Full Paper - International Journal of Pharmaceutical Erudition
... this is not the case. Although individuals with XYY syndrome have an increased risk for learning disabilities and behavioral problems, they are not overly aggressive, nor are they at an increased risk of any serious mental illness. Because these boys are at a higher risk for having learning disabili ...
... this is not the case. Although individuals with XYY syndrome have an increased risk for learning disabilities and behavioral problems, they are not overly aggressive, nor are they at an increased risk of any serious mental illness. Because these boys are at a higher risk for having learning disabili ...
Proviral amplification of the Gypsy endogenous retrovirus of
... We then addressed the question of whether this gypsy maternal effect would still be observed with mosaic mothers where a flam1/flam1 permissive germline would be surrounded by a flamovoD1/flam1 restrictive soma: no expression of the functional proviruses should be allowed in such females except for ...
... We then addressed the question of whether this gypsy maternal effect would still be observed with mosaic mothers where a flam1/flam1 permissive germline would be surrounded by a flamovoD1/flam1 restrictive soma: no expression of the functional proviruses should be allowed in such females except for ...
A Genomic Imprinting Test for Ordinal Traits in Pedigree Data
... generated 100 pedigrees with two parents and three offspring in each pedigree. A latent variable Uie was generated from N(0,1) that is shared by all family members, and a random noise eij was also generated from N(0,1) for each individual. For each founder in a pedigree, 20 highly polymorphic marker ...
... generated 100 pedigrees with two parents and three offspring in each pedigree. A latent variable Uie was generated from N(0,1) that is shared by all family members, and a random noise eij was also generated from N(0,1) for each individual. For each founder in a pedigree, 20 highly polymorphic marker ...
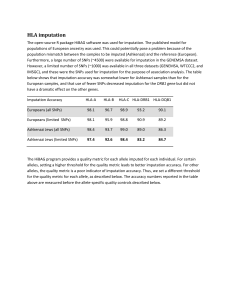
HLA imputation - BioMed Central
... populations of European ancestry was used. This could potentially pose a problem because of the population mismatch between the samples to be imputed (Ashkenazi) and the reference (European). Furthermore, a large number of SNPs (~4500) were available for imputation in the GENEMSA dataset. However, a ...
... populations of European ancestry was used. This could potentially pose a problem because of the population mismatch between the samples to be imputed (Ashkenazi) and the reference (European). Furthermore, a large number of SNPs (~4500) were available for imputation in the GENEMSA dataset. However, a ...
Alu
... A family of SINEs, short interspersed nuclear elements Replicating via LINE-mediated reverse transcription of an RNA polymerase Ⅲ transcript Roughly 280 bp The history of substitution patterns in the human genome Markers to determine genetic distances between human subpopulations – polymorphic Alu i ...
... A family of SINEs, short interspersed nuclear elements Replicating via LINE-mediated reverse transcription of an RNA polymerase Ⅲ transcript Roughly 280 bp The history of substitution patterns in the human genome Markers to determine genetic distances between human subpopulations – polymorphic Alu i ...
LIST OF CHECK-UP QUESTIONS for
... 8. A human has galactosemia — a disease of accumulation. Which genetic method can we use to diagnose the case? a) Cytogenetic. b) Biochemical. CORRECT c) Population-statistical. d) Pedigree analysis. 9. The intensity of human skin pigmentation is controlled by a few pairs of non-allelic dominant gen ...
... 8. A human has galactosemia — a disease of accumulation. Which genetic method can we use to diagnose the case? a) Cytogenetic. b) Biochemical. CORRECT c) Population-statistical. d) Pedigree analysis. 9. The intensity of human skin pigmentation is controlled by a few pairs of non-allelic dominant gen ...
DYAD in meiotic chromosome organisation - Development
... described and several have been characterized at the molecular level (Ross et al., 1997; Hulskamp et al., 1997; Spielman et al., 1997; Glover et al., 1998; He and Mascarenhas, 1998; Sanders et al., 1999). It is likely that the molecular analysis of these as well as meiotic mutants in maize [summaris ...
... described and several have been characterized at the molecular level (Ross et al., 1997; Hulskamp et al., 1997; Spielman et al., 1997; Glover et al., 1998; He and Mascarenhas, 1998; Sanders et al., 1999). It is likely that the molecular analysis of these as well as meiotic mutants in maize [summaris ...
a complex voyage to the X chromosome
... larvae that are formed by multiple rounds of DNA replication without cell division. Euchromatic regions are present in as many as 1024 copies, whereas heterochromatin is generally under-replicated. ...
... larvae that are formed by multiple rounds of DNA replication without cell division. Euchromatic regions are present in as many as 1024 copies, whereas heterochromatin is generally under-replicated. ...
X-Chromosome dosage compensation
... XX but not XO animals (DeLong et al., 1993; Hsu and Meyer, 1994; Meyer and Casson, 1986; Nusbaum and Meyer, 1989; Villeneuve and Meyer, 1987). XX animals that escape lethality have a dumpy (Dpy) phenotype caused by the over expression of X-linked genes. The specific X-linked genes that contribute to ...
... XX but not XO animals (DeLong et al., 1993; Hsu and Meyer, 1994; Meyer and Casson, 1986; Nusbaum and Meyer, 1989; Villeneuve and Meyer, 1987). XX animals that escape lethality have a dumpy (Dpy) phenotype caused by the over expression of X-linked genes. The specific X-linked genes that contribute to ...
IGA 8/e Chapter 2
... a. A diploid meiocyte that is heterozygous for one gene (for example, s+/s where s is the allele that confers the small colony phenotype) will, after replication and segregation, give two meiotic products of genotype s+ and two of s. If the random spores of many meiocytes are analyzed, you would exp ...
... a. A diploid meiocyte that is heterozygous for one gene (for example, s+/s where s is the allele that confers the small colony phenotype) will, after replication and segregation, give two meiotic products of genotype s+ and two of s. If the random spores of many meiocytes are analyzed, you would exp ...
Replication timing and transcriptional control: beyond
... assays for replication [29]. There are only two mammalian loci for which both replication-timing switches and origin localization have been studied. At the mouse immunoglobulin IgH locus, new origins are activated in pre-B cells when the promoter region of this locus becomes transcriptionally active ...
... assays for replication [29]. There are only two mammalian loci for which both replication-timing switches and origin localization have been studied. At the mouse immunoglobulin IgH locus, new origins are activated in pre-B cells when the promoter region of this locus becomes transcriptionally active ...
12 | mendel`s experiments and heredity
... separate probability analyses. For instance, performing a cross between a plant with green, wrinkled seeds and a plant with yellow, round seeds still produced offspring that had a 3:1 ratio of green:yellow seeds (ignoring seed texture) and a 3:1 ratio of round:wrinkled seeds (ignoring seed color). T ...
... separate probability analyses. For instance, performing a cross between a plant with green, wrinkled seeds and a plant with yellow, round seeds still produced offspring that had a 3:1 ratio of green:yellow seeds (ignoring seed texture) and a 3:1 ratio of round:wrinkled seeds (ignoring seed color). T ...
Plant speciation through chromosome instability and ploidy change
... such as aneuploidization and dysploidy (inversions and translocations). Despite the relevance of chromosomal instability as a driver for genome evolution and adaptation, little is yet known about the cellular mechanisms and processes that actually underlie these modifications. Here, in this paper, we ...
... such as aneuploidization and dysploidy (inversions and translocations). Despite the relevance of chromosomal instability as a driver for genome evolution and adaptation, little is yet known about the cellular mechanisms and processes that actually underlie these modifications. Here, in this paper, we ...
Number 48, 2001 35
... ascospores generated in the barren crosses may be the ones, in which RIP either had not occurred or was very inefficient. In agreement with this possibility, a low frequency of mutants for loci covered by the duplication was observed, amongst the survivors (Perkins et al. 1997 Genetics 147:125-136). ...
... ascospores generated in the barren crosses may be the ones, in which RIP either had not occurred or was very inefficient. In agreement with this possibility, a low frequency of mutants for loci covered by the duplication was observed, amongst the survivors (Perkins et al. 1997 Genetics 147:125-136). ...
Drosophila rhino Encodes a Female-Specific Chromo
... subfamily of chromo box proteins. rhino (rhi) is expressed only in females and chiefly in the germline, thus providing a new tool to dissect the role of chromo-domain proteins in development. Mutations in rhi disrupt eggshell and embryonic patterning and arrest nurse cell nuclei during a stage-speci ...
... subfamily of chromo box proteins. rhino (rhi) is expressed only in females and chiefly in the germline, thus providing a new tool to dissect the role of chromo-domain proteins in development. Mutations in rhi disrupt eggshell and embryonic patterning and arrest nurse cell nuclei during a stage-speci ...
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium
... Expected Allele Frequencies at 2nd Generation p = AA + Aa/2 = 0.64 + (0.32/2) = 0.8 q = aa + Aa/2 = 0.04 + (0.32/2) = 0.2 ...
... Expected Allele Frequencies at 2nd Generation p = AA + Aa/2 = 0.64 + (0.32/2) = 0.8 q = aa + Aa/2 = 0.04 + (0.32/2) = 0.2 ...
Achiasmate meiosis in fission yeast - Journal of Cell Science
... halves the DNA content from diploidy in the germline cells to haploidy in the gametes. This reduction is achieved by two consecutive rounds of chromosome segregation, which follow a single round of DNA replication. The first (reductional) division involves several meiosis-specific events. During mei ...
... halves the DNA content from diploidy in the germline cells to haploidy in the gametes. This reduction is achieved by two consecutive rounds of chromosome segregation, which follow a single round of DNA replication. The first (reductional) division involves several meiosis-specific events. During mei ...
Replication timing as an epigenetic mark
... consistent with increased intrinsic restrictions in cellular competence as cells become canalized farther down specific lineages.50 These restrictions are presumably due to changes in the epigenetic chromatin landscape that transcription factors must act upon during the reprogramming process. Howeve ...
... consistent with increased intrinsic restrictions in cellular competence as cells become canalized farther down specific lineages.50 These restrictions are presumably due to changes in the epigenetic chromatin landscape that transcription factors must act upon during the reprogramming process. Howeve ...
11.1 notes
... ordinary pea plants because they were small, easy to grow, produce hundreds of offspring, and were convenient to study. They are now known as the model system. ...
... ordinary pea plants because they were small, easy to grow, produce hundreds of offspring, and were convenient to study. They are now known as the model system. ...
Supplemental Material
... also posted at the AAA site, were also used in this analysis. The FlyBase inferred cytological map locations were assigned to all of the orthologs called in the four species. These associations were then ordered and sorted according to their scaffold assignments and molecular coordinates for each sp ...
... also posted at the AAA site, were also used in this analysis. The FlyBase inferred cytological map locations were assigned to all of the orthologs called in the four species. These associations were then ordered and sorted according to their scaffold assignments and molecular coordinates for each sp ...
Modest evidence for linkage and possible confirmation of
... The second approach uses the family based association test (FBAT) [Rabinowitz and Laird, 2000]. In addition to being able to use extended families, the FBAT also handles missing data appropriately, and so does not waste information. Association between a specific allele and schizophrenia is assessed ...
... The second approach uses the family based association test (FBAT) [Rabinowitz and Laird, 2000]. In addition to being able to use extended families, the FBAT also handles missing data appropriately, and so does not waste information. Association between a specific allele and schizophrenia is assessed ...
ch 11_4
... frequency of crossing-over between genes during meiosis might be a clue to the genes’ locations. Sturtevant reasoned that the farther apart two genes were on a chromosome, the more likely it would be that a crossover event would occur between them. If two genes are close together, then crossovers be ...
... frequency of crossing-over between genes during meiosis might be a clue to the genes’ locations. Sturtevant reasoned that the farther apart two genes were on a chromosome, the more likely it would be that a crossover event would occur between them. If two genes are close together, then crossovers be ...
Meiosis I - scecinascience
... frequency of crossing-over between genes during meiosis might be a clue to the genes’ locations. Sturtevant reasoned that the farther apart two genes were on a chromosome, the more likely it would be that a crossover event would occur between them. If two genes are close together, then crossovers be ...
... frequency of crossing-over between genes during meiosis might be a clue to the genes’ locations. Sturtevant reasoned that the farther apart two genes were on a chromosome, the more likely it would be that a crossover event would occur between them. If two genes are close together, then crossovers be ...
Spo13 protects meiotic cohesin at centromeres in meiosis I
... before spore formation. We followed meiotic progression in spo13⌬ diploids, assessing entry into and exit from meiosis I by the formation and disappearance of metaphase I spindles. Once recombination is complete, short spindles form (Padmore et al. 1991) and are maintained, whereas chromosomes attac ...
... before spore formation. We followed meiotic progression in spo13⌬ diploids, assessing entry into and exit from meiosis I by the formation and disappearance of metaphase I spindles. Once recombination is complete, short spindles form (Padmore et al. 1991) and are maintained, whereas chromosomes attac ...