Population genetics as a means to explore
... Embryology: species that are way different as adults (humans vs. chickens) look identical when embryos Biochemistry: DNA or RNA differences between species is good comparison (chimps & humans 98% identical) ...
... Embryology: species that are way different as adults (humans vs. chickens) look identical when embryos Biochemistry: DNA or RNA differences between species is good comparison (chimps & humans 98% identical) ...
Vocabulary to Know
... 1. Using the codon chart above, describe what effects would result from each of the mutations above and how the protein will be impacted. a. Mutation 1 – b. Mutation 2 – c. Mutation 3 – 2. A nucleotide is made up of a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. When DNA mutations occu ...
... 1. Using the codon chart above, describe what effects would result from each of the mutations above and how the protein will be impacted. a. Mutation 1 – b. Mutation 2 – c. Mutation 3 – 2. A nucleotide is made up of a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. When DNA mutations occu ...
vocab-genetics - WordPress.com
... 14 Communicate ideas clearly and concisely using the biological language relevant to this topic. Students will be expected to utilise the core knowledge outlined in the statements below to describe, explain and discuss aspects of ...
... 14 Communicate ideas clearly and concisely using the biological language relevant to this topic. Students will be expected to utilise the core knowledge outlined in the statements below to describe, explain and discuss aspects of ...
Microevolution 2
... - despite this fact, mutation rates are sufficient to generate large pools of genetic variation in natural populations. - this is because there are many loci capable of mutating and there are typically many individuals in a population in which these new mutations can occur. Migration/gene flow - gen ...
... - despite this fact, mutation rates are sufficient to generate large pools of genetic variation in natural populations. - this is because there are many loci capable of mutating and there are typically many individuals in a population in which these new mutations can occur. Migration/gene flow - gen ...
Genetics, Exam 2, Sample A Name ___________________________
... recessive male. What proportion (%) of her progeny would express each of the following phenotypes? Notched tail, white markings on dorsal fin _____________ Notched tail, no white markings on dorsal fin _____________ Smooth tail, white markings on dorsal fin _____________ Smooth tail, no white markin ...
... recessive male. What proportion (%) of her progeny would express each of the following phenotypes? Notched tail, white markings on dorsal fin _____________ Notched tail, no white markings on dorsal fin _____________ Smooth tail, white markings on dorsal fin _____________ Smooth tail, no white markin ...
Slide 1
... • Could be in charge of making a protein (like the gene for the molecule keratin has its nucleotides in an order such that the amino acid sequence that is made from those directions will make keratin) • Could be a ‘regulatory’ gene – like a foreman in a factory who produces nothing directly, but who ...
... • Could be in charge of making a protein (like the gene for the molecule keratin has its nucleotides in an order such that the amino acid sequence that is made from those directions will make keratin) • Could be a ‘regulatory’ gene – like a foreman in a factory who produces nothing directly, but who ...
Lecture #21 Date ______ Macroevolution
... Researchers from the University of Leiden placed males and females of Pundamilia pundamilia and P. nyererei together in two aquarium tanks, one with natural light and one with a monochromatic orange lamp. Under normal light, the two species are noticeably different in coloration; under monochromatic ...
... Researchers from the University of Leiden placed males and females of Pundamilia pundamilia and P. nyererei together in two aquarium tanks, one with natural light and one with a monochromatic orange lamp. Under normal light, the two species are noticeably different in coloration; under monochromatic ...
Week 11, Class 2
... Organisms are grouped together as species when they can be shown to represent a distinct clade ...
... Organisms are grouped together as species when they can be shown to represent a distinct clade ...
Crossingover and Gene Mapping
... rate. The further apart genes are from each other increases their chance of cross over. The closer genes are, the less likely they are to cross over so they remain on the same chromosome. The genes and the physical characteristics are now different than before crossing-over. This process is another ...
... rate. The further apart genes are from each other increases their chance of cross over. The closer genes are, the less likely they are to cross over so they remain on the same chromosome. The genes and the physical characteristics are now different than before crossing-over. This process is another ...
Evolution
... • Variation happens naturally and is inherited • Nature selects which traits are best suited for the environment ...
... • Variation happens naturally and is inherited • Nature selects which traits are best suited for the environment ...
Genetic disease and the genome
... The focus in the laboratory is to identify and characterize genes that cause human genetic disease. The diseases studied in the laboratory include the craniofacial disorder, Treacher Collins syndrome, the mental retardation syndrome, Cri du Chat and Wolfram Syndrome, a neurodegenerative disorder who ...
... The focus in the laboratory is to identify and characterize genes that cause human genetic disease. The diseases studied in the laboratory include the craniofacial disorder, Treacher Collins syndrome, the mental retardation syndrome, Cri du Chat and Wolfram Syndrome, a neurodegenerative disorder who ...
MacroEvolution - WordPress.com
... Microevolution: Changes in allele frequency in a population over time Macroevolution: Broad patterns of evolutionary change; large scale history of life Natural Selection as a Mechanism for Adaptive Evolution ...
... Microevolution: Changes in allele frequency in a population over time Macroevolution: Broad patterns of evolutionary change; large scale history of life Natural Selection as a Mechanism for Adaptive Evolution ...
TECHNICAL NOTE 4.1
... all of the “programming code” for the organism. The code for our observable characteristics (phenotype) such as hair and eye color, foot size, etc., is crammed into the nucleus.This code is called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). An organism’s basic complement of DNA is called its genome. DNA is essenti ...
... all of the “programming code” for the organism. The code for our observable characteristics (phenotype) such as hair and eye color, foot size, etc., is crammed into the nucleus.This code is called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). An organism’s basic complement of DNA is called its genome. DNA is essenti ...
PROBABILITY
... Genetic Disorders 1. Genetic disorders are caused by changes or ____________________ in the information in genes. this is called gene ___________________. 2. It is ________________ to have some gene mutations. Most of the time, cells can _______________ these mutations. Other times mutations can ca ...
... Genetic Disorders 1. Genetic disorders are caused by changes or ____________________ in the information in genes. this is called gene ___________________. 2. It is ________________ to have some gene mutations. Most of the time, cells can _______________ these mutations. Other times mutations can ca ...
View Syllabus
... The course material will explore fundamental concepts in genetics through the sophisticated “eyes” of geneticists working with model organisms. The goals are to attain an appreciation for remarkable biologi ...
... The course material will explore fundamental concepts in genetics through the sophisticated “eyes” of geneticists working with model organisms. The goals are to attain an appreciation for remarkable biologi ...
File
... The frequencies of the genotypes "AA" and "Aa." Answer: The frequency of AA is equal to p2, and the frequency of Aa is equal to 2pq. So, using the information above, the frequency of AA is 16% (i.e. p2 is 0.4 x 0.4 = 0.16) and Aa is 48% (2pq = 2 x 0.4 x 0.6 = 0.48). ...
... The frequencies of the genotypes "AA" and "Aa." Answer: The frequency of AA is equal to p2, and the frequency of Aa is equal to 2pq. So, using the information above, the frequency of AA is 16% (i.e. p2 is 0.4 x 0.4 = 0.16) and Aa is 48% (2pq = 2 x 0.4 x 0.6 = 0.48). ...
Name
... 30. A person who has one recessive allele and one dominant allele for a trait is called a ______________. 31. Characteristics are affected by the interactions between genes and the _________________________. 32. A ______________________ is the offspring of parents that have different alleles for a t ...
... 30. A person who has one recessive allele and one dominant allele for a trait is called a ______________. 31. Characteristics are affected by the interactions between genes and the _________________________. 32. A ______________________ is the offspring of parents that have different alleles for a t ...
Document
... Purging selection Recessive lethal or deleterious alleles become evident through inbreeding, and can therefore be eliminated (purged) via natural selection; ...
... Purging selection Recessive lethal or deleterious alleles become evident through inbreeding, and can therefore be eliminated (purged) via natural selection; ...
Speciation
... • Natural Selection and genetic drift effects • Many different species (from original populations) form during same time frame. ...
... • Natural Selection and genetic drift effects • Many different species (from original populations) form during same time frame. ...
DNA, RNA, Genetic Engineering
... Chromosomal # mutations (Meiosis Problems) 1. Nondisjunction (Aneuploidy) extra or missing chromosomes 2. Polyploidy (extra sets of chromosomes) • Works in plants (bigger, stronger, more flowers, etc.) • Does NOT work in animals (lethal) ...
... Chromosomal # mutations (Meiosis Problems) 1. Nondisjunction (Aneuploidy) extra or missing chromosomes 2. Polyploidy (extra sets of chromosomes) • Works in plants (bigger, stronger, more flowers, etc.) • Does NOT work in animals (lethal) ...
Punnetts 2
... • Because males have only one X chromosome, they show all the traitsgenes on that X. Females have two X’s, so they have two chances to get a gene that is good, and can show the good trait. Example: If females, have one gene on an X for colorblindness, and one gene on the other X for normal vision, s ...
... • Because males have only one X chromosome, they show all the traitsgenes on that X. Females have two X’s, so they have two chances to get a gene that is good, and can show the good trait. Example: If females, have one gene on an X for colorblindness, and one gene on the other X for normal vision, s ...
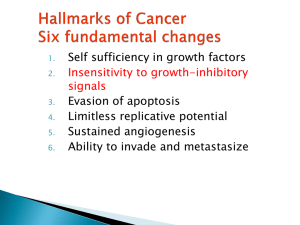
The 2 alleles on chromosome 13q14 must be inactivated
... Antigrowth signals can prevent cell proliferation by 2 mechanism: 1-Cause the dividing cell go to Go phase 2-The cell enter post-mitotic differentiated pool & lose replicative potential The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by ...
... Antigrowth signals can prevent cell proliferation by 2 mechanism: 1-Cause the dividing cell go to Go phase 2-The cell enter post-mitotic differentiated pool & lose replicative potential The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by ...