Homologous chromosomes
... Each organism has a specific amount of chromosomes in their cells. The number of chromosomes is not related to the complexity of an organism. Examples: Adder's Tongue Fern 1260(2n) 630(n) Fruit Fly 8(2n) 4(n) Humans 46(2n) 23(n) Autosomes chromosomes that contain genes for characteristics ...
... Each organism has a specific amount of chromosomes in their cells. The number of chromosomes is not related to the complexity of an organism. Examples: Adder's Tongue Fern 1260(2n) 630(n) Fruit Fly 8(2n) 4(n) Humans 46(2n) 23(n) Autosomes chromosomes that contain genes for characteristics ...
Unit 6 Review Answers File
... 2. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive. What do scientists use to show dominant and recessive traits? Is recessive always the “bad” trait? Dominant traits are more likely to be expressed and are shown using a capital letter. Recessive traits are only expressed if there is not domin ...
... 2. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive. What do scientists use to show dominant and recessive traits? Is recessive always the “bad” trait? Dominant traits are more likely to be expressed and are shown using a capital letter. Recessive traits are only expressed if there is not domin ...
DATE - MrD-Home
... A. produces genetically different cells B. produces haploid cells C. cells divide two times D. produces genetically identical cells 4. Gamete formation in males is different than in females because A. in males, meiosis begins before birth and stops until puberty B. in males, meiosis II occurs before ...
... A. produces genetically different cells B. produces haploid cells C. cells divide two times D. produces genetically identical cells 4. Gamete formation in males is different than in females because A. in males, meiosis begins before birth and stops until puberty B. in males, meiosis II occurs before ...
Primary School Presentation - Unique The Rare Chromosome
... Every cell in the human body normally contains 23 PAIRS of chromosomes, making 46 chromosomes in total Of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in each of these cells, one member of each pair is normally inherited from the father and the other member is normally inherited from the mother. ...
... Every cell in the human body normally contains 23 PAIRS of chromosomes, making 46 chromosomes in total Of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in each of these cells, one member of each pair is normally inherited from the father and the other member is normally inherited from the mother. ...
2) Overview of the human genome
... ATGCTAATGTGCCTAT ATACG This copy has lost 3 bases from each strand ...
... ATGCTAATGTGCCTAT ATACG This copy has lost 3 bases from each strand ...
Meiosis and Genetics Test Review Spring 2016
... b. If round and yellow are dominant traits, how many seeds will express this phenotype? c. What are the genotypes of the parents from this cross? 3. What are the sex chromosomes for normal male? 4. What are the sex chromosomes for a normal female? ...
... b. If round and yellow are dominant traits, how many seeds will express this phenotype? c. What are the genotypes of the parents from this cross? 3. What are the sex chromosomes for normal male? 4. What are the sex chromosomes for a normal female? ...
PowerPoint Presentation - LSU Museum of Natural Science
... copy of chromosome 4 had attached to the end of chromosome 2. It lost its centromere. Diagram all members of chromosomes II and IV during synapsis in Meiosis I -chromosomes replicated -two pairs of sister chromatids for II -one pair of sister chromatids for IV ...
... copy of chromosome 4 had attached to the end of chromosome 2. It lost its centromere. Diagram all members of chromosomes II and IV during synapsis in Meiosis I -chromosomes replicated -two pairs of sister chromatids for II -one pair of sister chromatids for IV ...
11–4 Meiosis - WordPress.com
... exchange portions of their chromatids in a process called crossing-over results in the exchange of alleles between homologous chromosomes and produces new combinations of alleles Alleles = alternative forms of the same gene (ex: blue eyes vs. brown eyes) ...
... exchange portions of their chromatids in a process called crossing-over results in the exchange of alleles between homologous chromosomes and produces new combinations of alleles Alleles = alternative forms of the same gene (ex: blue eyes vs. brown eyes) ...
Star review HW
... 15. Why are certain individuals part of the same species? Genetics 16. What are the chances of having male or female offspring? 17. How much information is passed from each parent to his or her offspring? ...
... 15. Why are certain individuals part of the same species? Genetics 16. What are the chances of having male or female offspring? 17. How much information is passed from each parent to his or her offspring? ...
Biology Ms. Frick 1-7-16 Homework: Finish Pogil, if did not get done
... Two types of cell reproduction 1. Asexual reproduction (mitosis) – two identical copies of the parent cell are produced to replace damaged cells and for growth a. Asexual reproduction occurs in somatic cells (body cells ex. Kidney, eye, skin, etc.) 2. Sexual reproduction (meiosis) –an organism creat ...
... Two types of cell reproduction 1. Asexual reproduction (mitosis) – two identical copies of the parent cell are produced to replace damaged cells and for growth a. Asexual reproduction occurs in somatic cells (body cells ex. Kidney, eye, skin, etc.) 2. Sexual reproduction (meiosis) –an organism creat ...
Body Cells
... are there? • In a human HAPLOID cell, how many chromosomes? • After fertilization takes place (sperm meets egg), the resulting cell (zygote) is .... Diploid or haploid? • Do you think the Y chromosome contains genes that are crucial to the organism’s survival? • Does mitosis or meiosis occur more fr ...
... are there? • In a human HAPLOID cell, how many chromosomes? • After fertilization takes place (sperm meets egg), the resulting cell (zygote) is .... Diploid or haploid? • Do you think the Y chromosome contains genes that are crucial to the organism’s survival? • Does mitosis or meiosis occur more fr ...
Term
... This is the pH at which an enzyme works best at. [The concept that]An enzyme will combine (usually) with only one substrate to form a product. Cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. The way organisms change genetically from pre-existing forms to produce new species over long ...
... This is the pH at which an enzyme works best at. [The concept that]An enzyme will combine (usually) with only one substrate to form a product. Cells which have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. The way organisms change genetically from pre-existing forms to produce new species over long ...
From Mendel to Human Genome
... _______________ were observed inside the _______________ of a cell. Who, in 1902, observed that chromosomes could be sorted into almost identical pairs. The two members of a pair, after the Greek word homologos. ...
... _______________ were observed inside the _______________ of a cell. Who, in 1902, observed that chromosomes could be sorted into almost identical pairs. The two members of a pair, after the Greek word homologos. ...
Document
... • Sperm fertilizes an egg-results in zygote (diploid) • Zygote develops by ______________ into a multi-cellular organism. • Reproduction —Production and subsequent fusion of haploid sex cells. ...
... • Sperm fertilizes an egg-results in zygote (diploid) • Zygote develops by ______________ into a multi-cellular organism. • Reproduction —Production and subsequent fusion of haploid sex cells. ...
1. The products of mitosis are .
... A. one nucleus containing twice as much DNA as the parent nucleus B. four genetically identical nuclei C. four nuclei containing half as much DNA as the parent nucleus D. two genetically identical nuclei E. two genetically identical cells 2. Genetically diverse offspring result from __________. A. b ...
... A. one nucleus containing twice as much DNA as the parent nucleus B. four genetically identical nuclei C. four nuclei containing half as much DNA as the parent nucleus D. two genetically identical nuclei E. two genetically identical cells 2. Genetically diverse offspring result from __________. A. b ...
Practice final - Iowa State University
... D. as one travels north form the South Pole to the equator E. as one travel north from the equator 22. Within any given type of terrestrial biome A. there is little or no vertical stratification B. periodic disturbance is rare C. species composition is typically uniform D. both B and C are true E. n ...
... D. as one travels north form the South Pole to the equator E. as one travel north from the equator 22. Within any given type of terrestrial biome A. there is little or no vertical stratification B. periodic disturbance is rare C. species composition is typically uniform D. both B and C are true E. n ...
EXAM 3.doc
... II. (15 points) Fill in the blanks with the correct word or statement. The value of each question is in the parentheses following the number. 1. (1) _________________________________________ is the situation where neither allele of a gene in the heterozygous condition is expressed; a kind of blendin ...
... II. (15 points) Fill in the blanks with the correct word or statement. The value of each question is in the parentheses following the number. 1. (1) _________________________________________ is the situation where neither allele of a gene in the heterozygous condition is expressed; a kind of blendin ...
11–4 Meiosis
... One egg produced and 3 polar bodies (egg is MUCH larger in size) The one egg receives the most cytoplasm One egg produced for each round of meiosis (and 3 polar bodies which can’t be fertilized) ...
... One egg produced and 3 polar bodies (egg is MUCH larger in size) The one egg receives the most cytoplasm One egg produced for each round of meiosis (and 3 polar bodies which can’t be fertilized) ...
LHWHS Biology
... ---Chromosome---5. In your cells, where are chromosomes located ? __________ What two type of biomolecules are chromosomes made of ? ----Parts of a Chromosome--6. Describe the centromere. ...
... ---Chromosome---5. In your cells, where are chromosomes located ? __________ What two type of biomolecules are chromosomes made of ? ----Parts of a Chromosome--6. Describe the centromere. ...
Document
... Cells that only contain one of the homologous chromosomes Cells have half the pair Only gametes (sex cells= egg/sperm, oocyte or ovum/spermatocyte) Haploid (n) number in humans = 23 (unpaired chromosomes) 1. Meiosis: a process of reduction division in which the number of chromosomes per ce ...
... Cells that only contain one of the homologous chromosomes Cells have half the pair Only gametes (sex cells= egg/sperm, oocyte or ovum/spermatocyte) Haploid (n) number in humans = 23 (unpaired chromosomes) 1. Meiosis: a process of reduction division in which the number of chromosomes per ce ...
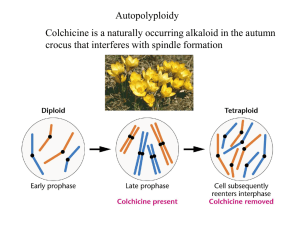
Ploidy
Ploidy is the number of sets of chromosomes in a cell. Usually a gamete (sperm or egg, which fuse into a single cell during the fertilization phase of sexual reproduction) carries a full set of chromosomes that includes a single copy of each chromosome, as aneuploidy generally leads to severe genetic disease in the offspring. The gametic or haploid number (n) is the number of chromosomes in a gamete. Two gametes form a diploid zygote with twice this number (2n, the zygotic or diploid number) i.e. two copies of autosomal chromosomes. For humans, a diploid species, n = 23. A typical human somatic cell contains 46 chromosomes: 2 complete haploid sets, which make up 23 homologous chromosome pairs.Because chromosome number is generally reduced only by the specialized process of meiosis, the somatic cells of the body inherit and maintain the chromosome number of the zygote. However, in many situations somatic cells double their copy number by means of endoreduplication as an aspect of cellular differentiation. For example, the hearts of two-year-old children contain 85% diploid and 15% tetraploid nuclei, but by 12 years of age the proportions become approximately equal, and adults examined contained 27% diploid, 71% tetraploid and 2% octaploid nuclei.Cells are described according to the number of sets present (the ploidy level): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is frequently used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes (triploid or higher ploidy).