Why Pea Plants? - New Century Academy
... Three characters (Flower color, Seed color, and Pod shape) are considered in a cross between two pea plants (PpYyIi X ppYyii) What fraction of offspring would be predicted to be homozygous recessive for at least two of the three characters ...
... Three characters (Flower color, Seed color, and Pod shape) are considered in a cross between two pea plants (PpYyIi X ppYyii) What fraction of offspring would be predicted to be homozygous recessive for at least two of the three characters ...
Gregor Mendel Power Point File
... TT - Represent offspring with straight hair Tt - Represent offspring with straight hair tt - Represents offspring with curly hair ...
... TT - Represent offspring with straight hair Tt - Represent offspring with straight hair tt - Represents offspring with curly hair ...
AP 15-16 Test Review When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red
... Which of the following is the meaning of the chromosome theory of inheritance as expressed in the early 20th century? In cats, black fur color is caused by an X–linked allele; the other allele at this locus causes orange color. The heterozygote is tortoiseshell. What kinds of offspring would you exp ...
... Which of the following is the meaning of the chromosome theory of inheritance as expressed in the early 20th century? In cats, black fur color is caused by an X–linked allele; the other allele at this locus causes orange color. The heterozygote is tortoiseshell. What kinds of offspring would you exp ...
GENETICS NOTES OUTLINE wksht
... _______ _______ _______ The ratio of a dihybrid heterozygous cross is always: ___________! ...
... _______ _______ _______ The ratio of a dihybrid heterozygous cross is always: ___________! ...
Vocab Puzzle
... nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. 16. Genotype of an individual with two of the same alleles for a given trait. 17. Any one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that may occur alternatively at a given site on ...
... nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. 16. Genotype of an individual with two of the same alleles for a given trait. 17. Any one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that may occur alternatively at a given site on ...
Mendelian Genetics Study Guide In Preparation for California
... Heredity- passing of traits from parents to offspring. Test cross- A procedure in which an individual of unknown genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the genotype of the unknown individual ...
... Heredity- passing of traits from parents to offspring. Test cross- A procedure in which an individual of unknown genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the genotype of the unknown individual ...
Species
... – No net mutations occur (alleles stay constant) – No one leaves or enters (population is constant) – Population is large (ideally, infinitely so) – Individuals mate randomly – Selection does not occur ...
... – No net mutations occur (alleles stay constant) – No one leaves or enters (population is constant) – Population is large (ideally, infinitely so) – Individuals mate randomly – Selection does not occur ...
Genes and Traits Handout
... Follow directions from your teacher for planting corn. Problem: How are traits inherited in corn? Observation: Some corn is yellow, some corn is white. Predict: Which is the dominant trait? Albino or normal color? _______________________ Complete a Punnett Square below to find the answer: ...
... Follow directions from your teacher for planting corn. Problem: How are traits inherited in corn? Observation: Some corn is yellow, some corn is white. Predict: Which is the dominant trait? Albino or normal color? _______________________ Complete a Punnett Square below to find the answer: ...
Mendellian Madness! - Effingham County Schools
... monohybrid cross uses a pair of contrasting traits. Ex: yellow/green dihybrid cross involves 2 characters, such as seed color and seed shape. ...
... monohybrid cross uses a pair of contrasting traits. Ex: yellow/green dihybrid cross involves 2 characters, such as seed color and seed shape. ...
Standards: Gen 2.7 Use Punnett squares to explain Mendel`s three
... Essential Questions: How did Gregor Mendel establish the basics of genetics? ...
... Essential Questions: How did Gregor Mendel establish the basics of genetics? ...
File
... a. ____________________________________ b. You have ________________________ 2. __________________- means two of same allele_________ 3. __________________- two different alleles ...
... a. ____________________________________ b. You have ________________________ 2. __________________- means two of same allele_________ 3. __________________- two different alleles ...
Study guide for Chapter 2 quiz full size
... Study guide for Chapter 2 quiz This quiz will cover lessons 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3, with an emphasis on lesson 2.3 Important Vocabulary: 2.1) traits, gene, chromosome, genotype, phenotype 2.2) genetics, heredity, allele, Punnett square, dominant, recessive, homozygous, heterozygous, principle of segregati ...
... Study guide for Chapter 2 quiz This quiz will cover lessons 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3, with an emphasis on lesson 2.3 Important Vocabulary: 2.1) traits, gene, chromosome, genotype, phenotype 2.2) genetics, heredity, allele, Punnett square, dominant, recessive, homozygous, heterozygous, principle of segregati ...
4.3-4.4 Genetics and Biotechnology Study Guide File
... Define genotype, phenotype, dominant allele, recessive allele, codominant alleles, locus, homozygous, heterozygous, carrier and test cross. o Genotype: the alleles of an organism. o Phenotype: the characteristics of an organism. o Dominant allele: an allele that has the same effect on the phenotype ...
... Define genotype, phenotype, dominant allele, recessive allele, codominant alleles, locus, homozygous, heterozygous, carrier and test cross. o Genotype: the alleles of an organism. o Phenotype: the characteristics of an organism. o Dominant allele: an allele that has the same effect on the phenotype ...
Honors Genetics Chapter 4 Vocabulary We learned several new
... 7. An offspring's phenotype is under the control of gene products in the egg MATERNAL EFFECT 9. Allele that results in complete loss of function NULL ALLELE 10. Genes that are inherited on the X chromosome show a unique inheritance pattern X-LINKAGE 11. The percentage of individuals that show some d ...
... 7. An offspring's phenotype is under the control of gene products in the egg MATERNAL EFFECT 9. Allele that results in complete loss of function NULL ALLELE 10. Genes that are inherited on the X chromosome show a unique inheritance pattern X-LINKAGE 11. The percentage of individuals that show some d ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... offspring, and have many traits that appear in two alternate forms that are easy to distinguish. It also is easy to hand-pollinate pea plants, so an investigator can control which plants mate with one another. 2. Dominant alleles appear in a phenotype whenever they are present; recessive alleles con ...
... offspring, and have many traits that appear in two alternate forms that are easy to distinguish. It also is easy to hand-pollinate pea plants, so an investigator can control which plants mate with one another. 2. Dominant alleles appear in a phenotype whenever they are present; recessive alleles con ...
Genetics Study Guide
... Allele: Different forms of a gene. Dominant allele: The allele that is always expressed if it is present. Recessive allele: The allele that is expressed only if the dominant allele is not present. Punnett Square: A tool used to visualize all the possible combination of alleles from the parents ...
... Allele: Different forms of a gene. Dominant allele: The allele that is always expressed if it is present. Recessive allele: The allele that is expressed only if the dominant allele is not present. Punnett Square: A tool used to visualize all the possible combination of alleles from the parents ...
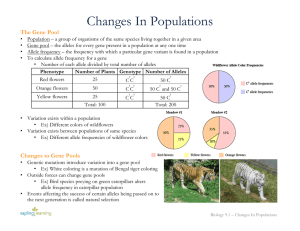
Changes In Populations
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
Ch 14 Review Questions
... example). By observing the phenotypes of the offspring resulting from this cross, we can deduce the genotype of the purple-flowered parent.” If the parent was homozygous dominant, none of the offspring will have the recessive phenotype. If the parent was heterozygous, there is a 50% chance of offspr ...
... example). By observing the phenotypes of the offspring resulting from this cross, we can deduce the genotype of the purple-flowered parent.” If the parent was homozygous dominant, none of the offspring will have the recessive phenotype. If the parent was heterozygous, there is a 50% chance of offspr ...
The Hardy Weinberg principle allows us to see if microevolution is
... population for a particular trait. In order for equilibrium to occur (no change in the frequency of the alleles….no microevolution) certain conditions must be met: 1. The population must be large 2. No mutations 3. No migration in or out of the population 4. Mating must be random In the Hardy Weinbe ...
... population for a particular trait. In order for equilibrium to occur (no change in the frequency of the alleles….no microevolution) certain conditions must be met: 1. The population must be large 2. No mutations 3. No migration in or out of the population 4. Mating must be random In the Hardy Weinbe ...
Study guide: Ch 4: Due Thursday (Test Friday)
... 1:What is the blood type of a child born to two parents with the genotypes IAIA and IBIB for blood type? AB 2: A carrier is a person who has one recessive allele and one dominant allele 3: What controls variations in skin color among humans? At least 3-4 genes 4:How does geneticist use pedigrees? Tr ...
... 1:What is the blood type of a child born to two parents with the genotypes IAIA and IBIB for blood type? AB 2: A carrier is a person who has one recessive allele and one dominant allele 3: What controls variations in skin color among humans? At least 3-4 genes 4:How does geneticist use pedigrees? Tr ...
200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100
... The cells in the stomach divide faster than the cells in the liver because they have more of this… ...
... The cells in the stomach divide faster than the cells in the liver because they have more of this… ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.