WOTD - Brookwood High School
... V:sex linked traits-traits that are found on either the x or y chromosome. ...
... V:sex linked traits-traits that are found on either the x or y chromosome. ...
24 Recombination Hotspots in Nonallelic Homologous Recombination
... Unfortunately, the relatively low frequency of recombination events across the genome as a whole (approx 50 crossovers per male meiosis) means that to obtain accurate estimates over even relatively large physical distances requires large numbers of meioses. It is not feasible to type the number of m ...
... Unfortunately, the relatively low frequency of recombination events across the genome as a whole (approx 50 crossovers per male meiosis) means that to obtain accurate estimates over even relatively large physical distances requires large numbers of meioses. It is not feasible to type the number of m ...
Chapter 16 Notes
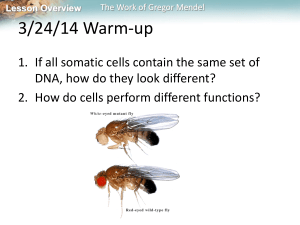
... This involves crossing the fly with a fly which is homozygous recessive for the trait being observed. By observing the phenotypes of the offspring, you can then determine the genotype of the unknown parent. Use Punnett squares to predict the percentages of phenotypes if a white eyed (homozygous ...
... This involves crossing the fly with a fly which is homozygous recessive for the trait being observed. By observing the phenotypes of the offspring, you can then determine the genotype of the unknown parent. Use Punnett squares to predict the percentages of phenotypes if a white eyed (homozygous ...
GCSE Science – Schemes of Work
... B2.1.1 This unit builds on the understanding that all living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. Students should be able to use their skills, knowledge and understanding to relate the structure of different types of cells to their f ...
... B2.1.1 This unit builds on the understanding that all living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. Students should be able to use their skills, knowledge and understanding to relate the structure of different types of cells to their f ...
Common Quantitative Trait Loci for Alcohol
... highly significant QTL was for the marker, D2MIT21, located at 80 cM on chromosome 2 (Markel et al., 1996), a locus linked to the region containing the high-affinity NT receptor gene, Ntsr (Laurent et al., 1994). Consideration of Ntsr as a candidate gene for regulation of ethanol sensitivity is cons ...
... highly significant QTL was for the marker, D2MIT21, located at 80 cM on chromosome 2 (Markel et al., 1996), a locus linked to the region containing the high-affinity NT receptor gene, Ntsr (Laurent et al., 1994). Consideration of Ntsr as a candidate gene for regulation of ethanol sensitivity is cons ...
Lesson Overview
... Whenever each of two gametes carried the t allele and then paired with the other gamete to produce an F2 plant, that plant was short. Every time one or more gametes carried the T allele and paired together, they produced a tall plant. The F2 generation had new combinations of alleles. ...
... Whenever each of two gametes carried the t allele and then paired with the other gamete to produce an F2 plant, that plant was short. Every time one or more gametes carried the T allele and paired together, they produced a tall plant. The F2 generation had new combinations of alleles. ...
The Living World
... What are called several traits that are affected by the same allele? In the human ABO blood grouping, there are four basic blood types, type A, type B, type AB, and type O. The blood proteins express themselves due to what trait? Foxes, cats, and rabbits have enzymes that are heat-sensitive. What ca ...
... What are called several traits that are affected by the same allele? In the human ABO blood grouping, there are four basic blood types, type A, type B, type AB, and type O. The blood proteins express themselves due to what trait? Foxes, cats, and rabbits have enzymes that are heat-sensitive. What ca ...
Genetic Analysis of Variation in Human Meiotic Recombination
... associated with recombination phenotypes. Two of these (RNF212 and an inversion on chromosome 17q21.31) were previously reported in the Icelandic population, and this is the first replication in any other population. Of the four newly identified loci (KIAA1462, PDZK1, UGCG, NUB1), results from expre ...
... associated with recombination phenotypes. Two of these (RNF212 and an inversion on chromosome 17q21.31) were previously reported in the Icelandic population, and this is the first replication in any other population. Of the four newly identified loci (KIAA1462, PDZK1, UGCG, NUB1), results from expre ...
Identification and Isolation of Dominant Susceptibility Loci for
... (15) in a system to examine the genetics of arthritis. Rat models that fulfil the criteria used for diagnosis of RA in humans include those with cartilage-restricted Ag-induced arthritis, such as collagen type II-induced arthritis (16), and pristane (2,6,10,14-tetramethylpentadecane)-induced arthrit ...
... (15) in a system to examine the genetics of arthritis. Rat models that fulfil the criteria used for diagnosis of RA in humans include those with cartilage-restricted Ag-induced arthritis, such as collagen type II-induced arthritis (16), and pristane (2,6,10,14-tetramethylpentadecane)-induced arthrit ...
Basic Principles of Heredity
... was able to follow the inheritance of individual characteristics for several generations. Had he chosen to work on an organism with a longer generation time—horses, for example— he might never have discovered the basis of inheritance. Pea plants also produce many offspring—their seeds—which allowed ...
... was able to follow the inheritance of individual characteristics for several generations. Had he chosen to work on an organism with a longer generation time—horses, for example— he might never have discovered the basis of inheritance. Pea plants also produce many offspring—their seeds—which allowed ...
www.psd150.org
... The yellow parent peas must be heterozygous. The yellow phenotype is expressed. Through meiosis and fertilisation, some offspring peas are homozygous recessive – they express a green colour. ...
... The yellow parent peas must be heterozygous. The yellow phenotype is expressed. Through meiosis and fertilisation, some offspring peas are homozygous recessive – they express a green colour. ...
Replication timing and transcriptional control: beyond
... when specific proteins are available for assembly into chromatin. For example, early replicating DNA would have a competitive advantage for binding limiting concentrations of transcriptional activators [11], whereas proteins that facilitate the assembly of heterochromatin would be available only lat ...
... when specific proteins are available for assembly into chromatin. For example, early replicating DNA would have a competitive advantage for binding limiting concentrations of transcriptional activators [11], whereas proteins that facilitate the assembly of heterochromatin would be available only lat ...
Biology - Medicine.careers360.com
... organic waste may result in :(1) Drying of the river very soon due to algal bloom. (2) Increased population of aquatic food web organisms. (3) An increased production of fish due to biodegradable nutrients. (4) Death of fish due to lack of oxygen. ...
... organic waste may result in :(1) Drying of the river very soon due to algal bloom. (2) Increased population of aquatic food web organisms. (3) An increased production of fish due to biodegradable nutrients. (4) Death of fish due to lack of oxygen. ...
The relationship between higher‑order chromatin structure and
... input chromatin fractions to a human chromosome 22q genomic array consisting of overlapping sequencing tiling path clones [21]. The average resolution of this array is 78 kb, but it contains regions where the clones are even smaller than the size of the chromatin fibres being examined (∼20 kb). The ...
... input chromatin fractions to a human chromosome 22q genomic array consisting of overlapping sequencing tiling path clones [21]. The average resolution of this array is 78 kb, but it contains regions where the clones are even smaller than the size of the chromatin fibres being examined (∼20 kb). The ...
Mendelian Genetics
... heredity. The hypotheses explain a simple form of inheritance in which two alleles of a gene are inherited to result in one of several traits in offspring. In modern terms, these hypotheses are: 1. There are different versions of genes. These different versions account for variations in characterist ...
... heredity. The hypotheses explain a simple form of inheritance in which two alleles of a gene are inherited to result in one of several traits in offspring. In modern terms, these hypotheses are: 1. There are different versions of genes. These different versions account for variations in characterist ...
Mendelian Genetics Chapter 12 Reading Mendellian Genetics
... he taught high school and cared for a garden. It was in this garden that he completed his important experiments. Most of Mendel’s experiments involved crossing different types of pea plants. In this case, the word cross means “to mate or breed two individuals.” Mendel crossed a type of garden pea pl ...
... he taught high school and cared for a garden. It was in this garden that he completed his important experiments. Most of Mendel’s experiments involved crossing different types of pea plants. In this case, the word cross means “to mate or breed two individuals.” Mendel crossed a type of garden pea pl ...
Full text PDF
... economical and practical means of controlling this insect. Field and greenhouse screening of introduced and local wheat germplasm at ICARDA resulted in the identification of several sources of resistance which were subsequently incorporated into ICARDA elite wheat germplasm and distributed as RWA ge ...
... economical and practical means of controlling this insect. Field and greenhouse screening of introduced and local wheat germplasm at ICARDA resulted in the identification of several sources of resistance which were subsequently incorporated into ICARDA elite wheat germplasm and distributed as RWA ge ...
Genetics of Clubroot Resistance inBrassicaSpecies | SpringerLink
... minimizing crop losses, especially when they are incorporated into systems of integrated control (see Diederichsen and others, this issue; Faggian and Strelkov, this issue; Donald and Porter, this issue). Sources of resistance have been identified and the genetic basis for resistance were studied in ...
... minimizing crop losses, especially when they are incorporated into systems of integrated control (see Diederichsen and others, this issue; Faggian and Strelkov, this issue; Donald and Porter, this issue). Sources of resistance have been identified and the genetic basis for resistance were studied in ...
What`s New in Evergreen Azaleas
... pistils and will set seed. Flowers that are hose-in-hose, or having the appearance of a corolla nested within another corolla, are usually female sterile. Occasionally, a hose-in-hose plant will produce a chance seedpod. One such pod from ‘H. H. Hume’ produced ‘Ring’s True.’ Polyploidy Concerns Most ...
... pistils and will set seed. Flowers that are hose-in-hose, or having the appearance of a corolla nested within another corolla, are usually female sterile. Occasionally, a hose-in-hose plant will produce a chance seedpod. One such pod from ‘H. H. Hume’ produced ‘Ring’s True.’ Polyploidy Concerns Most ...
Complex inheritance of larval adaptation in Plutella
... dominant or recessive and whether adaptations arising from human disturbance differ in their genetic architecture from those adaptations that arise under natural conditions. An understanding of the genetic architecture (that is, mode of inheritance, the number of genes involved) of a trait that allo ...
... dominant or recessive and whether adaptations arising from human disturbance differ in their genetic architecture from those adaptations that arise under natural conditions. An understanding of the genetic architecture (that is, mode of inheritance, the number of genes involved) of a trait that allo ...
Leukaemia Section Classification of acute myeloid leukemias Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... marker CD19 with CD33 and CD34 and less often CD56. CLINICAL FEATURES: t(8;21) is usually associated with a good response to chemotherapy and a high remission rate with long-term disease-free survival. A large number of patients demonstrate additional chromosome abnormalities: loss of sex chromosome ...
... marker CD19 with CD33 and CD34 and less often CD56. CLINICAL FEATURES: t(8;21) is usually associated with a good response to chemotherapy and a high remission rate with long-term disease-free survival. A large number of patients demonstrate additional chromosome abnormalities: loss of sex chromosome ...
Convergent Evolution in the Genetic Basis of Müllerian
... between the heterozygous Bb/Dd female (dark gray) and male (light gray). Crossing over of sister chromatids does not occur during oogenesis, so F2 progeny inherit either bD or Bd genotypes from the F1 female. As all LG18 chromosomal markers are completely linked when inherited from the F1 mother, mo ...
... between the heterozygous Bb/Dd female (dark gray) and male (light gray). Crossing over of sister chromatids does not occur during oogenesis, so F2 progeny inherit either bD or Bd genotypes from the F1 female. As all LG18 chromosomal markers are completely linked when inherited from the F1 mother, mo ...
Wheat biotechnology: A minireview
... considerable attention over the years from plant breeders with the purpose of increasing the grain yield and to minimize crop loss due to unfavourable environmental conditions, and attack by various pests and pathogens. In the early 60’s, conventional breeding coupled with improved farm management p ...
... considerable attention over the years from plant breeders with the purpose of increasing the grain yield and to minimize crop loss due to unfavourable environmental conditions, and attack by various pests and pathogens. In the early 60’s, conventional breeding coupled with improved farm management p ...
Convergent Evolution in the Genetic Basis of Müllerian Mimicry in
... between the heterozygous Bb/Dd female (dark gray) and male (light gray). Crossing over of sister chromatids does not occur during oogenesis, so F2 progeny inherit either bD or Bd genotypes from the F1 female. As all LG18 chromosomal markers are completely linked when inherited from the F1 mother, mo ...
... between the heterozygous Bb/Dd female (dark gray) and male (light gray). Crossing over of sister chromatids does not occur during oogenesis, so F2 progeny inherit either bD or Bd genotypes from the F1 female. As all LG18 chromosomal markers are completely linked when inherited from the F1 mother, mo ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.