Meiosis
... • The four cells produced by meiosis are gametes • In male animals, gametes are called sperm (some pollen grains also contain haploid sperm cells) • In female animals, only one of the cells produced by meiosis becomes an egg (egg cell in plants) • Fertilization generates new combinations of alleles ...
... • The four cells produced by meiosis are gametes • In male animals, gametes are called sperm (some pollen grains also contain haploid sperm cells) • In female animals, only one of the cells produced by meiosis becomes an egg (egg cell in plants) • Fertilization generates new combinations of alleles ...
Genetics
... The final four phases of meiosis II are similar to those is meiosis I. However, the result is four haploid daughter cells. ...
... The final four phases of meiosis II are similar to those is meiosis I. However, the result is four haploid daughter cells. ...
Chromosome Chromo
... cells are arrested in mitosis, and are then “harvested” for chromosome analysis After harvesting, the cell preparations are dropped onto glass slides and stained. For most chromosome analyses, a G-banding technique is utilized for staining. Metaphase spread ...
... cells are arrested in mitosis, and are then “harvested” for chromosome analysis After harvesting, the cell preparations are dropped onto glass slides and stained. For most chromosome analyses, a G-banding technique is utilized for staining. Metaphase spread ...
Polyploidy
... Transposable elements that had been repressed within each parent lineage may be activated in hybrids, and can facilitate the movement of genes and promote unequal crossing over. Polyploidy is an important factor in speciation. In particular, sexually reproducing autotetraploids are automatically iso ...
... Transposable elements that had been repressed within each parent lineage may be activated in hybrids, and can facilitate the movement of genes and promote unequal crossing over. Polyploidy is an important factor in speciation. In particular, sexually reproducing autotetraploids are automatically iso ...
Part I
... information of every type of characteristic and process. 5. Was meiosis an evolutionary necessity along with reproduction? a. Meiosis was a crucial evolutionary necessity because it produces gametes for reproduction. The finals products of meiosis are haploid cells, each containing half a set of chr ...
... information of every type of characteristic and process. 5. Was meiosis an evolutionary necessity along with reproduction? a. Meiosis was a crucial evolutionary necessity because it produces gametes for reproduction. The finals products of meiosis are haploid cells, each containing half a set of chr ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 25 –The Protists
... Figure 25.15 What are the functions of the micronucleus and the macronucleus? In Paramecium the micronucleus is diploid and divides by mitosis and transmits genetic information through meiosis and sexual reproduction. The macronucleus are polyploidy and divide by elongating and constricting, are inv ...
... Figure 25.15 What are the functions of the micronucleus and the macronucleus? In Paramecium the micronucleus is diploid and divides by mitosis and transmits genetic information through meiosis and sexual reproduction. The macronucleus are polyploidy and divide by elongating and constricting, are inv ...
Advanced Biology Vocabulary
... Autopolyploid An individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species. ...
... Autopolyploid An individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species. ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... 3) Have same genes but possibly different traits b. More chromosomes does NOT mean more complex 1) Fruit flies – 8 chromosomes 2) Fern – 1200+ chromosomes ...
... 3) Have same genes but possibly different traits b. More chromosomes does NOT mean more complex 1) Fruit flies – 8 chromosomes 2) Fern – 1200+ chromosomes ...
Chapter 10.2 Notes
... So possible sperm = 223 = over 8 million Possible eggs = 223 = over 8 million Multiplied together gives you over ______ trillion different zygotes that are possible! _________________ ______________________ – major source of genetic variation among organisms caused by re-assortment or ______________ ...
... So possible sperm = 223 = over 8 million Possible eggs = 223 = over 8 million Multiplied together gives you over ______ trillion different zygotes that are possible! _________________ ______________________ – major source of genetic variation among organisms caused by re-assortment or ______________ ...
Section 6.6 Introduction in Canvas
... In organisms that reproduce sexually, the independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis and the random fertilization of gametes creates a lot of new genetic combinations. In humans, for example, there are over 64 trillion different possible combinations of chromosomes. Sexual reproduction cre ...
... In organisms that reproduce sexually, the independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis and the random fertilization of gametes creates a lot of new genetic combinations. In humans, for example, there are over 64 trillion different possible combinations of chromosomes. Sexual reproduction cre ...
Meiosis Formation of Gametes (Eggs & Sperm)
... After 1 division - 23 double stranded chromosomes (n) After 2nd division - 23 single stranded chromosomes (n) Occurs in our germ cells that produce gametes ...
... After 1 division - 23 double stranded chromosomes (n) After 2nd division - 23 single stranded chromosomes (n) Occurs in our germ cells that produce gametes ...
Meiosis & Mitosis
... Gametes are sex cells – the male gametes are the sperm, and the female gametes are the eggs Gametes contain one set of genetic information, while body cells contain two sets of genetic information Fertilisation is the joining or fusion of a male gamete and a female gamete – the new cell that is form ...
... Gametes are sex cells – the male gametes are the sperm, and the female gametes are the eggs Gametes contain one set of genetic information, while body cells contain two sets of genetic information Fertilisation is the joining or fusion of a male gamete and a female gamete – the new cell that is form ...
Meiosis - cloudfront.net
... Cytokinesis I - ___________ new cells are formed. Each cell has only ________ of each gene and is _____________________ from the mother cell. Prophase II - _____________________________ dissolves. _____________ replicates Metaphase II - _______________________________________ line up in the center o ...
... Cytokinesis I - ___________ new cells are formed. Each cell has only ________ of each gene and is _____________________ from the mother cell. Prophase II - _____________________________ dissolves. _____________ replicates Metaphase II - _______________________________________ line up in the center o ...
Chapter 14 – Human Genome
... Males only have one X chromosome so they will have black spots or orange spots but not both ...
... Males only have one X chromosome so they will have black spots or orange spots but not both ...
Chromosomes and Cell Division
... Fertilization produces diploid cells • Example: Humans – The mother’s egg cell has 23 chromosomes – The father’s sperm cell has 23 chromosomes – When these cells fuse, the fertilized egg has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs); it is diploid. • Mitosis produces trillions of body cells that are all diploid. ...
... Fertilization produces diploid cells • Example: Humans – The mother’s egg cell has 23 chromosomes – The father’s sperm cell has 23 chromosomes – When these cells fuse, the fertilized egg has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs); it is diploid. • Mitosis produces trillions of body cells that are all diploid. ...
Key Concepts File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... coded for by more than two alleles, or by alleles displaying codominance or incomplete dominance. In higher organisms, meiosis produces gametes (sex cells) which contain half the number of chromosomes of the original parent cell (i.e., haploid cells). Eukaryotic multicellular organisms reproduce sex ...
... coded for by more than two alleles, or by alleles displaying codominance or incomplete dominance. In higher organisms, meiosis produces gametes (sex cells) which contain half the number of chromosomes of the original parent cell (i.e., haploid cells). Eukaryotic multicellular organisms reproduce sex ...
Lecture 14 – 10/5 – Dr. Wormington
... Each cell Contains single set of chromosomes Fertilization Generates 2n Zygote ...
... Each cell Contains single set of chromosomes Fertilization Generates 2n Zygote ...
Genetics Summary
... - Oogenesis —> creating egg, all of them are made before the female is born • When female hits puberty —> meiosis 1 is complete • When sperm attaches to egg —> meiosis 2 starts - Polytene chromosomes —> oversized chromosomes that keep duplication without cell division (used in slivery glands of dros ...
... - Oogenesis —> creating egg, all of them are made before the female is born • When female hits puberty —> meiosis 1 is complete • When sperm attaches to egg —> meiosis 2 starts - Polytene chromosomes —> oversized chromosomes that keep duplication without cell division (used in slivery glands of dros ...
File - Mrs. Riggs Online
... genetics: study of the inheritance of traits, passed from parents to offspring genes: units of genetic information in the cell chromosomes mitosis: process by which cell divides to form two new daughter cells; asexual reproduction requires only mitotic cell divisions differentiation: certain cells c ...
... genetics: study of the inheritance of traits, passed from parents to offspring genes: units of genetic information in the cell chromosomes mitosis: process by which cell divides to form two new daughter cells; asexual reproduction requires only mitotic cell divisions differentiation: certain cells c ...
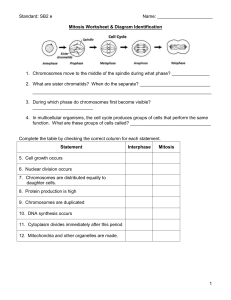
Mitosis Diagram Worksheet
... 18. What two main changes are taking place in cell B? ____________________________ 19. Sequence the six diagrams in order from first to last. ___________________________ 20. What is the end product of mitosis? ________________________________________ 21. What is the main difference between cytokines ...
... 18. What two main changes are taking place in cell B? ____________________________ 19. Sequence the six diagrams in order from first to last. ___________________________ 20. What is the end product of mitosis? ________________________________________ 21. What is the main difference between cytokines ...
Ploidy
Ploidy is the number of sets of chromosomes in a cell. Usually a gamete (sperm or egg, which fuse into a single cell during the fertilization phase of sexual reproduction) carries a full set of chromosomes that includes a single copy of each chromosome, as aneuploidy generally leads to severe genetic disease in the offspring. The gametic or haploid number (n) is the number of chromosomes in a gamete. Two gametes form a diploid zygote with twice this number (2n, the zygotic or diploid number) i.e. two copies of autosomal chromosomes. For humans, a diploid species, n = 23. A typical human somatic cell contains 46 chromosomes: 2 complete haploid sets, which make up 23 homologous chromosome pairs.Because chromosome number is generally reduced only by the specialized process of meiosis, the somatic cells of the body inherit and maintain the chromosome number of the zygote. However, in many situations somatic cells double their copy number by means of endoreduplication as an aspect of cellular differentiation. For example, the hearts of two-year-old children contain 85% diploid and 15% tetraploid nuclei, but by 12 years of age the proportions become approximately equal, and adults examined contained 27% diploid, 71% tetraploid and 2% octaploid nuclei.Cells are described according to the number of sets present (the ploidy level): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is frequently used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes (triploid or higher ploidy).