Relative Expression of a Dominant Mutated ABCC8
... FIG. 2. A: Representative Western blot of WT and 1508AS insertion mutant SUR1 coexpressed with Kir6.2 in COSm6 cells. M, mature complexglycosylated band; Im, immature core-glycosylated band; Un, untransfected COSm6 cells; WT, COSm6 cells transfected with wild type; Mutant, COSm6 cells transfected wi ...
... FIG. 2. A: Representative Western blot of WT and 1508AS insertion mutant SUR1 coexpressed with Kir6.2 in COSm6 cells. M, mature complexglycosylated band; Im, immature core-glycosylated band; Un, untransfected COSm6 cells; WT, COSm6 cells transfected with wild type; Mutant, COSm6 cells transfected wi ...
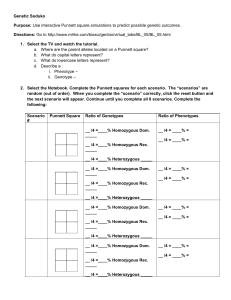
Genetic Soduko Purpose: Use interactive Punnett square
... __ /4 =____% Homozygous Rec. _____ __ /4 =____% Heterozygous _____ Conclusions: 1. Why can’t we always predict the genotype by observing the phenotype? 2. In which situation can we accurately predict the genotype by looking at the phenotype? 3. Purple is dominant over pink. Cross a Homozygous pink p ...
... __ /4 =____% Homozygous Rec. _____ __ /4 =____% Heterozygous _____ Conclusions: 1. Why can’t we always predict the genotype by observing the phenotype? 2. In which situation can we accurately predict the genotype by looking at the phenotype? 3. Purple is dominant over pink. Cross a Homozygous pink p ...
Create a Face Lab - McCarter Biology
... Why do people look so different from each other? Even close relatives often look very different from each other. This happens because a very large variety of traits exist in the human population and new variations are created as humans reproduce. Remember during meiosis there can be reshuffling and ...
... Why do people look so different from each other? Even close relatives often look very different from each other. This happens because a very large variety of traits exist in the human population and new variations are created as humans reproduce. Remember during meiosis there can be reshuffling and ...
The Famous Pea Experiment Mendel`s results depended on a lot of
... For two years, the scientist grew different varieties of peas to make sure that their offspring were always the same. Then be began breeding different varieties together to make hybrids. He brushed the pollen off yellow pea plants and put it on green pea plants, and did the same for plants with each ...
... For two years, the scientist grew different varieties of peas to make sure that their offspring were always the same. Then be began breeding different varieties together to make hybrids. He brushed the pollen off yellow pea plants and put it on green pea plants, and did the same for plants with each ...
S5a. Genetic Linkage-Tutorial Problem Set and
... involve linked genes. Be able to justify your analysis by describing the information in the data that allows you to determine genes are linked. Explain how crossing over (or recombination frequency) between two linked loci affects the genotype frequencies of the products of meiosis compared to loci ...
... involve linked genes. Be able to justify your analysis by describing the information in the data that allows you to determine genes are linked. Explain how crossing over (or recombination frequency) between two linked loci affects the genotype frequencies of the products of meiosis compared to loci ...
today
... Two programs worked well for me to align nucleotide sequences based on the amino acid alignment, One is seaview, the other is DAMBE (only for windows). This is a handy program for a lot of things, including reading a lot of different formats, calculating phylogenies, it even runs codeml (from PAML) ...
... Two programs worked well for me to align nucleotide sequences based on the amino acid alignment, One is seaview, the other is DAMBE (only for windows). This is a handy program for a lot of things, including reading a lot of different formats, calculating phylogenies, it even runs codeml (from PAML) ...
Essential Biology 04: Genetics (HL) DNA structure review: draw and
... a. Which statement is true of the gametes? A. They will be all Pl and pL B. They will be 25% each of Pl, pL, PL and pl C. There will be more pL gametes than PL gametes. D. There will be an equal number of PL and pL gametes. ...
... a. Which statement is true of the gametes? A. They will be all Pl and pL B. They will be 25% each of Pl, pL, PL and pl C. There will be more pL gametes than PL gametes. D. There will be an equal number of PL and pL gametes. ...
Observation
... purple or white color. When Mendel crossed the true-breeding purple and white flowers, he always obtained plants, the F1 generation, with purple flowers, but the allele for “white” is not lost: we refer to these individuals as heterozygous. When he then crossed two F1 heterozygotes and determined th ...
... purple or white color. When Mendel crossed the true-breeding purple and white flowers, he always obtained plants, the F1 generation, with purple flowers, but the allele for “white” is not lost: we refer to these individuals as heterozygous. When he then crossed two F1 heterozygotes and determined th ...
Sources of genetic variation
... length. Thus genes may be deleted altogether, or deleted genes may then be inserted in the wrong place, gene sequeneces may become inverted, or gene sequences may translocated, that is, broken off the end of one chromosome and added onto the end of another one. Although rare, these errors probably o ...
... length. Thus genes may be deleted altogether, or deleted genes may then be inserted in the wrong place, gene sequeneces may become inverted, or gene sequences may translocated, that is, broken off the end of one chromosome and added onto the end of another one. Although rare, these errors probably o ...
EQUATIONS USED IN 40-300 POPULATION GENETICS
... We can use OBSERVED values of FST to calculate the parameter Nem from the above equation. This estimate can be thought of as the combination of gene flow and drift that would result in the observed value of FST at equilibrium. When Nem = 1, subpopulations are exchanging one migrant per generation, o ...
... We can use OBSERVED values of FST to calculate the parameter Nem from the above equation. This estimate can be thought of as the combination of gene flow and drift that would result in the observed value of FST at equilibrium. When Nem = 1, subpopulations are exchanging one migrant per generation, o ...
From: colby@bio
... types of moths: brightly colored moths with and without tails, and dark moths with and without tails. All four can be produced when moths are brought into the lab and bred. However, only two of these types of moths are found in the wild: brightly colored moths with tails and darkly colored moths wit ...
... types of moths: brightly colored moths with and without tails, and dark moths with and without tails. All four can be produced when moths are brought into the lab and bred. However, only two of these types of moths are found in the wild: brightly colored moths with tails and darkly colored moths wit ...
geneticcounseling.pdf
... Caucasians and Ashkenazi Jews since it detects the mutations most commonly found in these populations. Soon there will be a genetic test that screens for the 90 most common mutations. ...
... Caucasians and Ashkenazi Jews since it detects the mutations most commonly found in these populations. Soon there will be a genetic test that screens for the 90 most common mutations. ...
Whoville_Genetics
... Whoville scientists been investigating the genetic makeup of the organisms in this community. Use the information provided and your knowledge of genetics to answer each question. 1. For each genotype below, indicate whether it is a heterozygous (He) OR homozygous (Ho). TT _____ Bb _____ DD _____ Ff ...
... Whoville scientists been investigating the genetic makeup of the organisms in this community. Use the information provided and your knowledge of genetics to answer each question. 1. For each genotype below, indicate whether it is a heterozygous (He) OR homozygous (Ho). TT _____ Bb _____ DD _____ Ff ...
BL414 Genetics Spring 2006 Linkage and Genetic Maps Outline February 22, 2006
... The standard in human genetics is to find an lod score for a pedigree or group of pedigrees. Lod represents a “log of odds” or the logarithm of the likelihood ratio between the likelihood of linkage and the likelihood of non-linkage. A frequency of recombination, r, that maximizes the lod score is d ...
... The standard in human genetics is to find an lod score for a pedigree or group of pedigrees. Lod represents a “log of odds” or the logarithm of the likelihood ratio between the likelihood of linkage and the likelihood of non-linkage. A frequency of recombination, r, that maximizes the lod score is d ...
Transcription-Dependent Somatic Hypermutation Occurs
... IgH locus, a linear correlation between expression and mutability has been reported (17–19). V(D)J rearrangement and presence of a V promoter are known as mandatory for high-level SHM (18, 20). Although unrearranged V segments and incomplete DJ rearrangements are transcribed at low levels in immatur ...
... IgH locus, a linear correlation between expression and mutability has been reported (17–19). V(D)J rearrangement and presence of a V promoter are known as mandatory for high-level SHM (18, 20). Although unrearranged V segments and incomplete DJ rearrangements are transcribed at low levels in immatur ...
Simulating the morphology of barley spike phenotypes using
... the value of M is equal to the sum of all active alleles, multiplied by ten. If G and H exhibit only inactive alleles, M will still adopt a basic value of M0. 2.4.3. Epistasis Figure 1. Simulated barley ears. Three parameters (see Tab. II) were varied while all others were set constant. The ears are ...
... the value of M is equal to the sum of all active alleles, multiplied by ten. If G and H exhibit only inactive alleles, M will still adopt a basic value of M0. 2.4.3. Epistasis Figure 1. Simulated barley ears. Three parameters (see Tab. II) were varied while all others were set constant. The ears are ...
Exam Format
... A) Populations within group A will be more similar to each other with respect to allele frequencies than those within group B B) On average, heterozygosities will be lower in group B C) On average, homozygosities will be higher in group A D) A B and C above are all false E) None of the statements ab ...
... A) Populations within group A will be more similar to each other with respect to allele frequencies than those within group B B) On average, heterozygosities will be lower in group B C) On average, homozygosities will be higher in group A D) A B and C above are all false E) None of the statements ab ...
Hey, J. 2003. Speciation and inversions: Chimps
... might happen if they share a common geographic or environmental boundary (parapatry). Next, suppose that each population has, at high frequency, alleles at one or more genes that are ‘incompatible’ with genes in the other population. Such incompatibilities might be manifested directly as inviable or ...
... might happen if they share a common geographic or environmental boundary (parapatry). Next, suppose that each population has, at high frequency, alleles at one or more genes that are ‘incompatible’ with genes in the other population. Such incompatibilities might be manifested directly as inviable or ...
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #9 “Mendelian Genetics II
... A fruit fly geneticist discovered a genetic mutation that resulted in pupae and young flies with dark pigment granules in the nuclei and cytoplasm of their fat cells. After studying the inheritance of the mutation, the geneticist named the gene Frd (for Freckled). What does this name tell you about ...
... A fruit fly geneticist discovered a genetic mutation that resulted in pupae and young flies with dark pigment granules in the nuclei and cytoplasm of their fat cells. After studying the inheritance of the mutation, the geneticist named the gene Frd (for Freckled). What does this name tell you about ...
Human Genetics
... Of the estimated 100,000 human genes, most are identical in all humans The relatively small number of “polymorphic” genes in humans account for only part of the variability that we see between humans While each human (except for identical twins) has a unique set of genetic information, variati ...
... Of the estimated 100,000 human genes, most are identical in all humans The relatively small number of “polymorphic” genes in humans account for only part of the variability that we see between humans While each human (except for identical twins) has a unique set of genetic information, variati ...
Requirements for Driving Antipathogen Effector Genes into
... One suggestion has been to develop genes encoding effector molecules that block parasite development within the vector, and then use the nuclease-based homing reaction as a form of gene drive to spread those genes through target populations. If the effector gene reduces the fitness of the mosquito an ...
... One suggestion has been to develop genes encoding effector molecules that block parasite development within the vector, and then use the nuclease-based homing reaction as a form of gene drive to spread those genes through target populations. If the effector gene reduces the fitness of the mosquito an ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.