Meiosis - Background Info - 20 slides
... Aim: How do organisms create offspring through sexual reproduction? ...
... Aim: How do organisms create offspring through sexual reproduction? ...
Meiosis
... Each organism must inherit one copy of every gene from both parents. Each organism has 2 complete sets of genes. Those two sets must be separated so that each gamete produced contains just one set of genes. ...
... Each organism must inherit one copy of every gene from both parents. Each organism has 2 complete sets of genes. Those two sets must be separated so that each gamete produced contains just one set of genes. ...
Genetics Test
... from your parents (one from your mother, one from your father) are called: a. sex chromosomes b. homologous chromosomes c. sister chromatids d. homozygous alleles ...
... from your parents (one from your mother, one from your father) are called: a. sex chromosomes b. homologous chromosomes c. sister chromatids d. homozygous alleles ...
How Do Chromosomes Carry Information?
... http://www.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/education/images.shtml ...
... http://www.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/education/images.shtml ...
How Do Chromosomes Carry Information?
... http://www.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/education/images.shtml ...
... http://www.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/education/images.shtml ...
Cell Division Homework #3
... ____________15 This type of cell division results in cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. ____________16 One Diploid (2N) cell Four Haploid (1N) cells ____________17 This type of cell division occurs in all body cells except for in the formation of sex cells. _______ ...
... ____________15 This type of cell division results in cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. ____________16 One Diploid (2N) cell Four Haploid (1N) cells ____________17 This type of cell division occurs in all body cells except for in the formation of sex cells. _______ ...
Science 9 – Section 6.1 3 The Process of Meiosis Meiosis I 1
... Number of chromosomes in daughter cells 2n n ...
... Number of chromosomes in daughter cells 2n n ...
Lecture 5
... - problems in meiosis with chromosome pairing and even distribution of chromosomes. - low or no seed set ...
... - problems in meiosis with chromosome pairing and even distribution of chromosomes. - low or no seed set ...
HL#1 Meiosis - hutchhighIBbiology
... the cytoplasm. •Nucleoli appear •At the end of meiosis, there are four haploid daughter cells. ...
... the cytoplasm. •Nucleoli appear •At the end of meiosis, there are four haploid daughter cells. ...
A4.3.1HowDoChromosomesCarryInformation
... 6. Where are centromeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its centromere is located. 7. Where are telomeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its telomeres are located. 8. From the variation window, select one of the chro ...
... 6. Where are centromeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its centromere is located. 7. Where are telomeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its telomeres are located. 8. From the variation window, select one of the chro ...
HEREDITY AND GENETICS vocabulary terms and
... The observable physical characteristics of an organism, determined by genetic ...
... The observable physical characteristics of an organism, determined by genetic ...
Section 6.1: Chromosomes and Meiosis
... two gametes that results in offspring that are a genetic mixture of both parents. • The actual fusion of an egg and a sperm cell is called fertilization. – When fertilization occurs, the nuclei of the egg and sperm cell fuse to form one nucleus. – The new nucleus must have the correct number of chro ...
... two gametes that results in offspring that are a genetic mixture of both parents. • The actual fusion of an egg and a sperm cell is called fertilization. – When fertilization occurs, the nuclei of the egg and sperm cell fuse to form one nucleus. – The new nucleus must have the correct number of chro ...
1. The products of mitosis are .
... A. one nucleus containing twice as much DNA as the parent nucleus B. four genetically identical nuclei C. four nuclei containing half as much DNA as the parent nucleus D. two genetically identical nuclei E. two genetically identical cells 2. Genetically diverse offspring result from __________. A. b ...
... A. one nucleus containing twice as much DNA as the parent nucleus B. four genetically identical nuclei C. four nuclei containing half as much DNA as the parent nucleus D. two genetically identical nuclei E. two genetically identical cells 2. Genetically diverse offspring result from __________. A. b ...
Name - gst boces
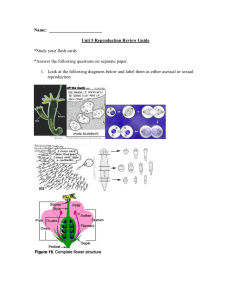
... Name: Unit 5 Reproduction Review Guide *Study your flash cards *Answer the following questions on separate paper. 1. Look at the following diagrams below and label them as either asexual or sexual reproduction ...
... Name: Unit 5 Reproduction Review Guide *Study your flash cards *Answer the following questions on separate paper. 1. Look at the following diagrams below and label them as either asexual or sexual reproduction ...
Supplemental File S10. Homologous
... Haploid: One complete set set of chromosomes (n),present in the egg and sperm cells of animals and in the egg and pollen cells of plants. Humans have 23 chromosomes in their sex cells (n=23). Homologous chromosomes: A pair of chromosomes that resemble each other and have nearly the same DNA sequence ...
... Haploid: One complete set set of chromosomes (n),present in the egg and sperm cells of animals and in the egg and pollen cells of plants. Humans have 23 chromosomes in their sex cells (n=23). Homologous chromosomes: A pair of chromosomes that resemble each other and have nearly the same DNA sequence ...
Meiosis simulation - sciencewithskinner
... cat has 38 chromosomes, and the mouse that it chases has 40 chromosomes! Within each individual in a species, every somatic cell contains the same number of chromosomes as every other. Humans (and most other animals) are diploid organisms meaning that each cell contains two complete chromosome sets. ...
... cat has 38 chromosomes, and the mouse that it chases has 40 chromosomes! Within each individual in a species, every somatic cell contains the same number of chromosomes as every other. Humans (and most other animals) are diploid organisms meaning that each cell contains two complete chromosome sets. ...
Unit 4 Genetics - Jamestown Public Schools
... - The human ____________, our ______________ set of ____________ information, includes 10’s of 1000’s of _______ - The _______ sequences on these ________ carry information for specifying many ________________ - Many genetic _____________ are caused by ______________ recessive __________ - However, ...
... - The human ____________, our ______________ set of ____________ information, includes 10’s of 1000’s of _______ - The _______ sequences on these ________ carry information for specifying many ________________ - Many genetic _____________ are caused by ______________ recessive __________ - However, ...
Chapter 13 - Warren County Schools
... Fertilization = combination of sperm + egg One haploid from each parent fuse to form a ZYGOTE The zygote is DIPLOID & represented by 2n ...
... Fertilization = combination of sperm + egg One haploid from each parent fuse to form a ZYGOTE The zygote is DIPLOID & represented by 2n ...
Meiosis - Grant County Schools
... different number of chromosomes • The chromosome numbers of a species is not related to the complexity of the organism ...
... different number of chromosomes • The chromosome numbers of a species is not related to the complexity of the organism ...
Brooker Chapter 2
... • Females include the worker bees and queen bees – They are diploid – Produced from fertilized eggs ...
... • Females include the worker bees and queen bees – They are diploid – Produced from fertilized eggs ...
MEDICAL EMBRYOLOGY
... membranes (i.e. the products of conception). It includes all structures that develop from the zygote, both embryonic and extra-embryonic. Trimester: A period of 3 months, one third of the length of a pregnancy. Used by Obstetricians. Abortion: premature stoppage of development and expulsion of a ...
... membranes (i.e. the products of conception). It includes all structures that develop from the zygote, both embryonic and extra-embryonic. Trimester: A period of 3 months, one third of the length of a pregnancy. Used by Obstetricians. Abortion: premature stoppage of development and expulsion of a ...
Genetics Crossword
... 15. chromosomes –two chromosomes that carry the same genes. (may have different alleles for the same genes.) 16. – union of sperm and egg form the same individual. (Common in some flowers.) 18. –single cell resulting the union of the sperm and egg. Only last for a few moments before the cell divides ...
... 15. chromosomes –two chromosomes that carry the same genes. (may have different alleles for the same genes.) 16. – union of sperm and egg form the same individual. (Common in some flowers.) 18. –single cell resulting the union of the sperm and egg. Only last for a few moments before the cell divides ...
Chromosome Chromo
... harvesting, the cell preparations are dropped onto glass slides and stained. For most chromosome analyses, a G-banding technique is utilized for staining. Metaphase spread ...
... harvesting, the cell preparations are dropped onto glass slides and stained. For most chromosome analyses, a G-banding technique is utilized for staining. Metaphase spread ...
Topic 4 Genes, Chromosomes
... Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes. Each gene in an organism’s DNA exists at a specific locus on a certain chromosome. We inherit one set of chromosomes from our mother and one set from our father. ...
... Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes. Each gene in an organism’s DNA exists at a specific locus on a certain chromosome. We inherit one set of chromosomes from our mother and one set from our father. ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.