MAX4906EF High-/Full-Speed USB 2.0 Switches with High ESD General Description
... The MAX4906EF are electrostatic discharge (ESD)-protected analog switches that combine low on-capacitance (CON) and low on-resistance (RON) necessary for highperformance switching applications. The COM_ inputs are protected against ±15kV ESD without latchup or damage. The device is designed for USB ...
... The MAX4906EF are electrostatic discharge (ESD)-protected analog switches that combine low on-capacitance (CON) and low on-resistance (RON) necessary for highperformance switching applications. The COM_ inputs are protected against ±15kV ESD without latchup or damage. The device is designed for USB ...
AP7335A-50 N E W P R O D U C T 300mA, LOW QUIESCENT
... 4. Stresses greater than the 'Absolute Maximum Ratings' specified above, may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions exceeding those indicated in this specification is not implied. Device reliability may ...
... 4. Stresses greater than the 'Absolute Maximum Ratings' specified above, may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only; functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions exceeding those indicated in this specification is not implied. Device reliability may ...
MAX1817 Compact, High-Efficiency, Dual-Output Step-Up DC-DC Converter General Description
... amplifier senses the output voltage is below the feedback threshold, turning on the internal N-channel MOSFET and initiating an on-time. The on-time is terminated when the 0.75A current limit is reached or when the maximum on-time is reached. The N-channel MOSFET remains off until the inductor curre ...
... amplifier senses the output voltage is below the feedback threshold, turning on the internal N-channel MOSFET and initiating an on-time. The on-time is terminated when the 0.75A current limit is reached or when the maximum on-time is reached. The N-channel MOSFET remains off until the inductor curre ...
Analog and Mixed Signal Circuits On Digital CMOS Processes
... can be made about element geometry. Transistor models and simulation tools can have problems not seen in digital simulations. Simulator accuracy of charge conservation and linearity of transistor models are frequently sources of error. Examination of changes in transistor performance due to short ch ...
... can be made about element geometry. Transistor models and simulation tools can have problems not seen in digital simulations. Simulator accuracy of charge conservation and linearity of transistor models are frequently sources of error. Examination of changes in transistor performance due to short ch ...
LLC Half-Bridge Controller for Multi-String LED
... Connect a DC power voltage to VCC. Bypass VCC to GND with a 0.47-µF or larger ceramic capacitor using short PC-board traces. VCC directly supplies power to the gate drivers and VREF which biases all circuit blocks in the UCC25710. Undervoltage lockout (UVLO) comparator prevents operation until VCC r ...
... Connect a DC power voltage to VCC. Bypass VCC to GND with a 0.47-µF or larger ceramic capacitor using short PC-board traces. VCC directly supplies power to the gate drivers and VREF which biases all circuit blocks in the UCC25710. Undervoltage lockout (UVLO) comparator prevents operation until VCC r ...
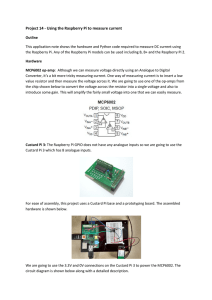
Project 14 - Using the Raspberry Pi to measure current
... Converter, it’s a bit more tricky measuring current. One way of measuring current is to insert a low value resistor and then measure the voltage across it. We are going to use one of the op-amps from the chip shown below to convert the voltage across the resistor into a single voltage and also to in ...
... Converter, it’s a bit more tricky measuring current. One way of measuring current is to insert a low value resistor and then measure the voltage across it. We are going to use one of the op-amps from the chip shown below to convert the voltage across the resistor into a single voltage and also to in ...
Lab #10: ADC
... 1. Marks will be instantly deducted from your lab if you fail to set the function generator or supply voltages properly. 2. Use the Experimenter’s board efficiently…the ADC circuit will be combined with the DAC lab to create an ADC-DAC lab. 3. Wiring neatness is important for this lab. All component ...
... 1. Marks will be instantly deducted from your lab if you fail to set the function generator or supply voltages properly. 2. Use the Experimenter’s board efficiently…the ADC circuit will be combined with the DAC lab to create an ADC-DAC lab. 3. Wiring neatness is important for this lab. All component ...
Diagnostic News On-Line Monitoring of Partial Discharge in Voltage Source January 2015
... power frequency AC cycle (a pulse phase analysis plot, sometimes known as a phase‐resolved PD plot—see Figure 2). In the past the TGA‐B was expecting either 50 Hz or 60 Hz power fre‐ quency. If the frequency was neither of these, then the instrument would not “synchronize”. ...
... power frequency AC cycle (a pulse phase analysis plot, sometimes known as a phase‐resolved PD plot—see Figure 2). In the past the TGA‐B was expecting either 50 Hz or 60 Hz power fre‐ quency. If the frequency was neither of these, then the instrument would not “synchronize”. ...
Series 935 Retrofit Guide
... Relay – refers to an electromechanical relay. Remote – set point is adjusted using a remote potentiometer. Panel – the form factor of this controller is mounted through a hole cut in the panel. PI – Proportional and Integral, a control algorithm mode with two functions: proportional action dampens t ...
... Relay – refers to an electromechanical relay. Remote – set point is adjusted using a remote potentiometer. Panel – the form factor of this controller is mounted through a hole cut in the panel. PI – Proportional and Integral, a control algorithm mode with two functions: proportional action dampens t ...
Series 965 Retrofit Guide
... Relay – refers to an electromechanical relay. Remote – set point is adjusted using a remote potentiometer. Panel – the form factor of this controller is mounted through a hole cut in the panel. PI – Proportional and Integral, a control algorithm mode with two functions: proportional action dampens t ...
... Relay – refers to an electromechanical relay. Remote – set point is adjusted using a remote potentiometer. Panel – the form factor of this controller is mounted through a hole cut in the panel. PI – Proportional and Integral, a control algorithm mode with two functions: proportional action dampens t ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.