Genetics Problems II
... 5. Albinism, the inability to produce chlorophyll, is a recessive trait in a number of plant species. If a tobacco plant known to be heterozygous for albinism is selfpollinated and 600 of its seeds are germinated: Genotypes of parents: _________________________ ...
... 5. Albinism, the inability to produce chlorophyll, is a recessive trait in a number of plant species. If a tobacco plant known to be heterozygous for albinism is selfpollinated and 600 of its seeds are germinated: Genotypes of parents: _________________________ ...
unit cover page - Bremen High School District 228
... Understand Mendel’s law of segregation and also that genes do not always separate as hypothesized by Mendel’s law of segregation. Understand that if genes are located close to each other on the same chromosome, then they are linked and may undergo independent assortment. Identify and be able to appl ...
... Understand Mendel’s law of segregation and also that genes do not always separate as hypothesized by Mendel’s law of segregation. Understand that if genes are located close to each other on the same chromosome, then they are linked and may undergo independent assortment. Identify and be able to appl ...
Evolution 2010 Wilkins
... unproblematic, and most likely indistinguishable from the evolutionary end point that would be reached by an unimprinted locus, because the phenotypes that maximize patrilineal and matrilineal fitness are likely to be quite similar in most cases. However, if we consider a pair of antagonistic loci ( ...
... unproblematic, and most likely indistinguishable from the evolutionary end point that would be reached by an unimprinted locus, because the phenotypes that maximize patrilineal and matrilineal fitness are likely to be quite similar in most cases. However, if we consider a pair of antagonistic loci ( ...
Chapter 10: Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
... positioned at the equator by the spindle fibers, as shown in Figure 10.5. During metaphase of mitosis, a diploid number of chromosomes line up at the equator. During metaphase II of meiosis, however, a haploid number of chromosomes line up at the equator. During anaphase II, the sister chromatids ar ...
... positioned at the equator by the spindle fibers, as shown in Figure 10.5. During metaphase of mitosis, a diploid number of chromosomes line up at the equator. During metaphase II of meiosis, however, a haploid number of chromosomes line up at the equator. During anaphase II, the sister chromatids ar ...
Correlated selection responses in animal domestication: chickens
... Such a common mechanism could be for example pleiotropy, which is the case when one gene affects several traits (e.g. by the gene product being involved in more than one biochemical pathway). The correlation between traits could also be a result of close linkage of different genes affecting differen ...
... Such a common mechanism could be for example pleiotropy, which is the case when one gene affects several traits (e.g. by the gene product being involved in more than one biochemical pathway). The correlation between traits could also be a result of close linkage of different genes affecting differen ...
The Coat of Many Colors
... black color comes through completely on some parts of the coat. The merle gene has the same affect on a genetically sable collie, turning most such collies a lighter sable. Of course, when a collie has one sable color allele and one black & tan color allele, it is still a sable, just a darker one. T ...
... black color comes through completely on some parts of the coat. The merle gene has the same affect on a genetically sable collie, turning most such collies a lighter sable. Of course, when a collie has one sable color allele and one black & tan color allele, it is still a sable, just a darker one. T ...
1 mec-15 Encodes an F-box Protein Required for Touch
... elegans motor neurons another F-box protein, FSN-1, forms an SCF complex with the Skp and Cullin homologues SKR-1 and CUL-1, respectively, to regulate levels of proteins involved in presynaptic differentiation (LIAO et al. 2004). This SCF complex associates with a large RING-finger protein, RPM-1, t ...
... elegans motor neurons another F-box protein, FSN-1, forms an SCF complex with the Skp and Cullin homologues SKR-1 and CUL-1, respectively, to regulate levels of proteins involved in presynaptic differentiation (LIAO et al. 2004). This SCF complex associates with a large RING-finger protein, RPM-1, t ...
Differential Regulation of Antagonistic Pleiotropy in Synthetic and
... The existence of such trade-offs in multiple phenotypes results in a paradigm where no single ...
... The existence of such trade-offs in multiple phenotypes results in a paradigm where no single ...
Changing of Gene Frequencies in Beetles
... recessive organisms you have and record in # of Beetles for Year 1 4. Record the total beetles under Total Hint: You can do this by counting all beetles or adding together the # of beetles 5. Calculate the gene frequency of the organism by one of the following methods: a. Use a calculator to divide ...
... recessive organisms you have and record in # of Beetles for Year 1 4. Record the total beetles under Total Hint: You can do this by counting all beetles or adding together the # of beetles 5. Calculate the gene frequency of the organism by one of the following methods: a. Use a calculator to divide ...
Warren, ST: Trinucleotide repetition and fragile X syndrome. Hospital Practice 32:73 - 98 (1997). cover illustration.
... P. Timmie Professor of Human Genetics, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta. ...
... P. Timmie Professor of Human Genetics, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta. ...
E-Halliburton chapter 13
... many practical desicions about procedures depend on its magnitude. The determination of heritability is one of the first objectives in the genetic study of a metric character. It is important to realize that the heritability is a property not only of a character but also of the population and of the ...
... many practical desicions about procedures depend on its magnitude. The determination of heritability is one of the first objectives in the genetic study of a metric character. It is important to realize that the heritability is a property not only of a character but also of the population and of the ...
Molybdenum cofactor-deficient mice resemble the phenotype of
... been firmly established that sulfite oxidase deficiency alone is responsible for the severe neurological damages in MoCo deficiency (1). The phenotypic variance of the MoCo-deficient mice, as expressed in a lifespan of 1–11 days, is very similar to that observed in human patients, who show a surviva ...
... been firmly established that sulfite oxidase deficiency alone is responsible for the severe neurological damages in MoCo deficiency (1). The phenotypic variance of the MoCo-deficient mice, as expressed in a lifespan of 1–11 days, is very similar to that observed in human patients, who show a surviva ...
Comprehensive analysis of thiopurine S
... Discordant cases between phenotype and genotype were systematically sequenced. A clearly defined trimodal frequency distribution of TPMT activity was found with 0.6% deficient, 9.9% intermediate and 89.5% normal to high methylators. The frequencies of the mutant alleles were 4.4% (*3A), 0.4% (*3C) a ...
... Discordant cases between phenotype and genotype were systematically sequenced. A clearly defined trimodal frequency distribution of TPMT activity was found with 0.6% deficient, 9.9% intermediate and 89.5% normal to high methylators. The frequencies of the mutant alleles were 4.4% (*3A), 0.4% (*3C) a ...
document
... 1. What is the bull’s genotype? What is the cow’s genotype? 2. Show the cross. 3. Give the phenotypic ratio. 4. How would this ratio change if skin color had been a codominant trait instead? ...
... 1. What is the bull’s genotype? What is the cow’s genotype? 2. Show the cross. 3. Give the phenotypic ratio. 4. How would this ratio change if skin color had been a codominant trait instead? ...
Unit A161/02 - Modules B1, B2, B3
... All humans have different phenotypes. (a) Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the statement that best explains the word phenotype. ...
... All humans have different phenotypes. (a) Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the statement that best explains the word phenotype. ...
Simple Sequence Repeats as Advantageous Mutators
... in phenotypic variation at the interspecies as well as at the individual level has recently been provided by Hammock and Young's elegant study of social behavior in voles (Microtus) [18, 25]. Prairie and pine voles (M. ochrogaster and M. pinetorum) are highly social, monogamous rodent species, while ...
... in phenotypic variation at the interspecies as well as at the individual level has recently been provided by Hammock and Young's elegant study of social behavior in voles (Microtus) [18, 25]. Prairie and pine voles (M. ochrogaster and M. pinetorum) are highly social, monogamous rodent species, while ...
Gene Section IL1RN (interleukin 1 receptor antagonist) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... The presence of IL1RN*2 allele was associated with significant susceptibility to septic shock in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia by (Zapata-Tarres et al., 2013). The patients studied by Zapata-Tarres and cols, were susceptible to septic shock. The association between sepsis and ...
... The presence of IL1RN*2 allele was associated with significant susceptibility to septic shock in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia by (Zapata-Tarres et al., 2013). The patients studied by Zapata-Tarres and cols, were susceptible to septic shock. The association between sepsis and ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Eunmi LEE
... allele of the receptor CCR5, where the deletion of a 32 base pair segment makes the receptor nonfunctional The allele has a negative effect upon T cell function, but appears to protect against smallpox and HIV HIV has no receptor to bind to and cannot enter the cell This allele is found in 14% of Eu ...
... allele of the receptor CCR5, where the deletion of a 32 base pair segment makes the receptor nonfunctional The allele has a negative effect upon T cell function, but appears to protect against smallpox and HIV HIV has no receptor to bind to and cannot enter the cell This allele is found in 14% of Eu ...
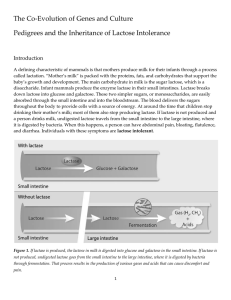
The Co-Evolution of Genes and Culture Pedigrees and the
... lactose tolerant, yet their son is lactose intolerant. Are these data consistent or inconsistent with the claim you made in question 3? Explain your answer. The two parents are lactose tolerant, meaning they can be homozygous or heterozygous for the dominant allele. The only way to explain how their ...
... lactose tolerant, yet their son is lactose intolerant. Are these data consistent or inconsistent with the claim you made in question 3? Explain your answer. The two parents are lactose tolerant, meaning they can be homozygous or heterozygous for the dominant allele. The only way to explain how their ...
Genome-wide deleterious mutation favors dispersal and
... frequency. The migrant relative fitness from fully recessive lethal mutations is W̄migrant/W̄local = enV(p). Migrant relative fitness increases with the between-population variation in allele frequency, V(p). Increasing the number of loci experiencing deleterious mutation, and hence the genome-wide ...
... frequency. The migrant relative fitness from fully recessive lethal mutations is W̄migrant/W̄local = enV(p). Migrant relative fitness increases with the between-population variation in allele frequency, V(p). Increasing the number of loci experiencing deleterious mutation, and hence the genome-wide ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.