Aa. If the alleles for both genes ...
... 46,XY 47,XXY 46,XX 45,X0 A boy, 9 years of age, is admitted to the pediatric ward with hemophilia A. He inherited this condition through a ___________ trait. X-linked dominant Y-linked Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive X-linked recessive Consider the cross Aa x Aa. If the alleles for both genes ...
14-2 Human Chromosomes
... On The X & Y Chromosome X – Contains > 100 Genes Y – Contains Only A Few Genes Foothill High School Science Department ...
... On The X & Y Chromosome X – Contains > 100 Genes Y – Contains Only A Few Genes Foothill High School Science Department ...
Pedigreesppt
... • If D is the disease allele and d is normal, then only dd genotypes are disease free* • Dominant trait/disease found in every generation* • Affected kid never** born to unaffected parents ...
... • If D is the disease allele and d is normal, then only dd genotypes are disease free* • Dominant trait/disease found in every generation* • Affected kid never** born to unaffected parents ...
Abnormalities - Spring Branch ISD
... Independent Assortment of Chromosomes • Mendel observed that combinations of traits in some offspring differ from either parent • Offspring with a phenotype matching one of the parental phenotypes are called parental types • Offspring with nonparental phenotypes (new combinations of traits) are call ...
... Independent Assortment of Chromosomes • Mendel observed that combinations of traits in some offspring differ from either parent • Offspring with a phenotype matching one of the parental phenotypes are called parental types • Offspring with nonparental phenotypes (new combinations of traits) are call ...
Lesson Overview
... located on the X chromosome. In males, a defective allele for any of these genes results in colorblindness, an inability to distinguish certain colors. The most common form, red-green colorblindness, occurs in about 1 in 12 males. Among females, however, colorblindness affects only about 1 in 200. I ...
... located on the X chromosome. In males, a defective allele for any of these genes results in colorblindness, an inability to distinguish certain colors. The most common form, red-green colorblindness, occurs in about 1 in 12 males. Among females, however, colorblindness affects only about 1 in 200. I ...
Slide 1 - Faculty Web Pages
... You should already know the genotype of the homozygous parent Do the genotypes give chromosome information? 3.) Write down chromosome from homozygous test-cross parent that crossprogeny inherited. Now you are set up to determine original chromosome configuration of heterozygous parent. 4.) Determine ...
... You should already know the genotype of the homozygous parent Do the genotypes give chromosome information? 3.) Write down chromosome from homozygous test-cross parent that crossprogeny inherited. Now you are set up to determine original chromosome configuration of heterozygous parent. 4.) Determine ...
Name - Humble ISD
... SpongeBob and his pal Patrick love to go jellyfishing at Jellyfish Fields! The fields are home to a special type of green jellyfish known as Goobers and only really great jellyfishermen are lucky enough to catch some on every trip. Many of the jellyfish are yellow (YY) or blue (BB), but some end up ...
... SpongeBob and his pal Patrick love to go jellyfishing at Jellyfish Fields! The fields are home to a special type of green jellyfish known as Goobers and only really great jellyfishermen are lucky enough to catch some on every trip. Many of the jellyfish are yellow (YY) or blue (BB), but some end up ...
Lack of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for the most prevalent
... Table 1). Under the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, with p = frequency of the normal alleles, q = frequency of R141H alleles and r = frequency of other CDG-Ia mutations, one can use the carrier frequency for R141H in the population (2pq) and the proportion of R141H compound heterozygotes among the patie ...
... Table 1). Under the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, with p = frequency of the normal alleles, q = frequency of R141H alleles and r = frequency of other CDG-Ia mutations, one can use the carrier frequency for R141H in the population (2pq) and the proportion of R141H compound heterozygotes among the patie ...
Pre-lab Homework Lab 5: Heredity I (Simple Mendelian Genetics)
... inherited from your mom; the other set you inherited from your dad. Between these set are homologous pairs of chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes- are similar in size, the order of genes and centromere position (represented here by the white magnetic links). Homologous chromosomes are not however id ...
... inherited from your mom; the other set you inherited from your dad. Between these set are homologous pairs of chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes- are similar in size, the order of genes and centromere position (represented here by the white magnetic links). Homologous chromosomes are not however id ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.