File
... cannot roll their tongues. Bob can roll his tongue, but his mother could not. He is married to Sally, who cannot roll her tongue. What is the probability that their first born child will not be able to roll his tongue? ...
... cannot roll their tongues. Bob can roll his tongue, but his mother could not. He is married to Sally, who cannot roll her tongue. What is the probability that their first born child will not be able to roll his tongue? ...
Heredity
... Ex) Brown hair is dominant over blonde hair, so if one brown allele is passed on from the parent the offspring will have brown hair ...
... Ex) Brown hair is dominant over blonde hair, so if one brown allele is passed on from the parent the offspring will have brown hair ...
The Fugates Inheritance
... Dominant vs recessive Dominant - a genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of that gene (example: BB or Bb) Recessive - the recessive form is overpowered by its counterpart, or dominant, form located on the other of a pair of chromosomes (example: bb ...
... Dominant vs recessive Dominant - a genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of that gene (example: BB or Bb) Recessive - the recessive form is overpowered by its counterpart, or dominant, form located on the other of a pair of chromosomes (example: bb ...
Genetics Clicker - Solon City Schools
... Heterozygous Homozygous recessive Homozygous dominant Tongue roller ...
... Heterozygous Homozygous recessive Homozygous dominant Tongue roller ...
The Story of Genetics
... It takes 2 genes to control a trait. One from the male and one from the female. The combination of the 2 genes control characteristics. ...
... It takes 2 genes to control a trait. One from the male and one from the female. The combination of the 2 genes control characteristics. ...
PUNNETT SQUARE PRACTICE
... A gardener has two tall pea plants. How can the gardener determine whether the two plants are homozygous or heterozygous for the gene determining tallness? Show the two Punnett squares as evidence for your conclusion. What is this type of cross called? ...
... A gardener has two tall pea plants. How can the gardener determine whether the two plants are homozygous or heterozygous for the gene determining tallness? Show the two Punnett squares as evidence for your conclusion. What is this type of cross called? ...
BIO 112 Review - Crossword Labs
... 16. The specialized form of gametogenesis in males 18. A fertilized egg 19. The likelihood that a possible future event will occur 21. When pollen (sperm) from a plant fertilizes an egg on the same plant 24. The physical appearance of a trait 25. Offspring of the P generation parents, have only one ...
... 16. The specialized form of gametogenesis in males 18. A fertilized egg 19. The likelihood that a possible future event will occur 21. When pollen (sperm) from a plant fertilizes an egg on the same plant 24. The physical appearance of a trait 25. Offspring of the P generation parents, have only one ...
Heredity
... The set of instructions that determine what traits an offspring has. There are at least two genes for every trait • Example: Some people inherit the genes (instructions) for making dimples. Genes are found in the base sequence of the DNA (the letters)! ...
... The set of instructions that determine what traits an offspring has. There are at least two genes for every trait • Example: Some people inherit the genes (instructions) for making dimples. Genes are found in the base sequence of the DNA (the letters)! ...
mendel and the gene idea - Phillips Scientific Methods
... is rarely simple Complete Dominance: heterozygote and homozygote for dominant allele are indistinguishable • Eg. YY or Yy = yellow seed Incomplete Dominance: F1 hybrids have appearance that is between that of 2 parents • Eg. red x white = pink flowers • *sometimes expressed as RR’ or CRCW ...
... is rarely simple Complete Dominance: heterozygote and homozygote for dominant allele are indistinguishable • Eg. YY or Yy = yellow seed Incomplete Dominance: F1 hybrids have appearance that is between that of 2 parents • Eg. red x white = pink flowers • *sometimes expressed as RR’ or CRCW ...
Grade 11 Genetics Answers
... 3. What is the predicted phenotypic ratio of the offspring from a dihybrid cross between two individuals that are heterozygous for both traits? b) 9:3:3:1 4. What is the goal of therapeutic cloning? a) to produce identical cells to treat disease 5. What are haploid and diploid cells? Where is each c ...
... 3. What is the predicted phenotypic ratio of the offspring from a dihybrid cross between two individuals that are heterozygous for both traits? b) 9:3:3:1 4. What is the goal of therapeutic cloning? a) to produce identical cells to treat disease 5. What are haploid and diploid cells? Where is each c ...
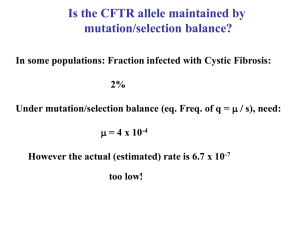
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... Under mutation/selection balance (eq. Freq. of q = m / s), need: m = 4 x 10-4 However the actual (estimated) rate is 6.7 x 10-7 too low! ...
... Under mutation/selection balance (eq. Freq. of q = m / s), need: m = 4 x 10-4 However the actual (estimated) rate is 6.7 x 10-7 too low! ...
Select one of your Biology instructors from another class and look
... (d) lf the allele responsible for the condition is rare, what are the most likely genotypes of all of the persons in the pedigree in generations I, II, and III? (Use A and a for the dominant and recessive alleles, respectively.) 2.9 Meiotic drive is a phenomenon observed occasionally in which a hete ...
... (d) lf the allele responsible for the condition is rare, what are the most likely genotypes of all of the persons in the pedigree in generations I, II, and III? (Use A and a for the dominant and recessive alleles, respectively.) 2.9 Meiotic drive is a phenomenon observed occasionally in which a hete ...
Ch 2: Heredity Worksheet 1. Chromosomes are found in the the cell
... reproductive system for fertilization is called__________________. 8. _______________________________ is when eggs and sperm are fertilized in a petri dish then placed in the mother’s uterus for further development. 9. During ____________________ the cell copies its own chromosome. 10. During_______ ...
... reproductive system for fertilization is called__________________. 8. _______________________________ is when eggs and sperm are fertilized in a petri dish then placed in the mother’s uterus for further development. 9. During ____________________ the cell copies its own chromosome. 10. During_______ ...
Study Guide - Mrs. Iufer
... Condition of Interest: Huntington's Disease (also known as HD or Huntington's chorea) Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia. Inheritance Pattern: the allele for the normal “Huntingtin” protein is auto ...
... Condition of Interest: Huntington's Disease (also known as HD or Huntington's chorea) Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia. Inheritance Pattern: the allele for the normal “Huntingtin” protein is auto ...
Mendel 2
... Inability to form blood clots, can bleed to death Rare recessive allele So rare women highly unlikely to inherit 2 Queen Victoria ...
... Inability to form blood clots, can bleed to death Rare recessive allele So rare women highly unlikely to inherit 2 Queen Victoria ...
Genetics - smithlhhsb121
... inheritance is determined by factors that are passed from one generation to the next Today, scientists call the factors that determine characteristics genes Each of the characters Mendel studied was controlled by one gene that occurred in two contrasting forms that produced different characters for ...
... inheritance is determined by factors that are passed from one generation to the next Today, scientists call the factors that determine characteristics genes Each of the characters Mendel studied was controlled by one gene that occurred in two contrasting forms that produced different characters for ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide
... Phenotype. The observable traits or properties of an organism. Refers to both genetic and non-genetic traits. Often used to refer to a single trait. For example: "My phenotype is hairy knuckles and my genotype is Hh." Population. A local group of individuals belonging to the same species, which are ...
... Phenotype. The observable traits or properties of an organism. Refers to both genetic and non-genetic traits. Often used to refer to a single trait. For example: "My phenotype is hairy knuckles and my genotype is Hh." Population. A local group of individuals belonging to the same species, which are ...
Ch6Sec4 Reiforce Tratis Genes Alleles
... the same locus on both chromosomes in a pair of homologous chromosomes. In genetics, scientists often focus on a single gene or set of genes. Genotype typically refers to the genetic makeup of a particular set of genes. Phenotype refers to the physical characteristics resulting from those genes. An ...
... the same locus on both chromosomes in a pair of homologous chromosomes. In genetics, scientists often focus on a single gene or set of genes. Genotype typically refers to the genetic makeup of a particular set of genes. Phenotype refers to the physical characteristics resulting from those genes. An ...
VOCAB- Evolution
... ADAPTIVE RADIATION (DIVERGENT EVOLUTION) – process by which a single species or small group of species evolves into several different forms that live in different ways; rapid growth in the diversity of a group of organisms. COEVOLUTION- process by which two species evolve in response to changes in e ...
... ADAPTIVE RADIATION (DIVERGENT EVOLUTION) – process by which a single species or small group of species evolves into several different forms that live in different ways; rapid growth in the diversity of a group of organisms. COEVOLUTION- process by which two species evolve in response to changes in e ...
BIOL 1406-61313 CHAPTER 14 AND 15 Dr
... 8. A particular allele can have different effects if it is inherited from a male rather than a female. This phenomenon is known as _____. extranuclear inheritance aneuploidy sex linkage Prader-Willi syndrome genomic imprinting 9. Human mitochondria _____. are inherited as an X-linked trait are all i ...
... 8. A particular allele can have different effects if it is inherited from a male rather than a female. This phenomenon is known as _____. extranuclear inheritance aneuploidy sex linkage Prader-Willi syndrome genomic imprinting 9. Human mitochondria _____. are inherited as an X-linked trait are all i ...
Mendel’s Laws of Heredity
... genes that make up a gene pair might or might not contain the same information about a trait. If a pair of chromosomes contains different alleles for a trait, that trait is called a hybrid . When a trait has two identical alleles, it’s called pure. ...
... genes that make up a gene pair might or might not contain the same information about a trait. If a pair of chromosomes contains different alleles for a trait, that trait is called a hybrid . When a trait has two identical alleles, it’s called pure. ...
Genetics - Midway ISD
... • Principle of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses. • Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. – Probability can predict the outcome of genetic crosses because alleles segregate randomly. ...
... • Principle of probability can be used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses. • Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. – Probability can predict the outcome of genetic crosses because alleles segregate randomly. ...
Genetics Practice Problems - Simple Worksheet
... 7. To a geneticist, the notation rr means two __________________________ alleles 8. To a geneticist, the notation Rr means one ____________________ and one ____________ allele 9. __________________________is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. 10. An organism that has two identical al ...
... 7. To a geneticist, the notation rr means two __________________________ alleles 8. To a geneticist, the notation Rr means one ____________________ and one ____________ allele 9. __________________________is the likelihood that a particular event will occur. 10. An organism that has two identical al ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.