Orthology, Paralogy, Chains, and Nets - CS273a
... chicken chicken ≈ 1013 copies (DNA) of egg (DNA) ...
... chicken chicken ≈ 1013 copies (DNA) of egg (DNA) ...
pages 163-171 Biolog.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... does not carry an allele for the eye-colour gene. Traits located on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked traits. The initial problem can now be reexamined. The pure-breeding, red-eyed female can be indicated by the genotype XRXR and the white-eyed male by the genotype XrY. The symbol XR indicates t ...
... does not carry an allele for the eye-colour gene. Traits located on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked traits. The initial problem can now be reexamined. The pure-breeding, red-eyed female can be indicated by the genotype XRXR and the white-eyed male by the genotype XrY. The symbol XR indicates t ...
PDF Barbara McClintock`s World
... University. Working in the College of Agriculture, she receives her undergraduate degree in 1923. Although she conducts her graduate research under the cytologist Lester Sharp, she associates most closely with the maize genetics group of Rollins A. Emerson. After receiving her Ph.D. in 1927, she sta ...
... University. Working in the College of Agriculture, she receives her undergraduate degree in 1923. Although she conducts her graduate research under the cytologist Lester Sharp, she associates most closely with the maize genetics group of Rollins A. Emerson. After receiving her Ph.D. in 1927, she sta ...
Using Meiosis to make a Mini-Manc
... This set of cards represents your gamete (egg or sperm), which has half the number of chromosomes of your parent Mini Manc (haploid number). 5. Now mate with your partner! Combine your 7 cards with your partner’s. This simulates random fertilisation. Remember you could have mated with any other Mini ...
... This set of cards represents your gamete (egg or sperm), which has half the number of chromosomes of your parent Mini Manc (haploid number). 5. Now mate with your partner! Combine your 7 cards with your partner’s. This simulates random fertilisation. Remember you could have mated with any other Mini ...
Chapter 12 Cell Cycle Functions of cell division. . Phases of the cell
... Phases of mitosis and describe the events characteristic of each phase. Recognize the phases of mitosis from diagrams and micrographs. Identify the following structures in the diagram: the mitotic spindle, including ...
... Phases of mitosis and describe the events characteristic of each phase. Recognize the phases of mitosis from diagrams and micrographs. Identify the following structures in the diagram: the mitotic spindle, including ...
Pipe Cleaner Babies
... In this activity you will play the role of a parent, your lab partner will play the role of the other parent. You will use chromosome and gene models to create an offspring. You will then use class data to determine how accurate Punnett squares are by comparing probability to what is actually seen i ...
... In this activity you will play the role of a parent, your lab partner will play the role of the other parent. You will use chromosome and gene models to create an offspring. You will then use class data to determine how accurate Punnett squares are by comparing probability to what is actually seen i ...
Sex Linkage - Ms. Petrauskas' Class
... • Can white eyed females possible occur in nature? • YES! For this to happen, the offspring would have to inherit ...
... • Can white eyed females possible occur in nature? • YES! For this to happen, the offspring would have to inherit ...
Objectives
... 7. Make a monohybrid (4-box) Punnett Square for Bb x Bb. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the Punnett Square? 8. Determine the gametes of a dihybrid cross. HhFf and Hhff. What are the possible gametes of each individual? 9. Complete the dihybrid Punnett Square of the individuals in #8 ...
... 7. Make a monohybrid (4-box) Punnett Square for Bb x Bb. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the Punnett Square? 8. Determine the gametes of a dihybrid cross. HhFf and Hhff. What are the possible gametes of each individual? 9. Complete the dihybrid Punnett Square of the individuals in #8 ...
Heredity and Prenatal Development
... • DNA breaks apart (unzips); and the double helix duplicates. • DNA forms two camps on either side of cell; cell divides. Each incomplete rung combines with its partner to form a new ladder; resulting identical copies of the DNA strand separate when cell divides; each is newly formed cell; genetic c ...
... • DNA breaks apart (unzips); and the double helix duplicates. • DNA forms two camps on either side of cell; cell divides. Each incomplete rung combines with its partner to form a new ladder; resulting identical copies of the DNA strand separate when cell divides; each is newly formed cell; genetic c ...
Ch. 6/7 Objectives 1. Identify the different phases of Mitosis and
... 7. Make a monohybrid (4-box) Punnett Square for Bb x Bb. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the Punnett Square? 8. Determine the gametes of a dihybrid cross. HhFf and Hhff. What are the possible gametes of each individual? 9. Complete the dihybrid Punnett Square of the individuals in #8 ...
... 7. Make a monohybrid (4-box) Punnett Square for Bb x Bb. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the Punnett Square? 8. Determine the gametes of a dihybrid cross. HhFf and Hhff. What are the possible gametes of each individual? 9. Complete the dihybrid Punnett Square of the individuals in #8 ...
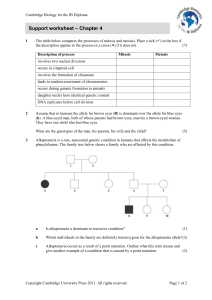
Support worksheet – Chapter 4 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Support worksheet – Chapter 4 ...
... Support worksheet – Chapter 4 ...
Mutation Notes
... ►A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
... ►A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... 2. shyness in humans has a genetic component – can be amplified or reduced by environment. a) ex. Tom Hanks 3. [READ] Avshalom Caspi and Terrie Moffitt [interview with Moffitt here on npr] made quite a splash in 2002 when they published the paper “Role of Genotype in the Cycle of Violence in Maltrea ...
... 2. shyness in humans has a genetic component – can be amplified or reduced by environment. a) ex. Tom Hanks 3. [READ] Avshalom Caspi and Terrie Moffitt [interview with Moffitt here on npr] made quite a splash in 2002 when they published the paper “Role of Genotype in the Cycle of Violence in Maltrea ...
Sex-Linked Inheritance
... Sex linked inheritance is a form of inheritance where genes or traits are coded for on the sex chromosomes, specifically on the X chromosome because very little gene information is found on the Y chromosome. Examples of sex linked traits are Color Blindness, Hemophilia, and eye color in fruit flies ...
... Sex linked inheritance is a form of inheritance where genes or traits are coded for on the sex chromosomes, specifically on the X chromosome because very little gene information is found on the Y chromosome. Examples of sex linked traits are Color Blindness, Hemophilia, and eye color in fruit flies ...
MUTATIONS - MsWalshMosher
... There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child ...
... There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child ...
EXAM 4-Fall2005.doc
... D) they all evolved from fish. E) they all possess DNA. 24) The many different breeds of domestic dog were produced by A) natural selection. B) artificial selection. C) kin selection D) mutation. E) divergent evolution. 25) Most commercial pesticides are effective for only 2-3 years. This is because ...
... D) they all evolved from fish. E) they all possess DNA. 24) The many different breeds of domestic dog were produced by A) natural selection. B) artificial selection. C) kin selection D) mutation. E) divergent evolution. 25) Most commercial pesticides are effective for only 2-3 years. This is because ...
Get Notes - Mindset Learn
... “Everything we see today arose from that which existed in the past; however it may look different because things change with time.” Name and describe the principle9s) that Lamarck and Darwin used to explain how evolution took place. In your explanation, give reasons why Lamarck’s theory was not acce ...
... “Everything we see today arose from that which existed in the past; however it may look different because things change with time.” Name and describe the principle9s) that Lamarck and Darwin used to explain how evolution took place. In your explanation, give reasons why Lamarck’s theory was not acce ...
MCA Test Prep Answers Part 1
... a) Describe how Mendel studied heredity. “By working with pea plants, he was able to keep accounts of traits passed down through generations and cross plants with different traits to see how it affected the offspring.” b) Write 1 question about inheritance that was answered by Mendel’s work. “Why do ...
... a) Describe how Mendel studied heredity. “By working with pea plants, he was able to keep accounts of traits passed down through generations and cross plants with different traits to see how it affected the offspring.” b) Write 1 question about inheritance that was answered by Mendel’s work. “Why do ...
The Search for LUCA Natural History Nov. 2000 Did the Last
... introns have been edited out by the spliceosome). Multiple copies of reverse transcriptase are present in all genomes, having been left there by retroviruses containing genes for the enzyme. The Forterre-Poole hypothesis envisages that some primitive retrovirus left behind a reverse transcriptase ge ...
... introns have been edited out by the spliceosome). Multiple copies of reverse transcriptase are present in all genomes, having been left there by retroviruses containing genes for the enzyme. The Forterre-Poole hypothesis envisages that some primitive retrovirus left behind a reverse transcriptase ge ...
Heredity and Meiosis - Chaparral Star Academy
... 2 organisms can look the same, but be very different genetically ...
... 2 organisms can look the same, but be very different genetically ...
BIOL 105 S 2014 QZM2 QA 140207.1
... A) fallopian tube. B) uterus. C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fe ...
... A) fallopian tube. B) uterus. C) peritoneal cavity. D) vagina. E) vas deferens Development 39. All of the changes that occur from the time an egg is fertilized through childhood, adolescence and adulthood are called A. metabolism. B. evolution. C. homeostasis. D. reproduction. E. development. 40. Fe ...
CHAPTER 15 THE CHROMOSOMAL BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... • In contrast, linked genes, genes located on the same chromosome, tend to move together through meiosis and fertilization. • Under normal Mendelian genetic rules, we would not expect linked genes to recombine into assortments of alleles not found in the parents. • If the seed color and seed coat g ...
... • In contrast, linked genes, genes located on the same chromosome, tend to move together through meiosis and fertilization. • Under normal Mendelian genetic rules, we would not expect linked genes to recombine into assortments of alleles not found in the parents. • If the seed color and seed coat g ...
Genetics PowerPoint
... Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes ● We have 23 pairs of chromosomes ● 1 pair are known as the sex chromosomes, which determines the sex of the offspring (and has other ...
... Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes ● We have 23 pairs of chromosomes ● 1 pair are known as the sex chromosomes, which determines the sex of the offspring (and has other ...
Study Guide for the Biology Midterm
... 19) Know what a Punnett square is. Be able to predict probability using a Punnett square and determine what offspring may be produced due to a cross. 20) Who is Gregor Mendel? What plant did he use in his experiments? 21) What does true breeding mean? 22) The original pair of plants that Mendel used ...
... 19) Know what a Punnett square is. Be able to predict probability using a Punnett square and determine what offspring may be produced due to a cross. 20) Who is Gregor Mendel? What plant did he use in his experiments? 21) What does true breeding mean? 22) The original pair of plants that Mendel used ...
LUCA - University of Washington
... would already have been in place: a single enzyme called reverse transcriptase. This enzyme makes a circular DNA copy of an RNA transcript (after the introns have been edited out by the spliceosome). Multiple copies of reverse transcriptase are present in all genomes, having been left there by retro ...
... would already have been in place: a single enzyme called reverse transcriptase. This enzyme makes a circular DNA copy of an RNA transcript (after the introns have been edited out by the spliceosome). Multiple copies of reverse transcriptase are present in all genomes, having been left there by retro ...
Polyploid
Polyploid cells and organisms are those containing more than two paired (homologous) sets of chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (Eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes—one set inherited from each parent. However, polyploidy is found in some organisms and is especially common in plants. In addition, polyploidy occurs in some tissues of animals that are otherwise diploid, such as human muscle tissues. This is known as endopolyploidy. Species whose cells do not have nuclei, that is, Prokaryotes, may be polyploid organisms, as seen in the large bacterium Epulopicium fishelsoni [1]. Hence ploidy is defined with respect to a cell. Most eukaryotes have diploid somatic cells, but produce haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) by meiosis. A monoploid has only one set of chromosomes, and the term is usually only applied to cells or organisms that are normally diploid. Male bees and other Hymenoptera, for example, are monoploid. Unlike animals, plants and multicellular algae have life cycles with two alternating multicellular generations. The gametophyte generation is haploid, and produces gametes by mitosis, the sporophyte generation is diploid and produces spores by meiosis.Polyploidy refers to a numerical change in a whole set of chromosomes. Organisms in which a particular chromosome, or chromosome segment, is under- or overrepresented are said to be aneuploid (from the Greek words meaning ""not"", ""good"", and ""fold""). Therefore the distinction between aneuploidy and polyploidy is that aneuploidy refers to a numerical change in part of the chromosome set, whereas polyploidy refers to a numerical change in the whole set of chromosomes.Polyploidy may occur due to abnormal cell division, either during mitosis, or commonly during metaphase I in meiosis.Polyploidy occurs in some animals, such as goldfish, salmon, and salamanders, but is especially common among ferns and flowering plants (see Hibiscus rosa-sinensis), including both wild and cultivated species. Wheat, for example, after millennia of hybridization and modification by humans, has strains that are diploid (two sets of chromosomes), tetraploid (four sets of chromosomes) with the common name of durum or macaroni wheat, and hexaploid (six sets of chromosomes) with the common name of bread wheat. Many agriculturally important plants of the genus Brassica are also tetraploids.Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by some chemicals: the best known is colchicine, which can result in chromosome doubling, though its use may have other less obvious consequences as well. Oryzalin will also double the existing chromosome content.