Powerpoint Slides
... Notice how the slope of the tangent line is changing. (For smaller voltages the slope is higher therefore the resistance is lower) In this case the temperature of the bulb is increasing with increasing power. As the temperature increases the resistance also increases ...
... Notice how the slope of the tangent line is changing. (For smaller voltages the slope is higher therefore the resistance is lower) In this case the temperature of the bulb is increasing with increasing power. As the temperature increases the resistance also increases ...
ET 13
... that the e.m.f per cell is raised from 1.8 to 2.2V. Determine the maximum number of carbon lamps of a parallel bank, which may be switched on in series with the circuit, so that the current from the 200V mains does not exceed 10A at the commencement of charging. If the circuit remains unaltered, cal ...
... that the e.m.f per cell is raised from 1.8 to 2.2V. Determine the maximum number of carbon lamps of a parallel bank, which may be switched on in series with the circuit, so that the current from the 200V mains does not exceed 10A at the commencement of charging. If the circuit remains unaltered, cal ...
9 electricity test - circuits
... 5) Draw a typical circuit you would use to test the resistance of a resistor. Make sure you include a voltmeter and an ammeter. ...
... 5) Draw a typical circuit you would use to test the resistance of a resistor. Make sure you include a voltmeter and an ammeter. ...
Topic 5 Review Multiple Choice Questions E1. Which graph shows
... E10. The work done on a positive point charge of magnitude 3.0 nC as it is moved at constant speed from one point to another is 12 nJ. The potential difference between the two points is A. 0.0 V. E11. ...
... E10. The work done on a positive point charge of magnitude 3.0 nC as it is moved at constant speed from one point to another is 12 nJ. The potential difference between the two points is A. 0.0 V. E11. ...
Lecture 10 - UConn Physics
... • I have two identical light bulbs. First I hook them up in series. Then I hook them up in parallel. In which case are the bulbs brighter? (The resistors represent light bulbs whose brightness is proportional to P = I2R through the resistor.) ...
... • I have two identical light bulbs. First I hook them up in series. Then I hook them up in parallel. In which case are the bulbs brighter? (The resistors represent light bulbs whose brightness is proportional to P = I2R through the resistor.) ...
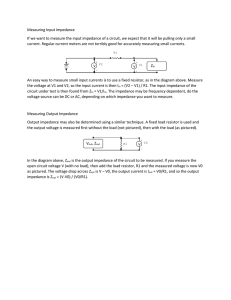
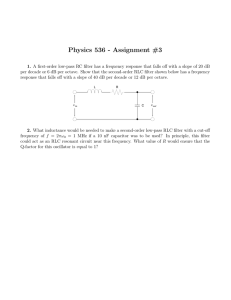
Measuring Input Impedance If we want to measure the input
... current. Regular current meters are not terribly good for accurately measuring small currents. R1 ...
... current. Regular current meters are not terribly good for accurately measuring small currents. R1 ...
Homework 4 - University of St. Thomas
... its safety. You know that under damp or sweaty conditions, the resistance between two points of unbroken skin on the human body can be as low as 500Ω. Your product uses a 72V battery whose internal resistance is 100Ω. Is it capable of passing a fatal 100mA through a damp human body? ...
... its safety. You know that under damp or sweaty conditions, the resistance between two points of unbroken skin on the human body can be as low as 500Ω. Your product uses a 72V battery whose internal resistance is 100Ω. Is it capable of passing a fatal 100mA through a damp human body? ...
What is Electronics?
... What is this Application? • To process signals (electrical current and voltage) to suit our needs What is this processing? Add, subtract, magnify, multiply, modify a known (or given) electrical signal to produce a desired outcome. ...
... What is this Application? • To process signals (electrical current and voltage) to suit our needs What is this processing? Add, subtract, magnify, multiply, modify a known (or given) electrical signal to produce a desired outcome. ...
Transistor Switch and Emitter Follower Phys 3610/6610 Lab 18 Student: TA:
... 1.) Apply the input and examine the output waveform using a scope. Document the phase shift. What is the output impedance when Vout = 5 V? 2.) Let us load this transistor switch with a 10 kΩ resistor to simulate the more realistic situation where your circuit drives some other input. How does the lo ...
... 1.) Apply the input and examine the output waveform using a scope. Document the phase shift. What is the output impedance when Vout = 5 V? 2.) Let us load this transistor switch with a 10 kΩ resistor to simulate the more realistic situation where your circuit drives some other input. How does the lo ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Portfolio
... Ohmmeter - an instrument for measuring electrical resistance. Ohm’s law - Electrical resistance is calculated by finding the ratio of the voltage across the load (V) to the current through the load (I). This is called Ohm’s Law. Resistor - a device having a designed resistance to the passage of an e ...
... Ohmmeter - an instrument for measuring electrical resistance. Ohm’s law - Electrical resistance is calculated by finding the ratio of the voltage across the load (V) to the current through the load (I). This is called Ohm’s Law. Resistor - a device having a designed resistance to the passage of an e ...
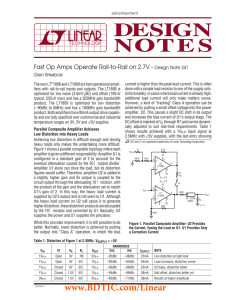
DN241 - Fast Op Amps Operate Rail-to-Rail on 2.7V
... reduce the effective bandwidth of the op amps. The tradeoff is that supply current increases, but the designer should remember that a 3VP-P signal requires ±30mA of peak current itself, so a 36mA supply current is modest considering the low distortion levels being achieved. This example was shown us ...
... reduce the effective bandwidth of the op amps. The tradeoff is that supply current increases, but the designer should remember that a 3VP-P signal requires ±30mA of peak current itself, so a 36mA supply current is modest considering the low distortion levels being achieved. This example was shown us ...
CN-0028 AD5547/AD5557 DAC的精密、双极性配置
... output DACs. Therefore, this circuit employs the AD8512 op amp, which has ultralow offset voltage (80 µV typical for B-grade device) and bias current (25 pA typical). C9 is a compensation capacitor. The value of C9 for this application is 2.2 pF, which is optimized to compensate for the external out ...
... output DACs. Therefore, this circuit employs the AD8512 op amp, which has ultralow offset voltage (80 µV typical for B-grade device) and bias current (25 pA typical). C9 is a compensation capacitor. The value of C9 for this application is 2.2 pF, which is optimized to compensate for the external out ...
3-Terminal Positive Regulators
... positive voltage regulators employ internal current-limiting, thermal shutdown and safe-area compensation, making them essentially indestructible. If adequate heat sinking is provided, they can deliver over 1.0A output current. They are intended as fixed voltage regulators in a wide range of applica ...
... positive voltage regulators employ internal current-limiting, thermal shutdown and safe-area compensation, making them essentially indestructible. If adequate heat sinking is provided, they can deliver over 1.0A output current. They are intended as fixed voltage regulators in a wide range of applica ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.