Module 7: Process Synchronization
... a critical region is a section of code that may be executed by only one process or thread at a time A common critical region ...
... a critical region is a section of code that may be executed by only one process or thread at a time A common critical region ...
Chapter4
... To do work each process must execute a program. In some systems a process may execute a series of different programs ( steps of a compiler) Of a program might consists of several distinct processes, each with a separate sequence of activities that continue at the same time. A process is not a data o ...
... To do work each process must execute a program. In some systems a process may execute a series of different programs ( steps of a compiler) Of a program might consists of several distinct processes, each with a separate sequence of activities that continue at the same time. A process is not a data o ...
What is an Operating System?
... control systems, and some display systems. Well-defined fixed-time constraints. Hard real-time system. Secondary storage limited or absent, data stored in short-term memory, or read-only memory (ROM) Conflicts with time-sharing systems, not supported by generalpurpose operating systems. Soft rea ...
... control systems, and some display systems. Well-defined fixed-time constraints. Hard real-time system. Secondary storage limited or absent, data stored in short-term memory, or read-only memory (ROM) Conflicts with time-sharing systems, not supported by generalpurpose operating systems. Soft rea ...
1 Introduction C H A P T E R
... other forms of memory as well. Because the read-only memory (ROM) cannot be changed, only static programs are stored there. The immutability of ROM is of use in game cartridges. EEPROM cannot be changed frequently and so contains mostly static programs. For example, smartphones have EEPROM to store ...
... other forms of memory as well. Because the read-only memory (ROM) cannot be changed, only static programs are stored there. The immutability of ROM is of use in game cartridges. EEPROM cannot be changed frequently and so contains mostly static programs. For example, smartphones have EEPROM to store ...
Process Description and Control
... then resume the running process or choose a process of higher priority Memory ...
... then resume the running process or choose a process of higher priority Memory ...
No Slide Title
... Executive, which runs in protected mode, provides the basic system services. On top of the executive, several server subsystems operate in user mode. Modular structure allows additional environmental subsystems to be added without affecting the executive. Portability — 2000 can be moved from ...
... Executive, which runs in protected mode, provides the basic system services. On top of the executive, several server subsystems operate in user mode. Modular structure allows additional environmental subsystems to be added without affecting the executive. Portability — 2000 can be moved from ...
ch22
... control objects (asynchronous procedure calls, interrupts, power notify, power status, process and profile objects.) Operating System Concepts ...
... control objects (asynchronous procedure calls, interrupts, power notify, power status, process and profile objects.) Operating System Concepts ...
MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS Third Edition ANDREW S. …
... Security in Symbian OS (1) Steps when an application requires signing: 1. The software developer must obtain a vendor ID from a trusted third party. 2. When developer has developed software package, wants to distribute, developer must submit package to trusted third party for validation. ...
... Security in Symbian OS (1) Steps when an application requires signing: 1. The software developer must obtain a vendor ID from a trusted third party. 2. When developer has developed software package, wants to distribute, developer must submit package to trusted third party for validation. ...
No Slide Title
... decisions, I/O processing, and other system activities; while the other processors just execute user code. ...
... decisions, I/O processing, and other system activities; while the other processors just execute user code. ...
Operating System Tutorial
... File ........................................................................................................................................................ 57 File Structure ............................................................................................................................ ...
... File ........................................................................................................................................................ 57 File Structure ............................................................................................................................ ...
TransOS: a transparent computing-based operating system for the
... 2008, cloud computing is an emerging hot topic in computing research and related industrial development (Armbrust et al., 2010). The defining characteristic of this new computing paradigm is that the computation and storage of software, originally done on a stand-alone computer, are now separated an ...
... 2008, cloud computing is an emerging hot topic in computing research and related industrial development (Armbrust et al., 2010). The defining characteristic of this new computing paradigm is that the computation and storage of software, originally done on a stand-alone computer, are now separated an ...
資工系網媒所NEWS實驗室Chapter 13
... Swap-space can be carved out of the normal file system, or, more commonly, it can be in a separate disk partition. Swap-space management 4.3BSD allocates swap space when process starts; holds text segment (the program) and data segment. Kernel uses swap maps to track swap-space use. Solaris 2 alloca ...
... Swap-space can be carved out of the normal file system, or, more commonly, it can be in a separate disk partition. Swap-space management 4.3BSD allocates swap space when process starts; holds text segment (the program) and data segment. Kernel uses swap maps to track swap-space use. Solaris 2 alloca ...
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 7th Edition
... 9) The earliest computers employed __________ processing, a name derived by the way the users have access to the systems. Answer: serial 10) __________ was designed to keep the processor and I/O devices, including storage devices, simultaneously busy to achieve maximum efficiency. Answer: Multiprogr ...
... 9) The earliest computers employed __________ processing, a name derived by the way the users have access to the systems. Answer: serial 10) __________ was designed to keep the processor and I/O devices, including storage devices, simultaneously busy to achieve maximum efficiency. Answer: Multiprogr ...
Chapter13 - Website Staff UI
... • Real-time operation • Reactive operation – Respond to external events ...
... • Real-time operation • Reactive operation – Respond to external events ...
Survery of Operating Systems 2nd Edition
... – You can identify most of the functions provided by your operating system by careful observation. For instance, evidence of support of the security function includes a required logon procedure when you start your computer, and the need for authorization to access resources on your local compu ...
... – You can identify most of the functions provided by your operating system by careful observation. For instance, evidence of support of the security function includes a required logon procedure when you start your computer, and the need for authorization to access resources on your local compu ...
Chapter 10: Multiprocessor and Real
... • Concerned with how long the operating system delays before acknowledging an interrupt and there is sufficient capacity to handle all the requests within the required ...
... • Concerned with how long the operating system delays before acknowledging an interrupt and there is sufficient capacity to handle all the requests within the required ...
Operating Systems
... • Concerned with how long the operating system delays before acknowledging an interrupt and there is sufficient capacity to handle all the requests within the required ...
... • Concerned with how long the operating system delays before acknowledging an interrupt and there is sufficient capacity to handle all the requests within the required ...
2013chapter0.ppt [兼容模式]
... n Sharing: how are resources shared among users ? n Naming: how are resources named by users or programs ? n Protection: how is one user/program protected from another ? n Security: how to authenticate, control access, secure ...
... n Sharing: how are resources shared among users ? n Naming: how are resources named by users or programs ? n Protection: how is one user/program protected from another ? n Security: how to authenticate, control access, secure ...
Abstract View of System Components
... programs (both source and object forms) and data in bytes. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connections with file management: File creation and deletion. Directory creation and deletion. Support of primitives for manipulating files and directories. Mappin ...
... programs (both source and object forms) and data in bytes. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connections with file management: File creation and deletion. Directory creation and deletion. Support of primitives for manipulating files and directories. Mappin ...
The init process cont. - Workshops
... The root partition is where critical system files live, including the programs necessary to boot the system in to “single user” mode. The idea is that this part of the system does not grow or change, but rather stays isolated from the rest of the operating system. If you give enough room to /usr and ...
... The root partition is where critical system files live, including the programs necessary to boot the system in to “single user” mode. The idea is that this part of the system does not grow or change, but rather stays isolated from the rest of the operating system. If you give enough room to /usr and ...
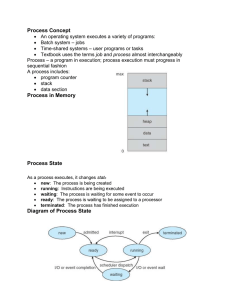
Process State
... Process Termination Process executes last statement and asks the operating system to delete it (exit) Output data from child to parent (via wait) Process’ resources are deallocated by operating system Parent may terminate execution of children processes (abort) Child has exceeded allocated ...
... Process Termination Process executes last statement and asks the operating system to delete it (exit) Output data from child to parent (via wait) Process’ resources are deallocated by operating system Parent may terminate execution of children processes (abort) Child has exceeded allocated ...
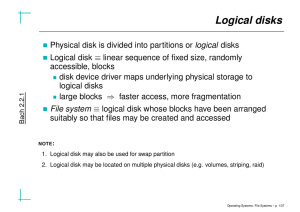
File Systems
... Compulsory entries: current directory (.) and parent directory (..) for root, parent directory = root Inode number = 0 ⇒ empty directory entry ...
... Compulsory entries: current directory (.) and parent directory (..) for root, parent directory = root Inode number = 0 ⇒ empty directory entry ...
Lecture #14: Deadlocks
... Request = request vector for process Pi. If Requesti [j] = k then process Pi wants k instances of resource type Rj 1. If Requesti Needi go to step 2. Otherwise, raise error condition, since process has exceeded its maximum claim 2. If Requesti Available, go to step 3. Otherwise Pi must wait, sin ...
... Request = request vector for process Pi. If Requesti [j] = k then process Pi wants k instances of resource type Rj 1. If Requesti Needi go to step 2. Otherwise, raise error condition, since process has exceeded its maximum claim 2. If Requesti Available, go to step 3. Otherwise Pi must wait, sin ...
Critical Section
... Progress: If no process is executing in its critical section and some processes wish to enter their critical sections, then only those processes that are not executing in their remainder sections can decide which process will enter its critical section next, and this ...
... Progress: If no process is executing in its critical section and some processes wish to enter their critical sections, then only those processes that are not executing in their remainder sections can decide which process will enter its critical section next, and this ...















![2013chapter0.ppt [兼容模式]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002898662_1-e8a437736f7c2b25ea015c0d1428106d-300x300.png)