nature v. nurture
... How do environmental influences, such as exposure to pollutants, consumption of certain foods or perhaps even powerful emotional experiences, produce lasting and potentially life-altering changes in a person's DNA? Beyond its potential importance for understanding differences in identical twins, epi ...
... How do environmental influences, such as exposure to pollutants, consumption of certain foods or perhaps even powerful emotional experiences, produce lasting and potentially life-altering changes in a person's DNA? Beyond its potential importance for understanding differences in identical twins, epi ...
How can a four "letter" code provide information that determines
... How can a four "letter" code provide information that determines many, many different traits? ...
... How can a four "letter" code provide information that determines many, many different traits? ...
Units 8 and 9: Mendelian and Human Genetics
... The law (principle) of segregation explains how alleles are separate into different gametes during meiosis. The law (principle) of independent assortment states that the segregation of the alleles of one trait does not affect the segregation of the alleles of another trait; Genes on separate chr ...
... The law (principle) of segregation explains how alleles are separate into different gametes during meiosis. The law (principle) of independent assortment states that the segregation of the alleles of one trait does not affect the segregation of the alleles of another trait; Genes on separate chr ...
Cells - Troup County High School
... Important Genetic Vocabulary • trait: a characteristic of an organism that is inherited (examples: eye color, hair type, etc.) • gene: basic unit of heredity made of DNA that determines the characteristics of a trait • allele: the two different versions of a gene for a particular trait (one receive ...
... Important Genetic Vocabulary • trait: a characteristic of an organism that is inherited (examples: eye color, hair type, etc.) • gene: basic unit of heredity made of DNA that determines the characteristics of a trait • allele: the two different versions of a gene for a particular trait (one receive ...
Genetics Exam 5
... _____ To prepare clones representing expressed genes from a eukaryotic cell, you would mix total cellular mRNA with A. reverse transcriptase B. RNA polymerase C. DNA polymerase D. integrase E. RNAse _____ Polyploid plants found in nature usually have even numbers of chromosomes because organisms hav ...
... _____ To prepare clones representing expressed genes from a eukaryotic cell, you would mix total cellular mRNA with A. reverse transcriptase B. RNA polymerase C. DNA polymerase D. integrase E. RNAse _____ Polyploid plants found in nature usually have even numbers of chromosomes because organisms hav ...
Common Misconceptions in Genetics
... factors that increase risk for a disease. For example, recent studies suggest 50 to 60 percent of alcoholism risk is genetic (National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism). This means the other 40 to 50 percent of the risk is environmental. A person may be genetically predisposed to alcoholism ...
... factors that increase risk for a disease. For example, recent studies suggest 50 to 60 percent of alcoholism risk is genetic (National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism). This means the other 40 to 50 percent of the risk is environmental. A person may be genetically predisposed to alcoholism ...
Document
... Legislative Analyst - presents the necessary scientific background required to understand the genetic engineering application and the proposition – the law that is being proposed. Paper and presentation should include: Description of proposition Explanation of SCIENCE background relevant to proposi ...
... Legislative Analyst - presents the necessary scientific background required to understand the genetic engineering application and the proposition – the law that is being proposed. Paper and presentation should include: Description of proposition Explanation of SCIENCE background relevant to proposi ...
Population Genetics and the Hardy-Weinberg Equation
... Population Genetics • In order for their equation to work the population has to be in genetic EQUILIBRIUM – There is no change in the gene pool = no evolution ...
... Population Genetics • In order for their equation to work the population has to be in genetic EQUILIBRIUM – There is no change in the gene pool = no evolution ...
Table 3.
... melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
... melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
下載 - 國立高雄師範大學
... (A) Genes are unable to pass from one sibling species’ gene pool to the others (B) They shared a common ancestor recently in evolutionary time (C) They are unable to produce hybrid offspring upon interbreeding (D) Their reproductive isolation from each other is complete (E) They are the result of an ...
... (A) Genes are unable to pass from one sibling species’ gene pool to the others (B) They shared a common ancestor recently in evolutionary time (C) They are unable to produce hybrid offspring upon interbreeding (D) Their reproductive isolation from each other is complete (E) They are the result of an ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... pass on these mutations to their offspring experience an increased risk of cancer develop entirely new DNA sequences in all cells experience difficulties replicating RNA ...
... pass on these mutations to their offspring experience an increased risk of cancer develop entirely new DNA sequences in all cells experience difficulties replicating RNA ...
15.3 Applications of Genetic Engineering
... suffered a massive reaction from the viruses used to carry genes into his liver cells, and he died a few days later. For gene therapy to become an accepted treatment, we need more reliable ways to insert working genes and to ensure that the DNA used in the therapy does no harm. ...
... suffered a massive reaction from the viruses used to carry genes into his liver cells, and he died a few days later. For gene therapy to become an accepted treatment, we need more reliable ways to insert working genes and to ensure that the DNA used in the therapy does no harm. ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... pass on these mutations to their offspring experience an increased risk of cancer develop entirely new DNA sequences in all cells experience difficulties replicating RNA ...
... pass on these mutations to their offspring experience an increased risk of cancer develop entirely new DNA sequences in all cells experience difficulties replicating RNA ...
This is Option 1
... c. Review figure 8-15 on pg 298 of your textbook and then examine info on Family GK. Explain how a base-pair change in an intron could affect protein function. Be very explicit and use proper terminology. 2-3 sentences connecting the dots – starting with the mutation at the DNA level. Don’t worry ab ...
... c. Review figure 8-15 on pg 298 of your textbook and then examine info on Family GK. Explain how a base-pair change in an intron could affect protein function. Be very explicit and use proper terminology. 2-3 sentences connecting the dots – starting with the mutation at the DNA level. Don’t worry ab ...
Genes Are the Codes for Polypeptides
... 1. Begin by having students sketch a gene individually in journals and develop two or three questions that they have about their gene. 2. Students get into groups of 4 students and develop white boards with a sketch and 2-3 questions. 3. Class discusses sketches and questions in a “board meeting.” 4 ...
... 1. Begin by having students sketch a gene individually in journals and develop two or three questions that they have about their gene. 2. Students get into groups of 4 students and develop white boards with a sketch and 2-3 questions. 3. Class discusses sketches and questions in a “board meeting.” 4 ...
Genes - Unit3and4Biology
... These differences are called variation. Most characteristics, such as height, are determined by several genes working together. They are also influenced by environmental factors such as climate, diet and lifestyle. Variation among individuals is due to meiosis. During meiosis Anaphase I, the chromos ...
... These differences are called variation. Most characteristics, such as height, are determined by several genes working together. They are also influenced by environmental factors such as climate, diet and lifestyle. Variation among individuals is due to meiosis. During meiosis Anaphase I, the chromos ...
Ch 12-15 Unit Overvi..
... Meiosis – purpose; location; compare/contrast meiosis I and meiosis II, which is most similar to mitosis? Does meiosis I or II reduce the chromosome number by half? How is anaphase I different from anaphase II? Metaphase I from II? When does cross over take place? Independent assortment? Segregation ...
... Meiosis – purpose; location; compare/contrast meiosis I and meiosis II, which is most similar to mitosis? Does meiosis I or II reduce the chromosome number by half? How is anaphase I different from anaphase II? Metaphase I from II? When does cross over take place? Independent assortment? Segregation ...
here
... the gradualist point of view Evolution occurs within populations where the fittest organisms have a selective advantage. Over time the advantages genes become fixed in a population and the population gradually changes. Note: this is not in contradiction to the the theory of neutral evolution. (which ...
... the gradualist point of view Evolution occurs within populations where the fittest organisms have a selective advantage. Over time the advantages genes become fixed in a population and the population gradually changes. Note: this is not in contradiction to the the theory of neutral evolution. (which ...
Genetics 1
... the nucleus of every cell is the genetic information “blueprint” to construct the individual. • It is the Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) • Function of DNA – Genetic code for almost every organism. – Provide template for protein synthesis. ...
... the nucleus of every cell is the genetic information “blueprint” to construct the individual. • It is the Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) • Function of DNA – Genetic code for almost every organism. – Provide template for protein synthesis. ...
Molecular Genetics
... of genes and chromosomes in individuals from generation to generation. Molecular Genetics: focuses on the structure and function of genes at the molecular level. Evolutionary genetics: focus on the study of genetic basis of changes in organism over time Population Genetics: focuses on heredity i ...
... of genes and chromosomes in individuals from generation to generation. Molecular Genetics: focuses on the structure and function of genes at the molecular level. Evolutionary genetics: focus on the study of genetic basis of changes in organism over time Population Genetics: focuses on heredity i ...
Chapter 14 * The Human Genome
... This also implies that the person who passed the trait on was heterozygous because they were able to pass along a recessive allele ...
... This also implies that the person who passed the trait on was heterozygous because they were able to pass along a recessive allele ...
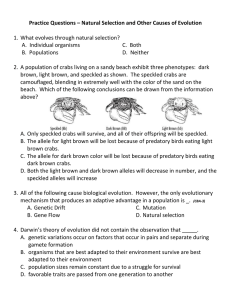
Evolution Practice Questions
... 12. Birds and reptiles are similar in that they are vertebrates and lay eggs. They differ in that reptiles have teeth, and birds have beaks. Some birds do possess teeth; however, these teeth are present only in the embryonic stage. What conclusion is best supported by the presence of teeth in bird e ...
... 12. Birds and reptiles are similar in that they are vertebrates and lay eggs. They differ in that reptiles have teeth, and birds have beaks. Some birds do possess teeth; however, these teeth are present only in the embryonic stage. What conclusion is best supported by the presence of teeth in bird e ...
Heredity 1)Heredity is the ______ of the qualities that were passed
... 17) The sex of a child is determined by the ______ _______________. Females have_____ X chromosomes and Males have one_____ and one ______ chromosome. The mother has only x chromosomes! Males pass either an ____ or _____ chromosome to the child which determined the gender of the child. 18) _________ ...
... 17) The sex of a child is determined by the ______ _______________. Females have_____ X chromosomes and Males have one_____ and one ______ chromosome. The mother has only x chromosomes! Males pass either an ____ or _____ chromosome to the child which determined the gender of the child. 18) _________ ...
Name
... This mutation results from the insertion of two nucleotides into the original sequence, which causes the reading frame of the sequence to change. This kind of mutation is ...
... This mutation results from the insertion of two nucleotides into the original sequence, which causes the reading frame of the sequence to change. This kind of mutation is ...