Course_Outline_for_BIO_201-1ef_1
... Cell division,fertilization and embryonic development or growth are the major features of any organism’s life cycle.Though some plants complete their life cycles without fusion of gametese.g cassava,yam etc sexually reproducing plants and animals can only complete their life cycles through the two p ...
... Cell division,fertilization and embryonic development or growth are the major features of any organism’s life cycle.Though some plants complete their life cycles without fusion of gametese.g cassava,yam etc sexually reproducing plants and animals can only complete their life cycles through the two p ...
Bb - gpisd
... • X linked alleles __________ show up in _______ whether ___________ or _____________ because males have only _____ X chromosome ...
... • X linked alleles __________ show up in _______ whether ___________ or _____________ because males have only _____ X chromosome ...
Spring Final Review - Summit School District
... zygote, gametes -Explain the process of non-disjunction and the results. Example: Trisomy 21. -Name a specific chromosomal disorder that is caused by non-disjunction and the effects it has on the individual. -Draw and label the cell cycle. ...
... zygote, gametes -Explain the process of non-disjunction and the results. Example: Trisomy 21. -Name a specific chromosomal disorder that is caused by non-disjunction and the effects it has on the individual. -Draw and label the cell cycle. ...
1. Which organelles does the process of Adenosine triphosphate
... 57. When a living human red blood cell is placed in pure fresh water the cell will swell and burst. What is the reason for this? A) Water molecules move from higher to lower concentrations of dissolved particles. B) The cell membrane dissolves in water. C) Cells lose stability outside the human body ...
... 57. When a living human red blood cell is placed in pure fresh water the cell will swell and burst. What is the reason for this? A) Water molecules move from higher to lower concentrations of dissolved particles. B) The cell membrane dissolves in water. C) Cells lose stability outside the human body ...
Controlling Growth
... Why is there a greater chance of recessive diseases being shown in inbreeding? In breeding is between close relatives which means both carry the same recessive genes and for the gene to express its self it is to be present in both the parents. ...
... Why is there a greater chance of recessive diseases being shown in inbreeding? In breeding is between close relatives which means both carry the same recessive genes and for the gene to express its self it is to be present in both the parents. ...
ppt
... C. Changes in ‘aneuploidy’ (changes in chromosome number) 1. Mechanism: Non-disjunction (failure of a homologous pair or sister chromatids to separate) ...
... C. Changes in ‘aneuploidy’ (changes in chromosome number) 1. Mechanism: Non-disjunction (failure of a homologous pair or sister chromatids to separate) ...
Unit 9(Heredity and Evolution)
... 28. Mention three important features of fossils which help in the study of evolution. 29. Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X chromosome? 30. In human beings, the statistical probability of getting either a male or female child is 50 : 50. Give a suitable explanation. 31. A very ...
... 28. Mention three important features of fossils which help in the study of evolution. 29. Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X chromosome? 30. In human beings, the statistical probability of getting either a male or female child is 50 : 50. Give a suitable explanation. 31. A very ...
T - Center Grove Schools
... •Mendel studied seven different traits in pea plants. -Traits are inherited characteristics that vary from individual to individual. oEach trait each had two different forms or alleles. oPea plant height can be either tall (T) OR short (t). oAllele – the different possible forms of a trait ...
... •Mendel studied seven different traits in pea plants. -Traits are inherited characteristics that vary from individual to individual. oEach trait each had two different forms or alleles. oPea plant height can be either tall (T) OR short (t). oAllele – the different possible forms of a trait ...
PAG XXIV San Diego 2016 Duckweeds, the smallest flowering
... Leaves and stems are merged into a common flattened ovoid structure called a frond or thallus, some species have thread-like rootlets Propagation occurs primarily by budding of new fronds The entire plant body is composed of metabolically active cells rather than structural, supportive tissues so th ...
... Leaves and stems are merged into a common flattened ovoid structure called a frond or thallus, some species have thread-like rootlets Propagation occurs primarily by budding of new fronds The entire plant body is composed of metabolically active cells rather than structural, supportive tissues so th ...
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
... comprise the genetic "alphabet." The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Bases on opposite strands pair specifically: A’s always pair with T’s, and C’s always pair with G’s. The order of the A’s, T’s, C’s and G’s determines the meaning of the information encoded in DNA ...
... comprise the genetic "alphabet." The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Bases on opposite strands pair specifically: A’s always pair with T’s, and C’s always pair with G’s. The order of the A’s, T’s, C’s and G’s determines the meaning of the information encoded in DNA ...
Meiosis and Mendelian Genetics Digital
... Use all content and scientific process skills learned earlier in the course Describe the purpose of meiosis Summarize the events of meiosis Summarize the outcomes of Mendel’s experiments with garden peas Distinguish between dominant and recessive alleles Differentiate between the terms homozygous an ...
... Use all content and scientific process skills learned earlier in the course Describe the purpose of meiosis Summarize the events of meiosis Summarize the outcomes of Mendel’s experiments with garden peas Distinguish between dominant and recessive alleles Differentiate between the terms homozygous an ...
Chapter 11
... 1. Gamete = sperm/ovum B. Organisms inherit a single copy of every gene from each parent C. Produces gametes with only 1 set of genes D. Two divisions 1. Meiosis I and Meiosis II ...
... 1. Gamete = sperm/ovum B. Organisms inherit a single copy of every gene from each parent C. Produces gametes with only 1 set of genes D. Two divisions 1. Meiosis I and Meiosis II ...
Supplemental File S3. Homologous Chromosomes
... “Summary of Maps”, which includes how large the chromosome is in base pairs, how many genes are on the chromosome, and links to other information. Note that you can also zoom in and zoom out on sections of the chromosomes. To view the entire chromosome and answer the questions below, you will need t ...
... “Summary of Maps”, which includes how large the chromosome is in base pairs, how many genes are on the chromosome, and links to other information. Note that you can also zoom in and zoom out on sections of the chromosomes. To view the entire chromosome and answer the questions below, you will need t ...
03-Heredity & Environment
... Genome = Code for making an individual 20,000 genes (99% in other creatures also) Genotype = The full set of genes for a specific orgasm ...
... Genome = Code for making an individual 20,000 genes (99% in other creatures also) Genotype = The full set of genes for a specific orgasm ...
Genes By Cindy Grigg 1 Have you ever seen a cat with a litter of
... Your genes determine your skin color, whether your hair is curly or straight, and whether or not you can roll your tongue into a U-shape. Each of these three traits is controlled by a gene. Humans have thousands of different genes. They are located on the 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nuclei of our ...
... Your genes determine your skin color, whether your hair is curly or straight, and whether or not you can roll your tongue into a U-shape. Each of these three traits is controlled by a gene. Humans have thousands of different genes. They are located on the 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nuclei of our ...
Genes
... People inherit two genes for every characteristic, and they get one gene from each parent. Sometimes the two genes for one trait contain different codes. This affects how the trait appears in the child. For example, maybe both parents have brown eyes. Let's say that they each have one gene for brown ...
... People inherit two genes for every characteristic, and they get one gene from each parent. Sometimes the two genes for one trait contain different codes. This affects how the trait appears in the child. For example, maybe both parents have brown eyes. Let's say that they each have one gene for brown ...
G 1
... • Meiosis, a reduction division followed by fertilization, ensures genetic diversity in sexually reproducing organisms – Ensures each gamete receives one complete haploid (1n) set of chromosomes – Homologous chromosomes are paired with one homologue originating from the maternal parent and one from ...
... • Meiosis, a reduction division followed by fertilization, ensures genetic diversity in sexually reproducing organisms – Ensures each gamete receives one complete haploid (1n) set of chromosomes – Homologous chromosomes are paired with one homologue originating from the maternal parent and one from ...
Introduction to BST775: Statistical Methods for Genetic Analysis I
... DNA is information store • Encodes the information required for cells and organisms to function and produce new cells and organisms. • DNA variation is responsible for many individual differences, some of which are medically important. ...
... DNA is information store • Encodes the information required for cells and organisms to function and produce new cells and organisms. • DNA variation is responsible for many individual differences, some of which are medically important. ...
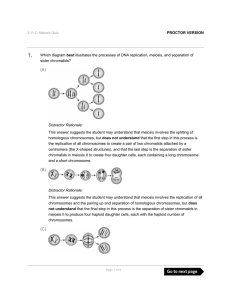
(A) (B) (C)
... would not be an issue with a genetic marker because markers are traced using molecular biology techniques, and even if a recessive trait were not expressed in an individual’s phenotype, it would still be present on the individual’s chromosome and detected during analysis. In addition, only 50% of a ...
... would not be an issue with a genetic marker because markers are traced using molecular biology techniques, and even if a recessive trait were not expressed in an individual’s phenotype, it would still be present on the individual’s chromosome and detected during analysis. In addition, only 50% of a ...
II-TERM QUESTION BANK (2016-17) Std: X Sub: Biology Topic : 1
... 2) Fossils furnish the direct and most reliable evidence for evolution. 7. How does the creation of variation in a species promote survival? 8. Only variation that confers an advantage to an individual organism will survive in population.”Comment on the statement. 9. Do genetic combination of mother ...
... 2) Fossils furnish the direct and most reliable evidence for evolution. 7. How does the creation of variation in a species promote survival? 8. Only variation that confers an advantage to an individual organism will survive in population.”Comment on the statement. 9. Do genetic combination of mother ...
File
... Meiosis creates haploid (halved) gametes or sex cells containing only one member of each chromosome pair from the diploid parent cells. Egg Cell Fertilization results in the formation of a diploid embryo, which contains chromosomes donated by both parents. ...
... Meiosis creates haploid (halved) gametes or sex cells containing only one member of each chromosome pair from the diploid parent cells. Egg Cell Fertilization results in the formation of a diploid embryo, which contains chromosomes donated by both parents. ...
Introduction to Animal Genetics
... Gregor Mendel discovered the principles of inheritance using peas as a subject. Alleles affect the same trait, but each allele causes the production of a different protein and how the trait is expressed. The locus of alleles on a chromosome is said to be homozygous if the alleles are identical. Unli ...
... Gregor Mendel discovered the principles of inheritance using peas as a subject. Alleles affect the same trait, but each allele causes the production of a different protein and how the trait is expressed. The locus of alleles on a chromosome is said to be homozygous if the alleles are identical. Unli ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.