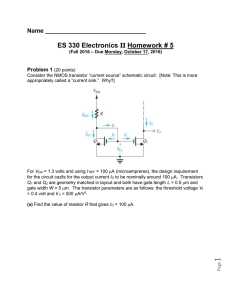
Solid State Relais
... Triac created by small spikes. To create the posibility to switch this circuit with different voltages, a FET BF256A has been added. This FET acts like a currentsource by means of connecting the source (s) with the gate (g). What this means is that this FET determines the current through the TIL111, ...
... Triac created by small spikes. To create the posibility to switch this circuit with different voltages, a FET BF256A has been added. This FET acts like a currentsource by means of connecting the source (s) with the gate (g). What this means is that this FET determines the current through the TIL111, ...
Component Selection
... Output Noise Voltage (40uV TYPICAL) Ripple Rejection (41dB MIN) Dropout Voltage (1.7V TYPICAL) ...
... Output Noise Voltage (40uV TYPICAL) Ripple Rejection (41dB MIN) Dropout Voltage (1.7V TYPICAL) ...
Electrical-and-Electronic-Principles-P1
... Using the triangle or the related formulae, finding the total current flowing through the circuit is easy enough. I = V/R ...
... Using the triangle or the related formulae, finding the total current flowing through the circuit is easy enough. I = V/R ...
Specification Status: Released 2Pro Device Series
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, users should independently evaluate the suitability of and test each product selected for their own applications. Tyco Electronics Corporation and its affiliates in the TE Connectivity Ltd. group of companies (“TE”) reserves the ...
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, users should independently evaluate the suitability of and test each product selected for their own applications. Tyco Electronics Corporation and its affiliates in the TE Connectivity Ltd. group of companies (“TE”) reserves the ...
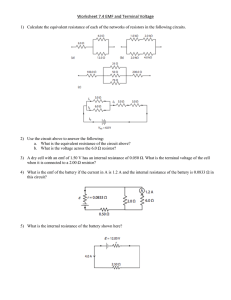
Parallel Circuits Test
... b. Violate Kirchhoff’s voltage law if they have different output voltages c. Cancel each other, producing a net voltage of zero. d. Are more economical than a single large voltage source. ...
... b. Violate Kirchhoff’s voltage law if they have different output voltages c. Cancel each other, producing a net voltage of zero. d. Are more economical than a single large voltage source. ...
+ 12 V
... a) the intensity of bulb A increases b) the intensity of bulb A decreases c) the intensity of bulb B increases d) the intensity of bulb B decreases e) nothing changes ...
... a) the intensity of bulb A increases b) the intensity of bulb A decreases c) the intensity of bulb B increases d) the intensity of bulb B decreases e) nothing changes ...
USC Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical Engineering
... 6. A student connects the two leads from a “meter” to two separate nodes. This is: (a) unacceptable for an ammeter because it has large Thevenin resistance (b) unacceptable for an ammeter because it has small Thevenin resistance (c) unacceptable for a voltmeter because it has large Thevenin resistan ...
... 6. A student connects the two leads from a “meter” to two separate nodes. This is: (a) unacceptable for an ammeter because it has large Thevenin resistance (b) unacceptable for an ammeter because it has small Thevenin resistance (c) unacceptable for a voltmeter because it has large Thevenin resistan ...
Ground-Reference Popless Stereo Headphone Driver
... The G1412 stereo headphone driver is designed for portable equipment where board space is limited. The G1412 uses the dual external power supplies PVDD/NVDD to produce a ground-reference output, eliminating the need for large DC-blocking capacitors, saving cost, board space, and component height. Th ...
... The G1412 stereo headphone driver is designed for portable equipment where board space is limited. The G1412 uses the dual external power supplies PVDD/NVDD to produce a ground-reference output, eliminating the need for large DC-blocking capacitors, saving cost, board space, and component height. Th ...
Power Quality Terminology
... Harmonic resonance. A condition in which the power system is resonating near one of the major harmonics being harmonics being produced by nonlinear elements in the system, thus exacerbating the harmonic distortion. Impulse transient. A sudden nonpower frequency change in the steady-state condition ...
... Harmonic resonance. A condition in which the power system is resonating near one of the major harmonics being harmonics being produced by nonlinear elements in the system, thus exacerbating the harmonic distortion. Impulse transient. A sudden nonpower frequency change in the steady-state condition ...
ac-circuits-test-16
... 2. Consider an LCR series circuit connected to an ac source of variable frequency but with a constant rms voltage. Draw the frequency response curve for the circuit. Indicate in the graph frequency ranges where the circuit is (a) inductive and (b) capacitive. (2) ...
... 2. Consider an LCR series circuit connected to an ac source of variable frequency but with a constant rms voltage. Draw the frequency response curve for the circuit. Indicate in the graph frequency ranges where the circuit is (a) inductive and (b) capacitive. (2) ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.