Unit 8 Homework Packet
... 26. Although they were formerly called the inert gases, at least the heavier elements of Group 8 do form relatively stable compounds. For example, xenon combines directly with elemental fluorine at elevated temperatures in the presence of a nickel catalyst. Xe(g) + 2F2(g) → XeF4(s) ...
... 26. Although they were formerly called the inert gases, at least the heavier elements of Group 8 do form relatively stable compounds. For example, xenon combines directly with elemental fluorine at elevated temperatures in the presence of a nickel catalyst. Xe(g) + 2F2(g) → XeF4(s) ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... of 100% whereas substitution reactions are less efficient. Carry out calculations to determine the atom economy of a reaction. Describe the benefits of developing chemical processes with a high atom economy in terms of fewer waste materials. Explain that a reaction may have a high percentage yield b ...
... of 100% whereas substitution reactions are less efficient. Carry out calculations to determine the atom economy of a reaction. Describe the benefits of developing chemical processes with a high atom economy in terms of fewer waste materials. Explain that a reaction may have a high percentage yield b ...
X012/11/02
... 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of ...
... 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number) and Centre Name printed on it. Do not change any of these details. 4 If any of ...
Packet #7- Chemical Reactions
... An explosion is a very fast reaction that releases a large volume of gaseous products. There is a danger of explosion in factories that handle powdered, flammable substances. These substances include custard powder, flour and powdered sulfur. Effect of catalysts The rate of a reaction can be increas ...
... An explosion is a very fast reaction that releases a large volume of gaseous products. There is a danger of explosion in factories that handle powdered, flammable substances. These substances include custard powder, flour and powdered sulfur. Effect of catalysts The rate of a reaction can be increas ...
CHEM102 Chemistry II Spring 11-12 Mid
... 28) Which of the following can serve as the solvent in a solution? 28) ______ A) a liquid B) a gas C) a solid D) a mixture of comingled liquids E) all of the above 29) If the concentration of H3O+ is 3.5 × 10-3 M, the concentration of OH- is ________ M. 29) ______ A) 3.5 × 10-11 B) 1.0 × 10-12 C) 2. ...
... 28) Which of the following can serve as the solvent in a solution? 28) ______ A) a liquid B) a gas C) a solid D) a mixture of comingled liquids E) all of the above 29) If the concentration of H3O+ is 3.5 × 10-3 M, the concentration of OH- is ________ M. 29) ______ A) 3.5 × 10-11 B) 1.0 × 10-12 C) 2. ...
Practice Test 2
... A) present in greatest quantity B) limits the number of reagents present C) determined by the amount of reactants present D) that determines the maximum amount of possible product ...
... A) present in greatest quantity B) limits the number of reagents present C) determined by the amount of reactants present D) that determines the maximum amount of possible product ...
IGCSE SoW 2013
... Describe and explain the main reactions involved in the extraction of iron from iron ore (haematite), using coke, limestone and air in a blast furnace ...
... Describe and explain the main reactions involved in the extraction of iron from iron ore (haematite), using coke, limestone and air in a blast furnace ...
Comparison of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis
... (SI) engine vehicles and the latter is used in compression ignition (CI) engine vehicles. These fuels take a long span of time in its formation and are considered a non-renewable source of energy. Out of the various modes of transportation, road emission amounts for 80% of emissions followed by rail ...
... (SI) engine vehicles and the latter is used in compression ignition (CI) engine vehicles. These fuels take a long span of time in its formation and are considered a non-renewable source of energy. Out of the various modes of transportation, road emission amounts for 80% of emissions followed by rail ...
Chemistry - NIC Karnataka
... General introduction to p– block elements-electronic configuration, oxidation states, inert pair effect, anomalous behavior of first member of each group. Group 13 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence , variation of atomic radii, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity ...
... General introduction to p– block elements-electronic configuration, oxidation states, inert pair effect, anomalous behavior of first member of each group. Group 13 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence , variation of atomic radii, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity ...
unit 7 h chem notes - chemical equations
... I. Chemical Reactions and their equations. 1. The materials which you can start with are written first, and are called reactants. If there is more than one reactant, a plus (+) sign separates each individual reactant. Example: Sodium reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride (NaCl). An arrow is w ...
... I. Chemical Reactions and their equations. 1. The materials which you can start with are written first, and are called reactants. If there is more than one reactant, a plus (+) sign separates each individual reactant. Example: Sodium reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride (NaCl). An arrow is w ...
CHEE 221: Chemical Processes and Systems
... 1. Material balances – for a nonreactive process, usually but not always, the maximum number of independent equations that can be written equals the number of chemical species in the process 2. Process constraints– given in the problem statement 3. Physical constraints – e.g., mass or mole fractio ...
... 1. Material balances – for a nonreactive process, usually but not always, the maximum number of independent equations that can be written equals the number of chemical species in the process 2. Process constraints– given in the problem statement 3. Physical constraints – e.g., mass or mole fractio ...
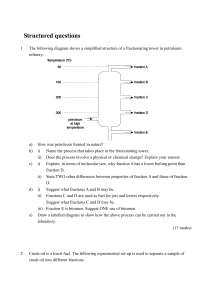
Structured questions
... i) sootiness of flame when burnt; ii) viscosity; and iii) molecular size. In the world, the demand for lower boiling fractions of crude oil is greater than its supply while the supply of higher boiling fractions of crude oil is in excess. i) ii) ...
... i) sootiness of flame when burnt; ii) viscosity; and iii) molecular size. In the world, the demand for lower boiling fractions of crude oil is greater than its supply while the supply of higher boiling fractions of crude oil is in excess. i) ii) ...
Theoretical problems (official version)
... worried about the possibility of spontaneous decomposition of hydrates caused by the raising ocean temperature. It is believed that if a sufficient amount of methane is released into the atmosphere, the oceans will warm up quicker due to the greenhouse effect, further accelerating the decomposition ...
... worried about the possibility of spontaneous decomposition of hydrates caused by the raising ocean temperature. It is believed that if a sufficient amount of methane is released into the atmosphere, the oceans will warm up quicker due to the greenhouse effect, further accelerating the decomposition ...
SPRING 2002 Test 2 1. Which of the following statements is
... B. N2 + 3H2 <=> 2 NH3 C. 2 CO + O2 <=> 2 CO2 D. N2O4 <=> 2 NO2 E. N2 + O2 <=> 2 NO Ans. E 12. Consider the exothermic reaction between N2 and H2 to produce NH3. In order to produce as much NH3 as possible, this reaction should be run at A. low temperature and low pressure B. low temperature and high ...
... B. N2 + 3H2 <=> 2 NH3 C. 2 CO + O2 <=> 2 CO2 D. N2O4 <=> 2 NO2 E. N2 + O2 <=> 2 NO Ans. E 12. Consider the exothermic reaction between N2 and H2 to produce NH3. In order to produce as much NH3 as possible, this reaction should be run at A. low temperature and low pressure B. low temperature and high ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... The following reaction is exothermic: Ti(s) + 2 Cl2(g) TiCl4(g) + energy(exothermic) List all the ways the yield of the product TiCl4 could be increased. 1) Lower the temperature 2) Increase the pressure 3) Increase the concentration of chlorine gas added to the reaction vessel ...
... The following reaction is exothermic: Ti(s) + 2 Cl2(g) TiCl4(g) + energy(exothermic) List all the ways the yield of the product TiCl4 could be increased. 1) Lower the temperature 2) Increase the pressure 3) Increase the concentration of chlorine gas added to the reaction vessel ...
Make Your Own Summary 1. single displacement reaction 2
... which prevents the reaction from being a double displacement reaction. The products are two compounds, which prevent the reaction from being a single displacement reaction. ...
... which prevents the reaction from being a double displacement reaction. The products are two compounds, which prevent the reaction from being a single displacement reaction. ...
RES8_chemcontentchecklist
... have different electronegativities, resulting in a polar bond. Describe intermolecular forces based on permanent dipoles, as in hydrogen chloride, and instantaneous dipoles (van der Waals’ forces), as in the noble gases. Describe hydrogen bonding, including the role of a lone pair, between molecules ...
... have different electronegativities, resulting in a polar bond. Describe intermolecular forces based on permanent dipoles, as in hydrogen chloride, and instantaneous dipoles (van der Waals’ forces), as in the noble gases. Describe hydrogen bonding, including the role of a lone pair, between molecules ...
Questions 1-2
... filtrate and a bright yellow precipitate was produced. The white precipitate remaining on the filter paper was readily soluble in ammonia solution. What two ions could have been present in the unknown? (A) Ag+ and Hg22+ (B) Ag+ and Pb2+ (C) Ba2+ and Ag+ (D) Ba2+ and Hg22+ 37. HCO3-(aq) + OH-(aq) H ...
... filtrate and a bright yellow precipitate was produced. The white precipitate remaining on the filter paper was readily soluble in ammonia solution. What two ions could have been present in the unknown? (A) Ag+ and Hg22+ (B) Ag+ and Pb2+ (C) Ba2+ and Ag+ (D) Ba2+ and Hg22+ 37. HCO3-(aq) + OH-(aq) H ...
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Technical Information
... products. These high performance materials have high surface areas and unique morphologies which make them uniquely different from conventional counterparts. This high chemical reactivity led to development of several formulations that are very effective at treating a broad range of chemical hazards ...
... products. These high performance materials have high surface areas and unique morphologies which make them uniquely different from conventional counterparts. This high chemical reactivity led to development of several formulations that are very effective at treating a broad range of chemical hazards ...
File
... product of the following reactions: 2 Na(s) + SrBr2(aq) NR CrI3(aq) + 3 KCl(aq) CrCl3(s) + 3 KI(aq) (DR – ppt) Zn(s) + H2SO3(aq) ZnSO3(aq) + H2(g) (SR – metal + acid) K2CO3(aq) + 2 HI(aq) 2 KI(aq) + H2CO3(aq) (DR – gas) ...
... product of the following reactions: 2 Na(s) + SrBr2(aq) NR CrI3(aq) + 3 KCl(aq) CrCl3(s) + 3 KI(aq) (DR – ppt) Zn(s) + H2SO3(aq) ZnSO3(aq) + H2(g) (SR – metal + acid) K2CO3(aq) + 2 HI(aq) 2 KI(aq) + H2CO3(aq) (DR – gas) ...
AP Chem Chapter 16 Review Packet
... harvesting the hydrogen for fuel. The free energy of this reaction is so positive that there is no hope of causing the reaction to occur without coupling it to another process. For example, it has been proposed that the reaction can be promoted by first reacting silver with water to produce hydrogen ...
... harvesting the hydrogen for fuel. The free energy of this reaction is so positive that there is no hope of causing the reaction to occur without coupling it to another process. For example, it has been proposed that the reaction can be promoted by first reacting silver with water to produce hydrogen ...
Chemistry Exam 2 Specifications and Sample Exam
... Ethanol is not the only alcohol gaining in popularity as a fuel. Methanol, CH3OH, is also the subject of considerable research; especially for use in fuel cells. The commercial production of methanol, however, is quite different to that of ethanol and involves a two step process. Step 1 Production o ...
... Ethanol is not the only alcohol gaining in popularity as a fuel. Methanol, CH3OH, is also the subject of considerable research; especially for use in fuel cells. The commercial production of methanol, however, is quite different to that of ethanol and involves a two step process. Step 1 Production o ...
Final Exam SG Part 1 (Unit 5).
... c. How many moles are produced from the moles of the reactants? d. If you double the amount of white molecules (so now you have 8 pairs) but keep the same amount of black molecules, how many molecules can you produce? 4. Percent Yield a. ___Sb4O6 + ____C → ____Sb + ____CO Determine the percent yield ...
... c. How many moles are produced from the moles of the reactants? d. If you double the amount of white molecules (so now you have 8 pairs) but keep the same amount of black molecules, how many molecules can you produce? 4. Percent Yield a. ___Sb4O6 + ____C → ____Sb + ____CO Determine the percent yield ...
Critical Point Dryer
... First precursor gas (A Source) is introduced into the process chamber and produces a monolayer on the wafer surface. Then a second precursor gas (B Source) is introduced into the chamber, which reacts with the first precursor to produce a monolayer of film on the wafer surface. Separation of the pre ...
... First precursor gas (A Source) is introduced into the process chamber and produces a monolayer on the wafer surface. Then a second precursor gas (B Source) is introduced into the chamber, which reacts with the first precursor to produce a monolayer of film on the wafer surface. Separation of the pre ...
Catalytic reforming

Catalytic reforming is a chemical process used to convert petroleum refinery naphthas distilled from crude oil (typically having low octane ratings) into high-octane liquid products called reformates, which are premium blending stocks for high-octane gasoline. The process converts low-octane linear hydrocarbons (paraffins) into branched alkanes (isoparaffins) and cyclic naphthenes, which are then partially dehydrogenated to produce high-octane aromatic hydrocarbons. The dehydrogenation also produces significant amounts of byproduct hydrogen gas, which is fed into other refinery processes such as hydrocracking. A side reaction is hydrogenolysis, which produces light hydrocarbons of lower value, such as methane, ethane, propane and butanes.In addition to a gasoline blending stock, reformate is the main source of aromatic bulk chemicals such as benzene, toluene, xylene and ethylbenzene which have diverse uses, most importantly as raw materials for conversion into plastics. However, the benzene content of reformate makes it carcinogenic, which has led to governmental regulations effectively requiring further processing to reduce its benzene content.This process is quite different from and not to be confused with the catalytic steam reforming process used industrially to produce products such as hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol from natural gas, naphtha or other petroleum-derived feedstocks. Nor is this process to be confused with various other catalytic reforming processes that use methanol or biomass-derived feedstocks to produce hydrogen for fuel cells or other uses.