Foundations of Biology
... Micro-mutations tend to have a dramatic effect on proteins as all codons down stream from the mutation are changed and thus code for different amino acids. As a result, the length of the polypeptide may also be changed as a stop codon will probably come at a different spot than the original stop cod ...
... Micro-mutations tend to have a dramatic effect on proteins as all codons down stream from the mutation are changed and thus code for different amino acids. As a result, the length of the polypeptide may also be changed as a stop codon will probably come at a different spot than the original stop cod ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint.ppt
... females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
... females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint
... females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
... females have 2 X chromosomes and males have only 1 • In each female cell, 1 X chromosome is inactivated and is highly condensed into a Barr body • Females heterozygous for genes on the X chromosome are genetic mosaics ...
Inheritance Patterns and Human Genetics
... Rh Factor Problems • The woman’s first child will not be affected. • If the woman has any other children, her antibodies can attack the babies blood causing death to the baby. • There are injections that are given to women today to keep this from being a problem. ...
... Rh Factor Problems • The woman’s first child will not be affected. • If the woman has any other children, her antibodies can attack the babies blood causing death to the baby. • There are injections that are given to women today to keep this from being a problem. ...
Chapter 3: Genetics: From Genotype to Phenotype
... During the formation of gametes, the paired unit factors separate, or segregate, randomly so that each sex cell receives one or the other with equal likelihood. Mendel’s law of segregation: the two alleles of a gene found on each of a pair of chromosomes segregate independently of one another int ...
... During the formation of gametes, the paired unit factors separate, or segregate, randomly so that each sex cell receives one or the other with equal likelihood. Mendel’s law of segregation: the two alleles of a gene found on each of a pair of chromosomes segregate independently of one another int ...
Answers to 14.1 Genetics questions
... pedigree shows the dominant trait of a white hair flock in humans. 22. What is the genotype of anyone with a “white” symbol on the chart? 23. How is it possible to ...
... pedigree shows the dominant trait of a white hair flock in humans. 22. What is the genotype of anyone with a “white” symbol on the chart? 23. How is it possible to ...
A single characteristic may be influenced by many genes
... Males need only one Sex linked traits more common in males The individual who has one recessive allele for a trait is called a carrier ...
... Males need only one Sex linked traits more common in males The individual who has one recessive allele for a trait is called a carrier ...
Y Chromosome: Unraveling the Mystery and Exploring
... • 23 pairs (46 total) • One inherited from maternal parent; one from paternal parent • All are homologous – they have a matching pair – EXCEPT! • Males: 23rd chromosome ...
... • 23 pairs (46 total) • One inherited from maternal parent; one from paternal parent • All are homologous – they have a matching pair – EXCEPT! • Males: 23rd chromosome ...
Mutation
... People who have Turner syndrome develop as females. The genes affected are involved in growth and sexual development, which is why girls with the disorder are shorter than normal, inability to produce egg cells and have abnormal sexual characteristics. ...
... People who have Turner syndrome develop as females. The genes affected are involved in growth and sexual development, which is why girls with the disorder are shorter than normal, inability to produce egg cells and have abnormal sexual characteristics. ...
BIO114H - willisworldbio
... It is caused by a _______ of 3 base pairs in the middle of a sequence for a protein. Sickle cell disease cause RBC to be _____ and _______. ...
... It is caused by a _______ of 3 base pairs in the middle of a sequence for a protein. Sickle cell disease cause RBC to be _____ and _______. ...
Ch 14-2 DR
... How does it occur?_________________________________________________________________ What are effects?___________________________________________________________________ What does the karyotype 45, X tell us about this person?___________________________________ 27. What can nondisjunction in males le ...
... How does it occur?_________________________________________________________________ What are effects?___________________________________________________________________ What does the karyotype 45, X tell us about this person?___________________________________ 27. What can nondisjunction in males le ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... __________________ is the transmission of characteristics from parents to ____________________. We study this as a means of understanding why people behave as they do. Heredity plays a key role in the development of _________, and psychological disorders. Genes and Chromosomes _____________ are the ...
... __________________ is the transmission of characteristics from parents to ____________________. We study this as a means of understanding why people behave as they do. Heredity plays a key role in the development of _________, and psychological disorders. Genes and Chromosomes _____________ are the ...
Ch. 10.5 Sex-Linked Traits
... Human X-linked recessive traits. • Hemophilia- bleeding disorder • Red-green color blindness. – more males with the disorder compared to females. – Females can be carriers- have one recessive allele- do not have the disorder, but can pass on the recessive allele to offspring. – Mothers pass trait o ...
... Human X-linked recessive traits. • Hemophilia- bleeding disorder • Red-green color blindness. – more males with the disorder compared to females. – Females can be carriers- have one recessive allele- do not have the disorder, but can pass on the recessive allele to offspring. – Mothers pass trait o ...
What is Phelan-McDermid Syndrome?
... Deletion sizes, SHANK3 gene mutations and the clinical features of Phelan-McDermid Syndrome are all highly variable. Nonetheless, studies suggest that individuals with larger deletions are more likely than those with smaller deletions to have characteristic body features, neonatal hypotonia, neonata ...
... Deletion sizes, SHANK3 gene mutations and the clinical features of Phelan-McDermid Syndrome are all highly variable. Nonetheless, studies suggest that individuals with larger deletions are more likely than those with smaller deletions to have characteristic body features, neonatal hypotonia, neonata ...
File ap notes chapter 15
... genes are located on different chromosomes When recombinant frequency is less than 50% genes are located on the same chromosome; recombinants result from crossing over; amount of recombinants is related to the distance between the two gene’s loci ...
... genes are located on different chromosomes When recombinant frequency is less than 50% genes are located on the same chromosome; recombinants result from crossing over; amount of recombinants is related to the distance between the two gene’s loci ...
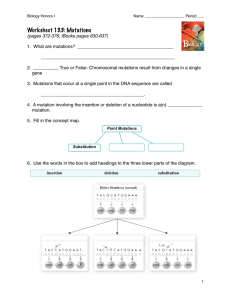
Worksheet 13.3
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
Mutations
... "reading frame" is changed so that all the codons read after the mutation are incorrect, even though the bases themselves may be still present. ...
... "reading frame" is changed so that all the codons read after the mutation are incorrect, even though the bases themselves may be still present. ...
8. Elvia Jimenez Ramos - Spastic Cerebral Palsy
... Treatment • There is NO cure, it is a lifelong disorder • Therapies – Physical therapy – OccupaLonal therapy – Speech therapy ...
... Treatment • There is NO cure, it is a lifelong disorder • Therapies – Physical therapy – OccupaLonal therapy – Speech therapy ...
Karyotyping
... microscope to identify chromosome abnormalities from malformation or disease. It examines the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a certain sample of cells. Extra, missing, or abnormal positions of chromosome pieces can cause problems with a person’s growth, development, and body functions. A ...
... microscope to identify chromosome abnormalities from malformation or disease. It examines the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a certain sample of cells. Extra, missing, or abnormal positions of chromosome pieces can cause problems with a person’s growth, development, and body functions. A ...
GeneticsPt1.ppt
... Who is Gregor Mendel and what did he have to do with alleles, chromosomes, traits, or this topic called genetics? ...
... Who is Gregor Mendel and what did he have to do with alleles, chromosomes, traits, or this topic called genetics? ...
Patterns of inheritance
... DNA is replicated as part of the process of mitochondrial division. A newly formed embryo receives all its mitochondria from the mother through the egg cell, so mitochondrial inheritance is through the maternal line. ...
... DNA is replicated as part of the process of mitochondrial division. A newly formed embryo receives all its mitochondria from the mother through the egg cell, so mitochondrial inheritance is through the maternal line. ...
SOLVING REAL WORLD PROBLEMS-
... 2) Synthesis phase S – the cells’ DNA is copied 3) Second growth phase G2 – prepares for nucleus to divide, microtubules(protein fibers) arranged 4) Mitosis – Nucleus divides into two, same number and type of chromosomes 5) Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm ...
... 2) Synthesis phase S – the cells’ DNA is copied 3) Second growth phase G2 – prepares for nucleus to divide, microtubules(protein fibers) arranged 4) Mitosis – Nucleus divides into two, same number and type of chromosomes 5) Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm ...
How is DNA packed in the nucleus?
... An individual with one copy of a recessive allele is called a carrier. Since most genetic disorders are recessive, they are self limiting. Males more commonly exhibit sex linked traits because they only need one recessive allele located on the X ...
... An individual with one copy of a recessive allele is called a carrier. Since most genetic disorders are recessive, they are self limiting. Males more commonly exhibit sex linked traits because they only need one recessive allele located on the X ...