Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)
... terminals are labeled D for Drain, G for Gate and S for Source. These can be loosely compared to the collector, base and emitter of an NPN transistor. The N-channel JFET is constructed by embedding a small piece of P-Type silicon (the Gate) into a block of N-Type silicon. One end of the N-Type block ...
... terminals are labeled D for Drain, G for Gate and S for Source. These can be loosely compared to the collector, base and emitter of an NPN transistor. The N-channel JFET is constructed by embedding a small piece of P-Type silicon (the Gate) into a block of N-Type silicon. One end of the N-Type block ...
liquid-crystal display
... a. When sufficient voltage is applied to the chip across the leads of the LED, electrons can move easily in only one direction across the junction between the p and n regions. When a voltage is applied and the current starts to flow, electrons in the n region have sufficient energy to move across ...
... a. When sufficient voltage is applied to the chip across the leads of the LED, electrons can move easily in only one direction across the junction between the p and n regions. When a voltage is applied and the current starts to flow, electrons in the n region have sufficient energy to move across ...
Applications in the Industrial Market
... AD8137: Low Power, Low Cost 10-12 Bit ADC Driver Key Features ...
... AD8137: Low Power, Low Cost 10-12 Bit ADC Driver Key Features ...
Direct Current (DC) Electric Circuits
... combining resistances in series into a single equivalent resistor Req. The equivalent resistance is the single resistance that could be used in the circuit to replace the three separate resistances. Req = R1 + R2 + R3 If R1 = 2 , R2 = 4 , and R3 = 8 , the equivalent resistance Req = 2 + ...
... combining resistances in series into a single equivalent resistor Req. The equivalent resistance is the single resistance that could be used in the circuit to replace the three separate resistances. Req = R1 + R2 + R3 If R1 = 2 , R2 = 4 , and R3 = 8 , the equivalent resistance Req = 2 + ...
STLVDS31B
... switching speeds and allows operations with a 3.3 V supply rail. Any of the four current mode drivers will deliver a minimum differential output voltage magnitude of 247 mV into a 100 Ω load when enabled. The intended application of this device and signalling technique is for point-to-point baseband ...
... switching speeds and allows operations with a 3.3 V supply rail. Any of the four current mode drivers will deliver a minimum differential output voltage magnitude of 247 mV into a 100 Ω load when enabled. The intended application of this device and signalling technique is for point-to-point baseband ...
Physics 1 Lab: Ohm`s Law
... interrupted to measure voltage. Simply touch the voltmeter probes across the circuit element whose voltage is to be measured. · Many meters have more than one input connection to allow the meter to be used over a wide range of values. The correct input must be used so that the current or voltage ...
... interrupted to measure voltage. Simply touch the voltmeter probes across the circuit element whose voltage is to be measured. · Many meters have more than one input connection to allow the meter to be used over a wide range of values. The correct input must be used so that the current or voltage ...
Coaxial Cable Protection
... For Quarter wave coaxial stubs, from 2GHz down, the inductance of the stub will still allow considerable voltage to be presented to the equipment input (+ 9Vpk, - 4Vpk ringing for the entire test pulse waveform) measured for a 900MHz 1/4 wave stub with a 3kA 8/20s test waveform and the stub output ...
... For Quarter wave coaxial stubs, from 2GHz down, the inductance of the stub will still allow considerable voltage to be presented to the equipment input (+ 9Vpk, - 4Vpk ringing for the entire test pulse waveform) measured for a 900MHz 1/4 wave stub with a 3kA 8/20s test waveform and the stub output ...
LED lighting presentation
... • COB Stands for Chip On Board, these compact high flux density light sources deliver uniform high quality illumination without pixilation or the multiple shadow effect caused by LED component based solutions, enabling both diffused and directional lamp replacements for a wide range of applications. ...
... • COB Stands for Chip On Board, these compact high flux density light sources deliver uniform high quality illumination without pixilation or the multiple shadow effect caused by LED component based solutions, enabling both diffused and directional lamp replacements for a wide range of applications. ...
– Simple turn-off description of Trench- Field-stop IGBT IGBT
... resistors ranging from 1 to 30 Ohm, the dV/dt of the collector voltage is constant. The dV/dt is intrinsically limited. The reason is the stored charge controlling the voltage rise. For gate resistors of more than 30 Ohm the dV/dt becomes reduced at controlled by the gatedrive condition, i.e. RG. Th ...
... resistors ranging from 1 to 30 Ohm, the dV/dt of the collector voltage is constant. The dV/dt is intrinsically limited. The reason is the stored charge controlling the voltage rise. For gate resistors of more than 30 Ohm the dV/dt becomes reduced at controlled by the gatedrive condition, i.e. RG. Th ...
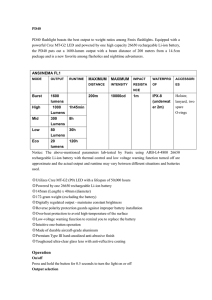
Fenix PD40 User Manual
... ◎Please don't disassemble the sealed head, doing so can cause damage to the flashlight and will void the warranty. ◎We recommend the use of high quality battery. If the flashlight is not to be used for an extended period, remove the battery, or the flashlight could be damaged by electrolyte leakage ...
... ◎Please don't disassemble the sealed head, doing so can cause damage to the flashlight and will void the warranty. ◎We recommend the use of high quality battery. If the flashlight is not to be used for an extended period, remove the battery, or the flashlight could be damaged by electrolyte leakage ...
Simple and Series Circuits
... b. The bulb between X and Y will be the brightest. c. The bulb between Y and Z will be the brightest. d. The bulb between Z and the battery will be the brightest. 6. Three small bulbs are connected in series. Their resistances are: 3.0, 6.0, and 9.0. They are placed in a circuit with a 12-volt ...
... b. The bulb between X and Y will be the brightest. c. The bulb between Y and Z will be the brightest. d. The bulb between Z and the battery will be the brightest. 6. Three small bulbs are connected in series. Their resistances are: 3.0, 6.0, and 9.0. They are placed in a circuit with a 12-volt ...
AK8111 - Asahi Kasei Microdevices
... (1) Stress beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only. Functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “Recommended Operating Conditions” is not implied. Exposure to abs ...
... (1) Stress beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only. Functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “Recommended Operating Conditions” is not implied. Exposure to abs ...
Resistive opto-isolator
Resistive opto-isolator (RO), also called photoresistive opto-isolator, vactrol (after a genericized trademark introduced by Vactec, Inc. in the 1960s), analog opto-isolator or lamp-coupled photocell, is an optoelectronic device consisting of a source and detector of light, which are optically coupled and electrically isolated from each other. The light source is usually a light-emitting diode (LED), a miniature incandescent lamp, or sometimes a neon lamp, whereas the detector is a semiconductor-based photoresistor made of cadmium selenide (CdSe) or cadmium sulfide (CdS). The source and detector are coupled through a transparent glue or through the air.Electrically, RO is a resistance controlled by the current flowing through the light source. In the dark state, the resistance typically exceeds a few MOhm; when illuminated, it decreases as the inverse of the light intensity. In contrast to the photodiode and phototransistor, the photoresistor can operate in both the AC and DC circuits and have a voltage of several hundred volts across it. The harmonic distortions of the output current by the RO are typically within 0.1% at voltages below 0.5 V.RO is the first and the slowest opto-isolator: its switching time exceeds 1 ms, and for the lamp-based models can reach hundreds of milliseconds. Parasitic capacitance limits the frequency range of the photoresistor by ultrasonic frequencies. Cadmium-based photoresistors exhibit a ""memory effect"": their resistance depends on the illumination history; it also drifts during the illumination and stabilizes within hours, or even weeks for high-sensitivity models. Heating induces irreversible degradation of ROs, whereas cooling to below −25 °C dramatically increases the response time. Therefore, ROs were mostly replaced in the 1970s by the faster and more stable photodiodes and photoresistors. ROs are still used in some sound equipment, guitar amplifiers and analog synthesizers owing to their good electrical isolation, low signal distortion and ease of circuit design.