Document
... Males and females can differ in sex-linked traits. • Genes on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked genes. – Y chromosome genes in mammals are responsible for male characteristics. About 78 genes (code for about 25 ...
... Males and females can differ in sex-linked traits. • Genes on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked genes. – Y chromosome genes in mammals are responsible for male characteristics. About 78 genes (code for about 25 ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... 10.4 More complex patterns of inheritance are an extension of Mendel's basic rules. Other types of inheritance patterns have been discovered since Mendel's initial work. Some alleles show incomplete dominance or co-dominance. Traits which show incomplete dominance have three phenotypes, the heterozy ...
... 10.4 More complex patterns of inheritance are an extension of Mendel's basic rules. Other types of inheritance patterns have been discovered since Mendel's initial work. Some alleles show incomplete dominance or co-dominance. Traits which show incomplete dominance have three phenotypes, the heterozy ...
Mendelian genetics complete
... Genotype ratio: _________________________________________ Phenotype ratio: ________________________________________ D. Use a Punnett square to determine the genotype and phenotype ratios of the offspring from a cross between a homozygous dominant yellow pea pea plant and a homozygous recessive green ...
... Genotype ratio: _________________________________________ Phenotype ratio: ________________________________________ D. Use a Punnett square to determine the genotype and phenotype ratios of the offspring from a cross between a homozygous dominant yellow pea pea plant and a homozygous recessive green ...
Pedigree
... • Because phenylalanine cannot be broken down, it and its by-products accumulate in the body and result in severe damage to the central nervous system. ...
... • Because phenylalanine cannot be broken down, it and its by-products accumulate in the body and result in severe damage to the central nervous system. ...
GRADE-8 SCIENCE
... recessive allele respectively). This is what occurred in Mendel’s first experiment since ___________________ is the dominant color and dominant alleles are always expressed over recessive alleles in a genotype. It is only when both alleles in a genotype are recessive that they are expressed (become ...
... recessive allele respectively). This is what occurred in Mendel’s first experiment since ___________________ is the dominant color and dominant alleles are always expressed over recessive alleles in a genotype. It is only when both alleles in a genotype are recessive that they are expressed (become ...
Chapter Eleven: Heredity
... • To better control his experiments, Mendel used a method called selfpollination. • The parts of the flower that contain pollen (the anthers) were removed so the flower could not self-pollinate. ...
... • To better control his experiments, Mendel used a method called selfpollination. • The parts of the flower that contain pollen (the anthers) were removed so the flower could not self-pollinate. ...
Genetic Diversity of Offspring
... • A dominant gene is one that will produce its observable effects in either the homozygous or heterozygous condition • A recessive gene is one that will only produce its observable effects in the homozygous condition ...
... • A dominant gene is one that will produce its observable effects in either the homozygous or heterozygous condition • A recessive gene is one that will only produce its observable effects in the homozygous condition ...
Test Review Genetics08-09
... between the phenotypes of the parents. Example: When red snapdragons are crossed with white snapdragons all the offspring have pink flowers 41. ______:The alleles for A and B blood types are codominant, and both are expressed in the phenotype 42. ______:A single gene may affect phenotype in many way ...
... between the phenotypes of the parents. Example: When red snapdragons are crossed with white snapdragons all the offspring have pink flowers 41. ______:The alleles for A and B blood types are codominant, and both are expressed in the phenotype 42. ______:A single gene may affect phenotype in many way ...
NOTES: 14.1 -14.2 HUMAN HEREDITY
... any of the 44 chromosomes—NOT the sex chromosomes) to express the disease • EX: Cystic Fibrosis ...
... any of the 44 chromosomes—NOT the sex chromosomes) to express the disease • EX: Cystic Fibrosis ...
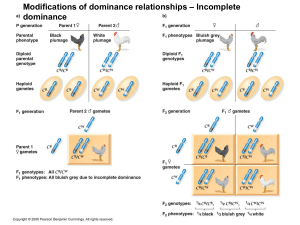
Modifications of dominance relationships – Incomplete dominance
... At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of gangliosides. ...
... At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of gangliosides. ...
Presentation
... that says a plant should have green seeds and the other parent contributes an allele that says the offspring should have yellow seeds, one of them will mask the other one. ...
... that says a plant should have green seeds and the other parent contributes an allele that says the offspring should have yellow seeds, one of them will mask the other one. ...
MODELING POLYGENIC INHERITANCE Polygenic traits are
... Directions for using our model 1. Assume 3 genes carried by 3 chromosomes (represented by 3 coins) determine human height. Heads (H) represent active alleles (A, B, C), while tails (T) represent inactive alleles (a, b, c). Tossing the coins represents meiosis; combining their outcomes represents fer ...
... Directions for using our model 1. Assume 3 genes carried by 3 chromosomes (represented by 3 coins) determine human height. Heads (H) represent active alleles (A, B, C), while tails (T) represent inactive alleles (a, b, c). Tossing the coins represents meiosis; combining their outcomes represents fer ...
Chapter 10, 11, 12, 13 Review Questions
... researched this? What specimen did this person use and why? What are some characteristics of this specimen? DNA; your features; from your parents; genes; alleles, sex cells; Mendel; pea plants, that was what he had on hand 2. What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? What does it mean t ...
... researched this? What specimen did this person use and why? What are some characteristics of this specimen? DNA; your features; from your parents; genes; alleles, sex cells; Mendel; pea plants, that was what he had on hand 2. What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? What does it mean t ...
www.njctl.org AP Biology Heredity Multiple Choice Review
... resulting in 200 offspring, how many offspring will be heterozygous for the trait? 2. In humans, having dimples (D) is dominant over not having dimples (d) and a cleft chin (C) is dominant over a smooth chin (c). If a male and female heterozygous for both genes have children, what percentage will ha ...
... resulting in 200 offspring, how many offspring will be heterozygous for the trait? 2. In humans, having dimples (D) is dominant over not having dimples (d) and a cleft chin (C) is dominant over a smooth chin (c). If a male and female heterozygous for both genes have children, what percentage will ha ...
Genetics - Spring Branch ISD
... What is the relationship between traits, genes, chromosomes, and alleles? A gene is a section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. Alleles are different forms of a gene that provide the code for specific inherited traits. Examples:hair color, eye color, leaf shape The code in the ...
... What is the relationship between traits, genes, chromosomes, and alleles? A gene is a section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. Alleles are different forms of a gene that provide the code for specific inherited traits. Examples:hair color, eye color, leaf shape The code in the ...
Chapter 13 Chromosomes
... a cataclysmic geological event that separates two populations, such as an earthquake or flood. ...
... a cataclysmic geological event that separates two populations, such as an earthquake or flood. ...
study of mendelian and non mendelian inheritance pattern
... NON-MENDELIAN INHERITANCE Non-Mendelian inheritance is a general term that refers to any pattern of inheritance in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel’s laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. In Mendelian inherita ...
... NON-MENDELIAN INHERITANCE Non-Mendelian inheritance is a general term that refers to any pattern of inheritance in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel’s laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. In Mendelian inherita ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... • Codominant alleles will both be completely expressed • Many genes may interact to produce one trait • The environment interacts with genotype ...
... • Codominant alleles will both be completely expressed • Many genes may interact to produce one trait • The environment interacts with genotype ...
Speciation
... of a new species Species: A group of similar organisms that breed together and produce fertile offspring. Gene pools must become separated for them to become different species. ...
... of a new species Species: A group of similar organisms that breed together and produce fertile offspring. Gene pools must become separated for them to become different species. ...
General Lesson Planning Format
... allele for a white coat. A black guinea pig was crossed with a white guinea pig. All F1 offspring have black coats. a) Describe how you can determine whether or not the black parent is homozygous or heterozygous for the condition. Indicate the letter you will use to represent an allele. b) If 10 off ...
... allele for a white coat. A black guinea pig was crossed with a white guinea pig. All F1 offspring have black coats. a) Describe how you can determine whether or not the black parent is homozygous or heterozygous for the condition. Indicate the letter you will use to represent an allele. b) If 10 off ...
Quiz 6-KEY
... 5. In snapdragons, heterozygotes have pink flowers while the two homozygotes have either red or white flowers. When plants with red flowers are crossed with plants with white flowers, what proportion of the offspring will have pink flowers? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% 6. The example in questi ...
... 5. In snapdragons, heterozygotes have pink flowers while the two homozygotes have either red or white flowers. When plants with red flowers are crossed with plants with white flowers, what proportion of the offspring will have pink flowers? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% 6. The example in questi ...
You Light Up My Life
... the first trait were to be assorted into gametes independently of the two “units” for the other trait Members of each pair of homologous chromosomes are sorted into gametes at ...
... the first trait were to be assorted into gametes independently of the two “units” for the other trait Members of each pair of homologous chromosomes are sorted into gametes at ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.