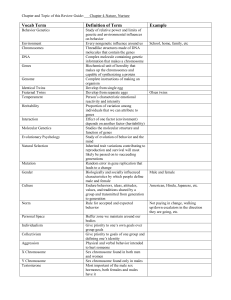
File
... flowers on same plant) Peas can crossfertilize (pollinate flowers on a different plant) ...
... flowers on same plant) Peas can crossfertilize (pollinate flowers on a different plant) ...
1 BIOL 213 Fifth Exam All atoms, chemical bonding and structures
... Text). "Whereas the general transcription factors that assemble at the promoter are the same for all genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II, the gene regulatory proteins and the locations of their binding sites are different for different genes." ...
... Text). "Whereas the general transcription factors that assemble at the promoter are the same for all genes transcribed by RNA polymerase II, the gene regulatory proteins and the locations of their binding sites are different for different genes." ...
Cribado genético del cáncer colorrectal mediante el estudio del
... mainly by colonoscopy, is low, particularly if compared with those for breast and cervical cancer. This fact must be due, among other reasons, to the discomfort generated in the patients, the high cost, the lack of awareness and, in general, to the low acceptability of the screening methods. For the ...
... mainly by colonoscopy, is low, particularly if compared with those for breast and cervical cancer. This fact must be due, among other reasons, to the discomfort generated in the patients, the high cost, the lack of awareness and, in general, to the low acceptability of the screening methods. For the ...
Gene selection: choice of parameters of the GA/KNN method
... Evolvability by introducing new genes Which chromosome? By a probability proportional to its fitness rank How many genes? Among 1 ~ 5, the number of mutations is assigned randomly with prob. 0.53125, 0.25 0.125, 0.0625, and 0.03125 ...
... Evolvability by introducing new genes Which chromosome? By a probability proportional to its fitness rank How many genes? Among 1 ~ 5, the number of mutations is assigned randomly with prob. 0.53125, 0.25 0.125, 0.0625, and 0.03125 ...
Evidence of Evolution Notes
... humans can manipulate objects, walk, run, swim, etc. Analogous Structures: Can be used for _________________________________ and can be superficially similar in construction but are ___________________________ from a common ancestor. Example: Insects and Birds 3.Embryology: Looks at ______________ ...
... humans can manipulate objects, walk, run, swim, etc. Analogous Structures: Can be used for _________________________________ and can be superficially similar in construction but are ___________________________ from a common ancestor. Example: Insects and Birds 3.Embryology: Looks at ______________ ...
Lecture on Population Genetics
... selection, or migration or by random sampling effects. In an idealized population, in which no forces of change are acting (such as mutation), a randomly interbreeding population would show constant genotypic frequencies for a given locus from one generation to the next. ...
... selection, or migration or by random sampling effects. In an idealized population, in which no forces of change are acting (such as mutation), a randomly interbreeding population would show constant genotypic frequencies for a given locus from one generation to the next. ...
Vocabulary Chp 15 - OCPS TeacherPress
... There is a competitive struggle for existence in the natural world if some competitors in this struggle are better equipped for survival than others, then those less equipped would die ...
... There is a competitive struggle for existence in the natural world if some competitors in this struggle are better equipped for survival than others, then those less equipped would die ...
How Does Evolution Occur? - Downtown Magnets High School
... • DNA: code that forms your traits. • DNA makes up genes- set of instructions for one trait. • Chromosomes carry the genes. • Some traits are dominant (shows up in offspring) or recessive (doesn’t show). ...
... • DNA: code that forms your traits. • DNA makes up genes- set of instructions for one trait. • Chromosomes carry the genes. • Some traits are dominant (shows up in offspring) or recessive (doesn’t show). ...
mendelian genetics vocabulary
... 16. Homozygous: a genotype consisting of two identical alleles of a gene for a particular trait. An individual may be homozygous dominant (AA) or homozygous recessive (aa). Individuals who are homozygous for a trait are also referred to as homozygotes. ...
... 16. Homozygous: a genotype consisting of two identical alleles of a gene for a particular trait. An individual may be homozygous dominant (AA) or homozygous recessive (aa). Individuals who are homozygous for a trait are also referred to as homozygotes. ...
Honors Biology
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
... 2. Relate the structure of the DNA molecule to the structure of chromatin and chromosomes. 3. Know the types and roles of RNAs. 4. Compare and contrast RNA with DNA (consider both the structure of each and the purpose of each in the cell). 5. Describe the process of protein synthesis (both transcrip ...
Semester 2 – Final Exam Review2016
... 8. List the steps of RNA transcription (ending with the product): ...
... 8. List the steps of RNA transcription (ending with the product): ...
DNA Manipulation
... Each person has a DNA fingerprint – a representation of parts of an individual’s DNA that can be used to identify a person at the molecular level. ...
... Each person has a DNA fingerprint – a representation of parts of an individual’s DNA that can be used to identify a person at the molecular level. ...
Chapter 6 – The History of Life on Earth
... 1. Scientists explore the concept of evolution. - In the 1800’s, Lamarck proposed that organisms acquired traits during their lifetimes, then passed these traits to their offspring but could not find evidence to support this idea. - About 50 years after Lamarck, Darwin made observations during a 5 y ...
... 1. Scientists explore the concept of evolution. - In the 1800’s, Lamarck proposed that organisms acquired traits during their lifetimes, then passed these traits to their offspring but could not find evidence to support this idea. - About 50 years after Lamarck, Darwin made observations during a 5 y ...
Chapter 4 - Nature v. Nurture and Evolution
... information that makes a chromosome Biochemical unit of heredity that makes up the chromosomes and capable of synthesizing a protein Complete instructions of making an organism Develop from single egg Develop from separate eggs Person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity Proportion of ...
... information that makes a chromosome Biochemical unit of heredity that makes up the chromosomes and capable of synthesizing a protein Complete instructions of making an organism Develop from single egg Develop from separate eggs Person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity Proportion of ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... What type of mutation is caused by the deletion of a nucleotide? Which type of mutation has no effect on phenotype? Mutations that can affect the offspring of an organism occur in what cell type? This is a single strand of DNA GGCATGA. What are the first three nucleotides of the other DNA strand? In ...
... What type of mutation is caused by the deletion of a nucleotide? Which type of mutation has no effect on phenotype? Mutations that can affect the offspring of an organism occur in what cell type? This is a single strand of DNA GGCATGA. What are the first three nucleotides of the other DNA strand? In ...
Meiosis and Genetic Variation
... – This results in organisms with unique phenotypes (an organisms physical characteristics). ...
... – This results in organisms with unique phenotypes (an organisms physical characteristics). ...
BIOL10005: Genetics and the Evolution of Life
... The method of DNA replication where the new molecule of DNA has one strand which comes from the parent molecule and one strand which is newly synthesised Nucleotides or nucleotide sequences that are able to base pair, for example G and C are complementary, as are A and T One of the two types of nitr ...
... The method of DNA replication where the new molecule of DNA has one strand which comes from the parent molecule and one strand which is newly synthesised Nucleotides or nucleotide sequences that are able to base pair, for example G and C are complementary, as are A and T One of the two types of nitr ...
Population
... Individuals Do Not Evolve • Individuals vary, but populations evolve • Natural selection pressures make an individual more or less likely to survive and reproduce • But, it is the cumulative effects of selection on the genetic makeup of the whole population that results in changes to the species Th ...
... Individuals Do Not Evolve • Individuals vary, but populations evolve • Natural selection pressures make an individual more or less likely to survive and reproduce • But, it is the cumulative effects of selection on the genetic makeup of the whole population that results in changes to the species Th ...
4.16.08 105 lecture
... is given a special name, a null allele). If the allele causes an increase above wild-type it is said to be a gain of function allele. ...
... is given a special name, a null allele). If the allele causes an increase above wild-type it is said to be a gain of function allele. ...
Slide 1
... equation is useful in public health science Public health scientists use the Hardy-Weinberg equation to estimate frequencies of diseasecausing alleles in the human population. One out of 10,000 babies born in the United States has phenylketonuria (PKU), an inherited inability to break down the a ...
... equation is useful in public health science Public health scientists use the Hardy-Weinberg equation to estimate frequencies of diseasecausing alleles in the human population. One out of 10,000 babies born in the United States has phenylketonuria (PKU), an inherited inability to break down the a ...
Document
... “Variation” can be of two types: Mutation occurs when something new is produced— different gene from what was there before. It requires a permanent change in the DNA pool. Adaptation occurs when something already present simply changes proportion—same genes that were there before. It requires only ...
... “Variation” can be of two types: Mutation occurs when something new is produced— different gene from what was there before. It requires a permanent change in the DNA pool. Adaptation occurs when something already present simply changes proportion—same genes that were there before. It requires only ...
Unit 3 Practice Exam
... c. their nucleotide sequences show many similarities. d. they all have the same number of chromosomes. 13. Refer to the illustration above. The similarity of these structures suggests that the organisms a. have a common ancestor. c. evolved slowly. b. all grow at different rates. d. live for a long ...
... c. their nucleotide sequences show many similarities. d. they all have the same number of chromosomes. 13. Refer to the illustration above. The similarity of these structures suggests that the organisms a. have a common ancestor. c. evolved slowly. b. all grow at different rates. d. live for a long ...
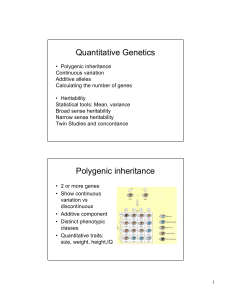
Quantitative Genetics Polygenic inheritance
... • F1 intermediate • F2 intermediate, normal distribution ...
... • F1 intermediate • F2 intermediate, normal distribution ...
sign - GVI.cz
... genetic base by any organism the mass of heredity determination by any sign = degree of heritability genotype + environment = phenotype ...
... genetic base by any organism the mass of heredity determination by any sign = degree of heritability genotype + environment = phenotype ...