REVIEW WORKSHEET
... 13. In cats short hair (H) is dominant over long hair (h) and is carried on the autosomes, not sex-linked. Another gene, (B) which is sex linked, produces yellow coat color; its allele (b) produces black coat color; and the heterozygous combination produces tortoise shell coat color. If a long hair ...
... 13. In cats short hair (H) is dominant over long hair (h) and is carried on the autosomes, not sex-linked. Another gene, (B) which is sex linked, produces yellow coat color; its allele (b) produces black coat color; and the heterozygous combination produces tortoise shell coat color. If a long hair ...
ppt
... clearly irreducible. However, if the loci are tightly linked, mixing performance will be poor. ...
... clearly irreducible. However, if the loci are tightly linked, mixing performance will be poor. ...
Population
... Recall basic genetic principles: • The total number of alleles for any gene in a population is the number of individuals in the population x 2 If the population has 10 individuals, there are 20 copies of the A gene – some “A” alleles and some “a” alleles ...
... Recall basic genetic principles: • The total number of alleles for any gene in a population is the number of individuals in the population x 2 If the population has 10 individuals, there are 20 copies of the A gene – some “A” alleles and some “a” alleles ...
Autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
... However, it was the morphological findings3 from the sural nerve biopsy of one patient, including severe depletion of myelinated fibres with small diameters and thin sheaths, relatively few and small onion bulbs in comparison with CMT1A and Schwann cells with multiple cytoplasmic processes which rea ...
... However, it was the morphological findings3 from the sural nerve biopsy of one patient, including severe depletion of myelinated fibres with small diameters and thin sheaths, relatively few and small onion bulbs in comparison with CMT1A and Schwann cells with multiple cytoplasmic processes which rea ...
univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... the nucleus of each cell. During normal (somatic) growth, mitotic cell divisions split each chromosomes with its complement of alleles into two identical parts each of which goes to the two new cells - and thereby keeping each cell of a given individual with the same double complement of chromosomes ...
... the nucleus of each cell. During normal (somatic) growth, mitotic cell divisions split each chromosomes with its complement of alleles into two identical parts each of which goes to the two new cells - and thereby keeping each cell of a given individual with the same double complement of chromosomes ...
univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... the nucleus of each cell. During normal (somatic) growth, mitotic cell divisions split each chromosomes with its complement of alleles into two identical parts each of which goes to the two new cells - and thereby keeping each cell of a given individual with the same double complement of chromosomes ...
... the nucleus of each cell. During normal (somatic) growth, mitotic cell divisions split each chromosomes with its complement of alleles into two identical parts each of which goes to the two new cells - and thereby keeping each cell of a given individual with the same double complement of chromosomes ...
document
... An example for a codeml.ctl file is codeml.hv1.sites.ctl This file directs codeml to run three different models: one with an omega fixed at 1, a second where each site can be either have an omega between 0 and 1, or an omega of 1, and third a model that uses three omegas as described before for MrBa ...
... An example for a codeml.ctl file is codeml.hv1.sites.ctl This file directs codeml to run three different models: one with an omega fixed at 1, a second where each site can be either have an omega between 0 and 1, or an omega of 1, and third a model that uses three omegas as described before for MrBa ...
Document
... the allelic combinations in the gametes from one sex in the F1, thus clearly showing the coupling that could only be inferred from Bateson and Punnett's F1 self. The testcross also reveals something new: there is approximately a 1:1 ratio not only between the two parental types, but also between the ...
... the allelic combinations in the gametes from one sex in the F1, thus clearly showing the coupling that could only be inferred from Bateson and Punnett's F1 self. The testcross also reveals something new: there is approximately a 1:1 ratio not only between the two parental types, but also between the ...
long eyelashes e
... 5. Hagrid found two baby dragons in the forest. Both are heterozygous for their fire-breathing ability, which is the dominant trait. Create a Punnett square to show the possibilities that would result if these two dragons had children. Use F for the dominant allele and f for the recessive. ...
... 5. Hagrid found two baby dragons in the forest. Both are heterozygous for their fire-breathing ability, which is the dominant trait. Create a Punnett square to show the possibilities that would result if these two dragons had children. Use F for the dominant allele and f for the recessive. ...
aps4-artifact
... answer in terms of Mendel’s first law. 2. Why are extremely rare autosomal recessive disorders more likely to appear in families in which blood relatives have children together? 3. Why are X-linked disorders more common in males than females? Can females be affected by a X-linked disorder? 4. What i ...
... answer in terms of Mendel’s first law. 2. Why are extremely rare autosomal recessive disorders more likely to appear in families in which blood relatives have children together? 3. Why are X-linked disorders more common in males than females? Can females be affected by a X-linked disorder? 4. What i ...
Name: Date: ____________ Class period: _____ Quick Lab: How is
... 5. Close your eyes and pick one bean from each cup to represent how each parent contributes a sex chromosome to a fertilized egg. 6. In your data table, record the color of each bean and the sex of an individual who would carry this pair of sex chromosomes. Also record how many X-linked alleles the ...
... 5. Close your eyes and pick one bean from each cup to represent how each parent contributes a sex chromosome to a fertilized egg. 6. In your data table, record the color of each bean and the sex of an individual who would carry this pair of sex chromosomes. Also record how many X-linked alleles the ...
Ch15ChromosomalInheritance
... • Application: Use of karyograms to deduce sex and diagnose Down syndrome in humans. • Application: Non-disjunction can cause Down syndrome and other chromosome abnormalities. • Application: Studies showing age of parents influences chances of nondisjunction. From Topic 3.4 Understandings: • Some ge ...
... • Application: Use of karyograms to deduce sex and diagnose Down syndrome in humans. • Application: Non-disjunction can cause Down syndrome and other chromosome abnormalities. • Application: Studies showing age of parents influences chances of nondisjunction. From Topic 3.4 Understandings: • Some ge ...
Lesson: Introduction to Genetic Traits - GK
... The complex subject of genetics is generally introduced by first observing and discussing how certain physical (or behavioral) characteristics occur in individuals from different generations of the same family. These inheritance traits are then explained by introducing the principles of Mendelian ge ...
... The complex subject of genetics is generally introduced by first observing and discussing how certain physical (or behavioral) characteristics occur in individuals from different generations of the same family. These inheritance traits are then explained by introducing the principles of Mendelian ge ...
Introduction Survival of the Fittest— Battling Beetles
... generation. Students should record the values of s and either record or print the values for p and q. During this exercise, the frequency of the dominant phenotype increases as the frequency of the recessive phenotype decreases. 17. The color of the landscape might change so that some members of the ...
... generation. Students should record the values of s and either record or print the values for p and q. During this exercise, the frequency of the dominant phenotype increases as the frequency of the recessive phenotype decreases. 17. The color of the landscape might change so that some members of the ...
Genetics of the Fruit Fly
... commonly, of a certain gene or a set of genes. Homozygous (gene pair): A gene pair having identical alleles in both copies – for example, A/A. Heterozygous (gene pair): A gene pair having different alleles in the two chromosome sets of the diploid individual – for example, A/a. Carrier: An individua ...
... commonly, of a certain gene or a set of genes. Homozygous (gene pair): A gene pair having identical alleles in both copies – for example, A/A. Heterozygous (gene pair): A gene pair having different alleles in the two chromosome sets of the diploid individual – for example, A/a. Carrier: An individua ...
Survival of the Fittest—Battling Beetles
... generation. Students should record the values of s and either record or print the values for p and q. During this exercise, the frequency of the dominant phenotype increases as the frequency of the recessive phenotype decreases. 17. The color of the landscape might change so that some members of the ...
... generation. Students should record the values of s and either record or print the values for p and q. During this exercise, the frequency of the dominant phenotype increases as the frequency of the recessive phenotype decreases. 17. The color of the landscape might change so that some members of the ...
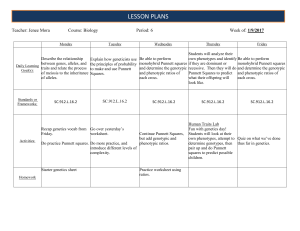
lesson Plans - Lemon Bay High School
... Punnett Squares to predict and phenotypic ratios of what their offspring will each cross. look like. ...
... Punnett Squares to predict and phenotypic ratios of what their offspring will each cross. look like. ...
Materials - Computer Science
... 08.SC.IS.04 Present and explain data and findings using multiple representations, including tables, graphs, mathematical and physical models, and demonstrations. 08.SC.IS.05 Draw conclusions based on data or evidence presented in tables or graphs, and make inferences based on patterns or trends in ...
... 08.SC.IS.04 Present and explain data and findings using multiple representations, including tables, graphs, mathematical and physical models, and demonstrations. 08.SC.IS.05 Draw conclusions based on data or evidence presented in tables or graphs, and make inferences based on patterns or trends in ...
File
... what exactly was inherited? Mendel lived out his life without knowing that the answer to that question was “genes.” The story of inheritance unfolds inside the cell. Everything is made of cells, and that’s where the information describing how to make you resides. Cells have many smaller structures ...
... what exactly was inherited? Mendel lived out his life without knowing that the answer to that question was “genes.” The story of inheritance unfolds inside the cell. Everything is made of cells, and that’s where the information describing how to make you resides. Cells have many smaller structures ...
Test Genetics Practice Problems #1-12
... 5. In unicorns, both the horn and wings are codominannt. Assume that horns are expressed from the homozygous CH genotype, wings from the homozygous CW genotype, and both from the heterozygous genotype. What will be the phenotypic ratio of the F1 generation resulting from a cross of two unicorns, one ...
... 5. In unicorns, both the horn and wings are codominannt. Assume that horns are expressed from the homozygous CH genotype, wings from the homozygous CW genotype, and both from the heterozygous genotype. What will be the phenotypic ratio of the F1 generation resulting from a cross of two unicorns, one ...
Ch10 2nd ½ Review - Plain Local Schools
... 2. In unicorns, both the horn and wings are codominannt. Assume that horns are expressed from the homozygous CH genotype, wings from the homozygous CW genotype, and both from the heterozygous genotype. What will be the phenotypic ratio of the F1 generation resulting from a cross of two unicorns, one ...
... 2. In unicorns, both the horn and wings are codominannt. Assume that horns are expressed from the homozygous CH genotype, wings from the homozygous CW genotype, and both from the heterozygous genotype. What will be the phenotypic ratio of the F1 generation resulting from a cross of two unicorns, one ...
Exam 2
... airway cells. The normal allele for the gene is introduced into the airway cells in delivery particles that have been built using highly modified components of the HIV-1 (AIDS) virus. ...
... airway cells. The normal allele for the gene is introduced into the airway cells in delivery particles that have been built using highly modified components of the HIV-1 (AIDS) virus. ...
(I) u--- ---d - uchicago hep
... An XX worm produces both ovum and sperm Thus, it can self-fertilize to produce progeny ...
... An XX worm produces both ovum and sperm Thus, it can self-fertilize to produce progeny ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.