PowerPoint Presentation - Viking Age Information for Primary
... them together and defines their shape. All true cells have a nucleus, that holds the main information. ...
... them together and defines their shape. All true cells have a nucleus, that holds the main information. ...
Bio Lab Rebop Genetics
... a. Which of Mendel’s laws is demonstrated in this step? b. In the real world, what is this process, which reduces the chromosome number in half, called? c. What type of cells result from this process? d. How many chromosomes are in each cell resulting from this process (in Rebops)? e. Are these game ...
... a. Which of Mendel’s laws is demonstrated in this step? b. In the real world, what is this process, which reduces the chromosome number in half, called? c. What type of cells result from this process? d. How many chromosomes are in each cell resulting from this process (in Rebops)? e. Are these game ...
Protists
... Basic sexual division - meiosis 0. chromosomes make copies of selves – stay connected 1. Chromosomes line up in pairs = diploid ...
... Basic sexual division - meiosis 0. chromosomes make copies of selves – stay connected 1. Chromosomes line up in pairs = diploid ...
Document
... proteins. • In many animals, sex is determined by a special pair of chromosomes, the X and Y. • Irregularities in the inheritance of an X-linked gene in Drosophila gave experimental proof of the chromosomal theory of heredity. ...
... proteins. • In many animals, sex is determined by a special pair of chromosomes, the X and Y. • Irregularities in the inheritance of an X-linked gene in Drosophila gave experimental proof of the chromosomal theory of heredity. ...
B5 5 a day - Science Revision
... DNA is made up of four different bases, A T, C and G. In a DNA sample, 23% of the bases are T. Calculate the percentage of bases that are G. Show your working!! ...
... DNA is made up of four different bases, A T, C and G. In a DNA sample, 23% of the bases are T. Calculate the percentage of bases that are G. Show your working!! ...
DNA Connection
... Line up of Genes • 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes in the human body. • Chromosomes are made of many genes joined together like beads on a string. ...
... Line up of Genes • 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes in the human body. • Chromosomes are made of many genes joined together like beads on a string. ...
Chromosomes and Karyotyping Instructions
... This week, you will gain experience in constructing and interpreting karyotypes. Unlike “old-fashioned” karyotypes that were generated from black-and-white photos, these karyotypes were prepared using a technique called FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization). In FISH, fluorescently-labeled DNA mo ...
... This week, you will gain experience in constructing and interpreting karyotypes. Unlike “old-fashioned” karyotypes that were generated from black-and-white photos, these karyotypes were prepared using a technique called FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization). In FISH, fluorescently-labeled DNA mo ...
Chapter-13-Mutations-and-Chromosomal-Abnormalities
... bring about only a minor change (ie one different amino acid); sometimes the organism is affected only slightly or not at all • FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS – insertion , deletion; leads to a large portion of the gene’s DNA to be misread; the protein produced differs from the normal protein by many amino ac ...
... bring about only a minor change (ie one different amino acid); sometimes the organism is affected only slightly or not at all • FRAMESHIFT MUTATIONS – insertion , deletion; leads to a large portion of the gene’s DNA to be misread; the protein produced differs from the normal protein by many amino ac ...
1- State what is meant by “species”
... Down’s Syndrome is a condition caused by one pair of chromosome which fails to separate during gamete formation. As the result, after fertilisation, the zygote has 3 copies of chromosomes 21. In bacteria: digest oil → used to clean oil spills. In a plant: agricultural wheat has more chromosomes than ...
... Down’s Syndrome is a condition caused by one pair of chromosome which fails to separate during gamete formation. As the result, after fertilisation, the zygote has 3 copies of chromosomes 21. In bacteria: digest oil → used to clean oil spills. In a plant: agricultural wheat has more chromosomes than ...
Chapter 13 Meiosisand Sexual Life Cycles
... 13) Which of these statements is false? A) In humans, each of the 22 maternal autosomes has a homologous paternal chromosome. B) In humans, the 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, determines whether the person is female (XX) or male (XY). C) Single, haploid (n) sets of chromosomes in ovum and sperm unit ...
... 13) Which of these statements is false? A) In humans, each of the 22 maternal autosomes has a homologous paternal chromosome. B) In humans, the 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, determines whether the person is female (XX) or male (XY). C) Single, haploid (n) sets of chromosomes in ovum and sperm unit ...
What do these 3 people have in common?
... How is this related to biology? In order to get XYY syndrome, some biological error must have happened that caused the individual to end up with an extra Y chromosome – What do you think may have happened to cause this error? – What process do you think was involved? ...
... How is this related to biology? In order to get XYY syndrome, some biological error must have happened that caused the individual to end up with an extra Y chromosome – What do you think may have happened to cause this error? – What process do you think was involved? ...
170-175
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
File
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
11.4 Meiosis
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
Mitosis – Pipe Cleaner Activity
... yarn. Place 4 pipe cleaners (2 of each color) in the center circle. This represents a cell with 4 uncopied chromosomes in Interphase – S Stage. Draw a picture of this cell on your Activity Report. Draw a nuclear membrane around these chromosomes to show the nucleus. Step 2: Group 2 pipe cleaners ...
... yarn. Place 4 pipe cleaners (2 of each color) in the center circle. This represents a cell with 4 uncopied chromosomes in Interphase – S Stage. Draw a picture of this cell on your Activity Report. Draw a nuclear membrane around these chromosomes to show the nucleus. Step 2: Group 2 pipe cleaners ...
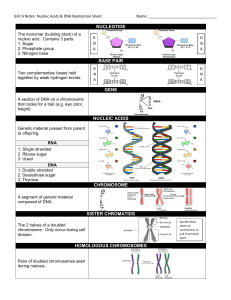
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
... A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
Introducing:
... •He suggested that the ‘factors’ (soon to be known as genes) that Mendel used to describe how character traits were inherited, were actually carried on chromosomes. •Although Sutton worked with grasshoppers, was not famous for any single experiment, but instead he brought together the research of ma ...
... •He suggested that the ‘factors’ (soon to be known as genes) that Mendel used to describe how character traits were inherited, were actually carried on chromosomes. •Although Sutton worked with grasshoppers, was not famous for any single experiment, but instead he brought together the research of ma ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... genes) which is half of amount that a normal body cell for that type of individual. 33. ___________________________ ...
... genes) which is half of amount that a normal body cell for that type of individual. 33. ___________________________ ...
2 Sex chromosomes
... b. Since disease strikes later in life, person can have children before disease appears. Allele is passed on even though disease is fatal ...
... b. Since disease strikes later in life, person can have children before disease appears. Allele is passed on even though disease is fatal ...
Section 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype Relate dominant
... phenotype. Much of what has been learned about human genes comes from studies of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because ...
... phenotype. Much of what has been learned about human genes comes from studies of genetic disorders. Many genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles on autosomes. People who have one dominant allele and one recessive, disorder-causing allele do not have the disorder, but can pass it on because ...
LAB- DETECTION GENETIC DISORDERS BY KARYOTYPE
... chromosomes, which specify gender (XX for female and XY for male). The pairs of autosomes are called "homologous chromosomes." One of each pair came from mom and the other came from dad. Homologous chromosomes have all of the same genes arranged in the same order, but with slight differences in the ...
... chromosomes, which specify gender (XX for female and XY for male). The pairs of autosomes are called "homologous chromosomes." One of each pair came from mom and the other came from dad. Homologous chromosomes have all of the same genes arranged in the same order, but with slight differences in the ...
Second Report: Involuntary or coerced sterilisation of intersex
... Intra-abdominal refers to the area of the body in which the ovaries and uterus are found. In some intersex conditions, the position of the testes is intra-abdominal rather than scrotal. Karyotype A karyotype refers to the number and structure of chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell; that is, the com ...
... Intra-abdominal refers to the area of the body in which the ovaries and uterus are found. In some intersex conditions, the position of the testes is intra-abdominal rather than scrotal. Karyotype A karyotype refers to the number and structure of chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell; that is, the com ...
Genetics - FAQ`s - El Camino College
... A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which occur in 23 pairs. WHAT IS A GENE? Even scientists disagree on how to define a gene. Generally, a gene is defin ...
... A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which occur in 23 pairs. WHAT IS A GENE? Even scientists disagree on how to define a gene. Generally, a gene is defin ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.