Genes - Unit3and4Biology
... (uppercase letters) qq stands for a homozygous recessive genotype (lowercase letters). Heterozygous means that each of the alleles are ...
... (uppercase letters) qq stands for a homozygous recessive genotype (lowercase letters). Heterozygous means that each of the alleles are ...
Pedigrees/Sex-linked traits - Liberty Union High School District
... A person with an autosomal recessive disorder must have a homozygous recessive genotype (hh). Carrier: a heterozygous person who does not have the disorder, but carries the recessive allele so that it can be passed on to future generations (Hh) ...
... A person with an autosomal recessive disorder must have a homozygous recessive genotype (hh). Carrier: a heterozygous person who does not have the disorder, but carries the recessive allele so that it can be passed on to future generations (Hh) ...
AI - tcurry1977
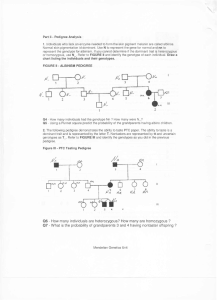
... 1. The following pedigrees will be used to determine whether the trait is autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. In tracing autosomal alleles, if both parents have the disorder and the offspring do not, the condition is autosomal dominant. If neither parent shows the disorder but some of their c ...
... 1. The following pedigrees will be used to determine whether the trait is autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. In tracing autosomal alleles, if both parents have the disorder and the offspring do not, the condition is autosomal dominant. If neither parent shows the disorder but some of their c ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... For example, plant height in our wildflower population includes short and tall plants and everything in between. Quantitative variation is usually due to polygenic inheritance in which the additive effects of two or more genes influence a single phenotypic character. Discrete characters, such as ...
... For example, plant height in our wildflower population includes short and tall plants and everything in between. Quantitative variation is usually due to polygenic inheritance in which the additive effects of two or more genes influence a single phenotypic character. Discrete characters, such as ...
Numbers of - TeacherWeb
... Using split peas, we will simulate a Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for one locus with 2 alleles. Working with a partner, obtain 100 yellow and 100 green split peas. Each pea represents an allele (y or g) at the “split pea” gene locus. The imaginary species is diploid, so each individual in the populati ...
... Using split peas, we will simulate a Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for one locus with 2 alleles. Working with a partner, obtain 100 yellow and 100 green split peas. Each pea represents an allele (y or g) at the “split pea” gene locus. The imaginary species is diploid, so each individual in the populati ...
Chapter 14
... a. To be expressed in females, there must be two copies of the allele, one on each of the two X chromosomes. d d ...
... a. To be expressed in females, there must be two copies of the allele, one on each of the two X chromosomes. d d ...
Chromosomes and Genetics
... Red eye female → XRXR White eye male → XrY XR is allele for red eye dominant Xr is allele for white eye recessive No symbol on Y because it doesn’t have an allele for the trait ...
... Red eye female → XRXR White eye male → XrY XR is allele for red eye dominant Xr is allele for white eye recessive No symbol on Y because it doesn’t have an allele for the trait ...
Traits ppt slides
... The dominant allele is the form of a gene that, when present, covers up the appearance of the recessive allele. The recessive allele is the form of a gene that is hidden when the dominant allele is present. ...
... The dominant allele is the form of a gene that, when present, covers up the appearance of the recessive allele. The recessive allele is the form of a gene that is hidden when the dominant allele is present. ...
genomic diversity and differentiation
... The classic example of phenomena well modelled by a Poisson process is deaths due to horse kick in the Prussian army, as shown by Ladislaus Bortkiewicz in 1898.[4][5] The following examples are also well-modeled by the Poisson process: •Requests for telephone calls at a switchboard. •Goals scored in ...
... The classic example of phenomena well modelled by a Poisson process is deaths due to horse kick in the Prussian army, as shown by Ladislaus Bortkiewicz in 1898.[4][5] The following examples are also well-modeled by the Poisson process: •Requests for telephone calls at a switchboard. •Goals scored in ...
Sexual reproduction
... Your cells have 2 sets of alleles for each trait (1 from each parent) Alleles are represented by letters. (AA, Aa, aa) ...
... Your cells have 2 sets of alleles for each trait (1 from each parent) Alleles are represented by letters. (AA, Aa, aa) ...
Genetics Review
... that, for a normal cell to become a cancer cell, a minimum of two genetic changes had to occur in that cell. Knudsen was studying retinoblastoma, a childhood cancer of the eye. If there are two children born from the same parents, and child one inherits a predisposition to retinoblastoma (one of the ...
... that, for a normal cell to become a cancer cell, a minimum of two genetic changes had to occur in that cell. Knudsen was studying retinoblastoma, a childhood cancer of the eye. If there are two children born from the same parents, and child one inherits a predisposition to retinoblastoma (one of the ...
NAME ___ANSWER KEY CH. 10 STUDY GUIDE
... f. Prophase II: nuclear membrane breaks down; nucleolus disappears; centrioles begin to migrate to opposite sides of both cells; spindle fibers begin to form; sister chromatids form g. Metaphase II: sister chromatids are lined up down the middle of both cells. h. Anaphase II: sister chromatids are p ...
... f. Prophase II: nuclear membrane breaks down; nucleolus disappears; centrioles begin to migrate to opposite sides of both cells; spindle fibers begin to form; sister chromatids form g. Metaphase II: sister chromatids are lined up down the middle of both cells. h. Anaphase II: sister chromatids are p ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... 15. Fur color in cats is controlled by an autosomal gene that can occur in the dominant form, (B), or the recessive form, (b). The length of the cat’s fur is controlled by another autosomal gene which occurs in the dominant form, (S), or the recessive form, (s). The table below shows the traits for ...
... 15. Fur color in cats is controlled by an autosomal gene that can occur in the dominant form, (B), or the recessive form, (b). The length of the cat’s fur is controlled by another autosomal gene which occurs in the dominant form, (S), or the recessive form, (s). The table below shows the traits for ...
2. Mendelian Pedigree patterns
... successive generations. Geneticists should avoid misinterpreting anticipation with variable expression. Anticipation is caused in cases that are due to unstable expandable trinucleotide repeats (e.g. Fragile-X) cause by misalignment of such repeats during crossing over. ...
... successive generations. Geneticists should avoid misinterpreting anticipation with variable expression. Anticipation is caused in cases that are due to unstable expandable trinucleotide repeats (e.g. Fragile-X) cause by misalignment of such repeats during crossing over. ...
All possible green x green in Blue world?
... Vocab Revisited • Gene: A stretch of DNA that represents all the information for a product as well as when and where to make the product • Allele: A version (or flavor) of a gene; two alleles of the same gene my differ by a nucleotide or dozens of them--generally a small number • Dominant/recessive ...
... Vocab Revisited • Gene: A stretch of DNA that represents all the information for a product as well as when and where to make the product • Allele: A version (or flavor) of a gene; two alleles of the same gene my differ by a nucleotide or dozens of them--generally a small number • Dominant/recessive ...
document
... that results in a longer X chromatid. A child receiving this chromosome can be male or female but mostly boys because it is a recessive trait to a ...
... that results in a longer X chromatid. A child receiving this chromosome can be male or female but mostly boys because it is a recessive trait to a ...
Ecology notes Key to fill in the blank STUDENT copy
... When writing – use a capital letter. I. Recessive trait – a characteristic allele that will require 2 of these traits to be present to observe (see) it in the offspring. When writing - use a lowercase letter. J. Heterozygous – both a dominant and recessive allele is present. In plants it is called a ...
... When writing – use a capital letter. I. Recessive trait – a characteristic allele that will require 2 of these traits to be present to observe (see) it in the offspring. When writing - use a lowercase letter. J. Heterozygous – both a dominant and recessive allele is present. In plants it is called a ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... 15. Fur color in cats is controlled by an autosomal gene that can occur in the dominant form, (B), or the recessive form, (b). The length of the cat’s fur is controlled by another autosomal gene which occurs in the dominant form, (S), or the recessive form, (s). The table below shows the traits for ...
... 15. Fur color in cats is controlled by an autosomal gene that can occur in the dominant form, (B), or the recessive form, (b). The length of the cat’s fur is controlled by another autosomal gene which occurs in the dominant form, (S), or the recessive form, (s). The table below shows the traits for ...
Slide 1
... A. For example, a purple flowered pea plant could be PP (homozygous dominant) or heterozygous (Pp). The purple flowered plant is crossed with a white flowered plant (pp) to determine the genotype of the first pea plant. ...
... A. For example, a purple flowered pea plant could be PP (homozygous dominant) or heterozygous (Pp). The purple flowered plant is crossed with a white flowered plant (pp) to determine the genotype of the first pea plant. ...
Sickle Cell Mutation WS - Lincoln Park High School
... Sickle Cell Allele Mutation WS Sickle cell disease is a disorder that gets its name from the sickle shape of red blood cells (RBCs) which normally have a round, disk-like shape. The sickle-shaped RBCs are caused by a faulty hemoglobin resulting from a point mutation in which just one nucleotide base ...
... Sickle Cell Allele Mutation WS Sickle cell disease is a disorder that gets its name from the sickle shape of red blood cells (RBCs) which normally have a round, disk-like shape. The sickle-shaped RBCs are caused by a faulty hemoglobin resulting from a point mutation in which just one nucleotide base ...
Synthetic theory of evolution. Peculiarities of action of evolutionary
... pair up by chance and not according to their genotypes or phenotypes. In human population, inbreeding increases the frequency of recessive abnormalities. Assortative mating occurs when individuals tend to mate with those that have the same phenotype with respect to some characteristic (in humans tal ...
... pair up by chance and not according to their genotypes or phenotypes. In human population, inbreeding increases the frequency of recessive abnormalities. Assortative mating occurs when individuals tend to mate with those that have the same phenotype with respect to some characteristic (in humans tal ...
solutions to genetics problems
... 50% of the offspring should be gray (Bb ) and 50% black (BB ) Problem 2 In some plants, a true-breeding, red-flowered strain gives all pink flowers when crossed with a white-flowered strain: RR (red) x rr (white) ---> Rr (pink). If flower position (axial or terminal) is inherited as it is in peas wh ...
... 50% of the offspring should be gray (Bb ) and 50% black (BB ) Problem 2 In some plants, a true-breeding, red-flowered strain gives all pink flowers when crossed with a white-flowered strain: RR (red) x rr (white) ---> Rr (pink). If flower position (axial or terminal) is inherited as it is in peas wh ...
Genetics Problems
... 10. In Drosophila, normal fruit flies are called "wildtypes." In wildtype flies the eye color is bright red (R). Some flies have a mutation which produces white eyes (r); they have a defect in their "white" gene. In these flies, the white gene is totally defective: it produces no red pigment at all ...
... 10. In Drosophila, normal fruit flies are called "wildtypes." In wildtype flies the eye color is bright red (R). Some flies have a mutation which produces white eyes (r); they have a defect in their "white" gene. In these flies, the white gene is totally defective: it produces no red pigment at all ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.