Transcription and Translation Exercise
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
... 7. The allele of the gene above is dominant and codes for red kernel pigment (it is designated as R). Another allele of this gene, the r allele (which is recessive), codes for white kernel pigment and is the result of a mutation in the R allele. In the r allele, the second nucleotide (base) in the s ...
CHAPTER 4
... • He tracked the inheritance of characters that occur as two alternative traits. Monohybrid Crosses • A monohybrid cross is a cross between parent plants that differ in only one character. • Mendel developed four hypotheses from the monohybrid cross: 1. There are alternative versions of genes, calle ...
... • He tracked the inheritance of characters that occur as two alternative traits. Monohybrid Crosses • A monohybrid cross is a cross between parent plants that differ in only one character. • Mendel developed four hypotheses from the monohybrid cross: 1. There are alternative versions of genes, calle ...
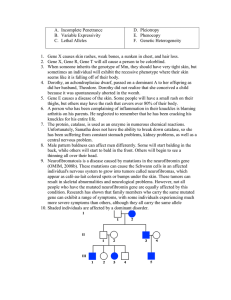
A. Incomplete Penetrance D. Pleiotropy B. Variable Expressivity
... 9. Neurofibromatosis is a disease caused by mutations in the neurofibromin gene (OMIM, 2008b). These mutations can cause the Schwann cells in an affected individual's nervous system to grow into tumors called neurofibromas, which appear as café-au-lait colored spots or bumps under the skin. These tu ...
... 9. Neurofibromatosis is a disease caused by mutations in the neurofibromin gene (OMIM, 2008b). These mutations can cause the Schwann cells in an affected individual's nervous system to grow into tumors called neurofibromas, which appear as café-au-lait colored spots or bumps under the skin. These tu ...
Enduring Understandings • The work of Gregor Mendel describes
... punnett square, dihybrid cross, pedigree, sex-linked (x-linked/xy inheritance), polygenic inheritance, incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, autosomal inheritance, sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, huntington’s disease Learning Targets 1. Be able to discuss the genotype ...
... punnett square, dihybrid cross, pedigree, sex-linked (x-linked/xy inheritance), polygenic inheritance, incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, autosomal inheritance, sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, huntington’s disease Learning Targets 1. Be able to discuss the genotype ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... Gametes are placed above and to the left of the square Offspring are placed in the square. Capital letters (Y) represent dominant alleles. Lower case letters (y) represent recessive alleles. ...
... Gametes are placed above and to the left of the square Offspring are placed in the square. Capital letters (Y) represent dominant alleles. Lower case letters (y) represent recessive alleles. ...
Section 6.5: Traits and Probabilities
... Phenotype can depend on interactions of alleles. • In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant nor completely recessive. – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes – Homozygous parental phenotypes not seen in F1 offspring ...
... Phenotype can depend on interactions of alleles. • In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant nor completely recessive. – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes – Homozygous parental phenotypes not seen in F1 offspring ...
Protein - UDKeystone
... 1. Dominant vs. Recessive – one allele completely masks another allele. 2. Incomplete Dominance 1. Definition : one allele is not completely dominant over another Ex: flowers – white x red flowers = pink flowers ...
... 1. Dominant vs. Recessive – one allele completely masks another allele. 2. Incomplete Dominance 1. Definition : one allele is not completely dominant over another Ex: flowers – white x red flowers = pink flowers ...
Honors Biology - ahs-guntherbiology-2009
... __________ 12. In Laborador retrievers, coat color is controlled by two genes. Black coat color (B) is dominat to brown coat color (b). However, dogs that are homozygous recessive at another unlinked gene (e) are yellow. A dog that has genotype EdBb (black) is bred with another dog whose genotype is ...
... __________ 12. In Laborador retrievers, coat color is controlled by two genes. Black coat color (B) is dominat to brown coat color (b). However, dogs that are homozygous recessive at another unlinked gene (e) are yellow. A dog that has genotype EdBb (black) is bred with another dog whose genotype is ...
meiosis_10
... within a population Imagine a population of aliens in which skin colour is conferred by one gene locus The alleles that may be found at this locus are SR coding for red pigment and SY coding for yellow pigment, in other words they are codominant. If an allele is present then the pigment that it code ...
... within a population Imagine a population of aliens in which skin colour is conferred by one gene locus The alleles that may be found at this locus are SR coding for red pigment and SY coding for yellow pigment, in other words they are codominant. If an allele is present then the pigment that it code ...
Slide 1
... • Heterozygote shows an intermediate, blended phenotype – example: • RR = red flowers • rr = white flowers • Rr = pink flowers ...
... • Heterozygote shows an intermediate, blended phenotype – example: • RR = red flowers • rr = white flowers • Rr = pink flowers ...
Introduction To Genetics
... C. Beyond Dominance and Recessive alleles 1. Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, and many traits are controlled by multiple alleles or multiple genes. 2. Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another are called incomplete dominance. ...
... C. Beyond Dominance and Recessive alleles 1. Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, and many traits are controlled by multiple alleles or multiple genes. 2. Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another are called incomplete dominance. ...
Mendel`s Hypotheses – Mendelian Theory of Heredity
... When gametes form, each receives only ______ out of the _______factors for each trait. ...
... When gametes form, each receives only ______ out of the _______factors for each trait. ...
Lab. 8 Deviation of Mendel`s first law “Monohybrid” part 1
... For example: In snapdragon flower, the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio for F2 generation is the same which is 1:2:1. This is due to incomplete dominance where recombinant progeny is produced. A red flower and white flower cross would produce 1 red flower, 2 pink flowers and 1 white flower. This ...
... For example: In snapdragon flower, the phenotypic ratio and genotypic ratio for F2 generation is the same which is 1:2:1. This is due to incomplete dominance where recombinant progeny is produced. A red flower and white flower cross would produce 1 red flower, 2 pink flowers and 1 white flower. This ...
Natural Selection Simulation Name: Introduction: Natural Selection
... We are going to be studying a population of insects focusing on the gene which codes for the color of these organisms. This is a case in incomplete dominance and the genotypes and phenotypes are as follows: AA= Yellow Aa= Green aa= Grey 2. If you cross a two green individuals what are the probable g ...
... We are going to be studying a population of insects focusing on the gene which codes for the color of these organisms. This is a case in incomplete dominance and the genotypes and phenotypes are as follows: AA= Yellow Aa= Green aa= Grey 2. If you cross a two green individuals what are the probable g ...
14.2 ws
... 1. The boxes below each show a step to explain how genetic disorders have a molecular basis. Number them so that the steps are in the correct order. A change in phenotype results. ...
... 1. The boxes below each show a step to explain how genetic disorders have a molecular basis. Number them so that the steps are in the correct order. A change in phenotype results. ...
Hereditary Traits and Pedigrees
... genotypes- RR and Rr • There non-rolling phenotype has only one possible genotype- rr. ...
... genotypes- RR and Rr • There non-rolling phenotype has only one possible genotype- rr. ...
Glossary AV 121017
... Identity by descent. The situation where alleles in two or more individuals are identical because of common ancestry. Identity by state. The situation where alleles in two or more individuals are identical due to coincidence or to common ancestry. kilo base pairs (1.103 bp). The tendency of DNA sequ ...
... Identity by descent. The situation where alleles in two or more individuals are identical because of common ancestry. Identity by state. The situation where alleles in two or more individuals are identical due to coincidence or to common ancestry. kilo base pairs (1.103 bp). The tendency of DNA sequ ...
Hardy-Weinberg Problem Set
... red blood cells, while Rh− individuals do not. There are two different alleles for the Rh factor known as Rh+ and rh. Assume that a dominant gene Rh produces the Rh+ phenotype, and that the recessive rh allele produces the Rh− phenotype.In a population that is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 160 out ...
... red blood cells, while Rh− individuals do not. There are two different alleles for the Rh factor known as Rh+ and rh. Assume that a dominant gene Rh produces the Rh+ phenotype, and that the recessive rh allele produces the Rh− phenotype.In a population that is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 160 out ...
Inheritance Practice Quiz
... a recessive allele, which allows the second allele to be expressed. Individuals with the brown allele have brown eyes regardless of the second gene. For the second gene, the green allele is dominant to the blue allele. (*this explains the majority of eye inheritance, but there are many exceptions an ...
... a recessive allele, which allows the second allele to be expressed. Individuals with the brown allele have brown eyes regardless of the second gene. For the second gene, the green allele is dominant to the blue allele. (*this explains the majority of eye inheritance, but there are many exceptions an ...
Chapter 20 Inheritance, Genetics, and Molecular Biology So how
... o e.g. skin color is influenced by sun exposure o e.g. height can be affected by nutrition Codominance o Occurs when two different alleles are equally expressed in a heterozygote Multiple alleles o The gene exists in several allelic forms o A person only has 2 of the possible alleles o A good exampl ...
... o e.g. skin color is influenced by sun exposure o e.g. height can be affected by nutrition Codominance o Occurs when two different alleles are equally expressed in a heterozygote Multiple alleles o The gene exists in several allelic forms o A person only has 2 of the possible alleles o A good exampl ...
Baby Boom Alien Crosses
... BI2. c. Students know how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. BI2. g. Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. BI3. a. Students know how to predict the prob ...
... BI2. c. Students know how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. BI2. g. Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. BI3. a. Students know how to predict the prob ...
Document
... Main idea: if affected siblings share more IBD alleles at some marker locus than randomly expected among siblings, then that locus might be near a locus of a predisposing gene. The idea is that any two siblings are expected to have one allele IBD by chance. When a deviation of this pattern is dete ...
... Main idea: if affected siblings share more IBD alleles at some marker locus than randomly expected among siblings, then that locus might be near a locus of a predisposing gene. The idea is that any two siblings are expected to have one allele IBD by chance. When a deviation of this pattern is dete ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.