Question Bank - Saraswathi Velu College of Engineering
... 13. Justify the reasons for using current sources in integrated circuits. 14. What is the advantage of widlar current source over constant current source? 15. Mention the advantages of Wilson current source. 16. Define sensitivity. 17. What are the limitations in a temperature compensated zener-refe ...
... 13. Justify the reasons for using current sources in integrated circuits. 14. What is the advantage of widlar current source over constant current source? 15. Mention the advantages of Wilson current source. 16. Define sensitivity. 17. What are the limitations in a temperature compensated zener-refe ...
Electric Circuits: Batteries and Resistors
... difference in energy density across a resistor or other electrical device is called voltage drop. In electric circuits (closed loops of wire with resistors and voltage sources) energy must be conserved. It follows that changes in energy density, the algebraic sum of voltage drops and voltage sources ...
... difference in energy density across a resistor or other electrical device is called voltage drop. In electric circuits (closed loops of wire with resistors and voltage sources) energy must be conserved. It follows that changes in energy density, the algebraic sum of voltage drops and voltage sources ...
Datasheet - Littelfuse
... DC Power Dissipation (Note 3) @ TA = 25°C Derate Above 25°C Thermal Resistance from Junction to Ambient ...
... DC Power Dissipation (Note 3) @ TA = 25°C Derate Above 25°C Thermal Resistance from Junction to Ambient ...
- Saraswathi Velu College of Engineering
... 13. Justify the reasons for using current sources in integrated circuits. 14. What is the advantage of widlar current source over constant current source? 15. Mention the advantages of Wilson current source. 16. Define sensitivity. 17. What are the limitations in a temperature compensated zener-refe ...
... 13. Justify the reasons for using current sources in integrated circuits. 14. What is the advantage of widlar current source over constant current source? 15. Mention the advantages of Wilson current source. 16. Define sensitivity. 17. What are the limitations in a temperature compensated zener-refe ...
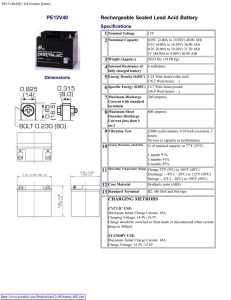
PE12V40 Rechargeable Sealed Lead Acid Battery
... Maximum Initial Charge Current: 10A Charging Voltage: 14.4V-14.7V Charge should be switched to float mode or disconnected when current drops to 400mA. STANDBY USE: Maximum Initial Charge Current: 10A Charge Voltage: 13.5V-13.8V ...
... Maximum Initial Charge Current: 10A Charging Voltage: 14.4V-14.7V Charge should be switched to float mode or disconnected when current drops to 400mA. STANDBY USE: Maximum Initial Charge Current: 10A Charge Voltage: 13.5V-13.8V ...
C 10:4X - Full Compass
... By offering an unmatched combination of channel density, operating efficiency and configuration flexibility, the C 10:4X presents convincing performance and cost-saving advantages. Applications include primary systems for theme parks, shopping malls, airports, hotels and restaurants as well as auxil ...
... By offering an unmatched combination of channel density, operating efficiency and configuration flexibility, the C 10:4X presents convincing performance and cost-saving advantages. Applications include primary systems for theme parks, shopping malls, airports, hotels and restaurants as well as auxil ...
NE5550234-EV04-A
... improve the stability margin. The gain is reduced by about 1-2dB when R3 is used. LDMOSFETs essentially draw no gate current under normal operation conditions. Therefore a large value resistor, in the order of kΩ, can be used for the bias at gate so that the RF path is completely isolated from the D ...
... improve the stability margin. The gain is reduced by about 1-2dB when R3 is used. LDMOSFETs essentially draw no gate current under normal operation conditions. Therefore a large value resistor, in the order of kΩ, can be used for the bias at gate so that the RF path is completely isolated from the D ...
phonic paa3 - Cascade Audio Engineering
... for boosting and cutting at the touch of a button • USB interface allows real-time computer operation • Seven hours of continuous operation with four AA batteries 31-band Real Time Spectrum Analyzer allows Db analysis of offending frequencies 31-band EQ setting value display (Boost/Cut) T60 measurem ...
... for boosting and cutting at the touch of a button • USB interface allows real-time computer operation • Seven hours of continuous operation with four AA batteries 31-band Real Time Spectrum Analyzer allows Db analysis of offending frequencies 31-band EQ setting value display (Boost/Cut) T60 measurem ...
Electric Circuits
... AC = Alternating Current- current reverses direction many times per second. This suggests that AC devices turn OFF and ON. Example: Wall outlet (progress energy) ...
... AC = Alternating Current- current reverses direction many times per second. This suggests that AC devices turn OFF and ON. Example: Wall outlet (progress energy) ...
Pure water is non-conducting Gas discharges Current– flow of
... current Æ you must check that whatever is plugged into it will not draw more current than the cord can handle safely. • power strips are also rated for maximum current Æ since they have multiple imputs you must check that the total current drawn by everything on it does not exceed the current rating ...
... current Æ you must check that whatever is plugged into it will not draw more current than the cord can handle safely. • power strips are also rated for maximum current Æ since they have multiple imputs you must check that the total current drawn by everything on it does not exceed the current rating ...
Experiment 4: Damped Oscillations and Resonance in RLC Circuits
... For the circuit with the R, L, and C values given in Figure 1, resonance will occur at a frequency around 15000 Hz, and the resonance amplitude should be about three-times the input amplitude. Vary the frequency from about 100 Hz to 25000 Hz in steps that will allow you to plot a smooth graph of res ...
... For the circuit with the R, L, and C values given in Figure 1, resonance will occur at a frequency around 15000 Hz, and the resonance amplitude should be about three-times the input amplitude. Vary the frequency from about 100 Hz to 25000 Hz in steps that will allow you to plot a smooth graph of res ...
SF6 CB
... * Separation of contacts causes the release of metal vapour from the contacts, the density of vapour depends on the fault current. * At current zero the vapour emission will tends to zero and the density will becomes zero and dielectric strength will build up and restriking will be prevented. * No e ...
... * Separation of contacts causes the release of metal vapour from the contacts, the density of vapour depends on the fault current. * At current zero the vapour emission will tends to zero and the density will becomes zero and dielectric strength will build up and restriking will be prevented. * No e ...
Kirchhoff`s Laws - Edvantage Science
... Using Ohm’s Law I = V/R, and knowing that the potential difference is the same in a parallel circuit the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit can be determined by: ...
... Using Ohm’s Law I = V/R, and knowing that the potential difference is the same in a parallel circuit the equivalent resistance in a parallel circuit can be determined by: ...
Electromotive Force and Potential difference
... This can be rearranged to give V = W/Q, which in physical terms means that the potential difference between two points can be defined as the work done as the charge goes from one point to the other divided by the charge itself. Don’t be too surprised if you find this stuff confusing. Not only is it ...
... This can be rearranged to give V = W/Q, which in physical terms means that the potential difference between two points can be defined as the work done as the charge goes from one point to the other divided by the charge itself. Don’t be too surprised if you find this stuff confusing. Not only is it ...
No Slide Title
... LEARNING EXAMPLE The MOSFET is used to switch 10A of current. The voltage drop across the FET in the on state must be less than 4% of the supply voltage. Find the maximum value of R_on ...
... LEARNING EXAMPLE The MOSFET is used to switch 10A of current. The voltage drop across the FET in the on state must be less than 4% of the supply voltage. Find the maximum value of R_on ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.