Section 6-1
... • Traits controlled by single genes with only two alleles – Height in pea plants – Widow’s peak – Stuff from last unit • Multiple Alleles – Some traits controlled by a single gene with more than two alleles • Blood type – controlled by three alleles – Type A – IAIA or IAi – Type B – IBIB or IBi – Ty ...
... • Traits controlled by single genes with only two alleles – Height in pea plants – Widow’s peak – Stuff from last unit • Multiple Alleles – Some traits controlled by a single gene with more than two alleles • Blood type – controlled by three alleles – Type A – IAIA or IAi – Type B – IBIB or IBi – Ty ...
Review Guide Genetics
... Ethical issues of genetic engineering – many people have different opinions on whether these things should be done with genetic engineering. Some of the common ideas/problems are are we “playing” or “messing” with genes are the end products safe how will the modified plants/animal affect the e ...
... Ethical issues of genetic engineering – many people have different opinions on whether these things should be done with genetic engineering. Some of the common ideas/problems are are we “playing” or “messing” with genes are the end products safe how will the modified plants/animal affect the e ...
Genetics BIO.B.1.2.1 Describe how the process of DNA replication
... Ethical issues of genetic engineering – many people have different opinions on whether these things should be done with genetic engineering. Some of the common ideas/problems are are we “playing” or “messing” with genes are the end products safe how will the modified plants/animal affect the e ...
... Ethical issues of genetic engineering – many people have different opinions on whether these things should be done with genetic engineering. Some of the common ideas/problems are are we “playing” or “messing” with genes are the end products safe how will the modified plants/animal affect the e ...
BioBoot Camp Genetics
... Dominant – trait where the phenotypic effect of one allele is completely expressed with in a homozygous or heterozygous genotype. When a dominant gene allele is present it will hide/mask the expression of other alleles and the organism will have the dominant characteristic. Recessive – trait where ...
... Dominant – trait where the phenotypic effect of one allele is completely expressed with in a homozygous or heterozygous genotype. When a dominant gene allele is present it will hide/mask the expression of other alleles and the organism will have the dominant characteristic. Recessive – trait where ...
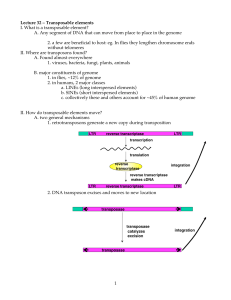
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
Genetics & Heredity
... – Mendel also crossed 2nd generation plants with each other and the recessive trait reappeared with a 3-1 dominant to recessive ratio. – Finally Mendel did a few backcrosses with the 2nd generation plants and their ...
... – Mendel also crossed 2nd generation plants with each other and the recessive trait reappeared with a 3-1 dominant to recessive ratio. – Finally Mendel did a few backcrosses with the 2nd generation plants and their ...
4 - On Cells, DNA, Proteins, and Populations
... • The number of chromosomes • The sequences of genes contained in the chromosomes ...
... • The number of chromosomes • The sequences of genes contained in the chromosomes ...
Sex Cells (gametes)
... • The number of chromosomes • The sequences of genes contained in the chromosomes ...
... • The number of chromosomes • The sequences of genes contained in the chromosomes ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? homozygous 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of a pair of bases. 3. What is heredity? Traits passing from parents to offspring 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? Sex cells have half as many c ...
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? homozygous 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of a pair of bases. 3. What is heredity? Traits passing from parents to offspring 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? Sex cells have half as many c ...
AP Biology - ReicheltScience.com
... Alterations of chromosome number • Nondisjunction – ▫ members of a pair of homologous chromosomes do not separate properly during meiosis I ▫ Or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II. ▫ Trisomic, monosomic cells ▫ Polyploid – organisms with more than two complete sets of chromosomes ...
... Alterations of chromosome number • Nondisjunction – ▫ members of a pair of homologous chromosomes do not separate properly during meiosis I ▫ Or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II. ▫ Trisomic, monosomic cells ▫ Polyploid – organisms with more than two complete sets of chromosomes ...
Genetic Disorders
... Mutation in gene on chromosome #11 1 in 12 people of African ancestry are carriers Hemoglobin protein is defective Red blood cells begin their life shaped normally, slowly lose round shape and become stiff and curved Symptoms include: Circulation problems Infections Internal bleeding Jaundice Pain f ...
... Mutation in gene on chromosome #11 1 in 12 people of African ancestry are carriers Hemoglobin protein is defective Red blood cells begin their life shaped normally, slowly lose round shape and become stiff and curved Symptoms include: Circulation problems Infections Internal bleeding Jaundice Pain f ...
Old Final Exam WITH ANSWERS!!
... __C__ 3. What is the term for mating pairs being more different (‘opposites attract’) than would be expected by chance? A. attraction of the fittest B. positive assortative mating C. negative assortative mating D. founder effect E. heritability. _D___ 4. Which genetic variance component is most impo ...
... __C__ 3. What is the term for mating pairs being more different (‘opposites attract’) than would be expected by chance? A. attraction of the fittest B. positive assortative mating C. negative assortative mating D. founder effect E. heritability. _D___ 4. Which genetic variance component is most impo ...
Sample File
... In biology, a population is a group of similar individuals that can and do interbreed. The gene pool refers to the genetic variants possessed by all members of a population. Natural selection also takes place within populations. Over generations, the relative proportions of alleles in a population c ...
... In biology, a population is a group of similar individuals that can and do interbreed. The gene pool refers to the genetic variants possessed by all members of a population. Natural selection also takes place within populations. Over generations, the relative proportions of alleles in a population c ...
Advanced Data Analysis
... – Parent / child network organized as a tree – Terms get more detailed as you move down the network ...
... – Parent / child network organized as a tree – Terms get more detailed as you move down the network ...
Ch 11- Introduction to Genetics
... Alleles of different genes tend to be inherited together from one generation to the next when those genes are located on the same chromosome. Genes that are far apart assort independently, genes that are linked are on the same chromosome. Genes that are close together on a chromosome are NOT likely ...
... Alleles of different genes tend to be inherited together from one generation to the next when those genes are located on the same chromosome. Genes that are far apart assort independently, genes that are linked are on the same chromosome. Genes that are close together on a chromosome are NOT likely ...
Expanded Genetic Code in a Bacterium
... Factory Microbes • The goal is for the cells with the synthetic nucleotides to begin to produce “unnatural ...
... Factory Microbes • The goal is for the cells with the synthetic nucleotides to begin to produce “unnatural ...
Name
... 4. Suppose a colorblind male and female with no recessive alleles for colorblindness have children. What is the probability they will have a colorblind son? A colorblind daughter? ...
... 4. Suppose a colorblind male and female with no recessive alleles for colorblindness have children. What is the probability they will have a colorblind son? A colorblind daughter? ...
File
... 6. Why is colorblindness more prevalent in males than females? Colorblindness is a sex-linked disease carried on the X chromosome. Males only have one X chromosome (from their mother), and if it codes for colorblindness they are affected. A female must get a bad X from Mom and Dad to be affected. ...
... 6. Why is colorblindness more prevalent in males than females? Colorblindness is a sex-linked disease carried on the X chromosome. Males only have one X chromosome (from their mother), and if it codes for colorblindness they are affected. A female must get a bad X from Mom and Dad to be affected. ...
No Slide Title
... • ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease) • Myocardial infarction • Cerebrovascular accident • Alzheimer’s disease • Embryological development ...
... • ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease) • Myocardial infarction • Cerebrovascular accident • Alzheimer’s disease • Embryological development ...
sex-linked traits
... Phenotype exhibited by a particular allele depends on which parent contributed the allele to the offspring Specific partial deletion of chromosome 15 results in ...
... Phenotype exhibited by a particular allele depends on which parent contributed the allele to the offspring Specific partial deletion of chromosome 15 results in ...