Name
... their X chromosome. o X-linked traits most likely will be _______________to the normal condition and the Y chromosome lacks the gene for a trait, so males have a higher chance of having the disorder. These traits generally do NOT show up in ______________ since females have genes on both their X c ...
... their X chromosome. o X-linked traits most likely will be _______________to the normal condition and the Y chromosome lacks the gene for a trait, so males have a higher chance of having the disorder. These traits generally do NOT show up in ______________ since females have genes on both their X c ...
Chapter 15 - ElderWiki
... •Surprisingly, the white-eyed trait appeared only in males. •All the females and half the males had red eyes. •Morgan concluded that a fly’s eye color was linked to its sex. •Morgan deduced that the gene with the white-eyed mutation is on the X chromosome alone, a sexlinked gene. •Females (XX) may h ...
... •Surprisingly, the white-eyed trait appeared only in males. •All the females and half the males had red eyes. •Morgan concluded that a fly’s eye color was linked to its sex. •Morgan deduced that the gene with the white-eyed mutation is on the X chromosome alone, a sexlinked gene. •Females (XX) may h ...
Leukaemia Section t(11;17)(p15;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2009 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
... This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2009 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
Unit 3 Post Test Heredity and Genetics
... cells in the reproduction of the bacteria and the fish shown in the chart. Part C Explain one advantage for the type of reproduction used by bacteria. Part D Compare the genes in the fist offspring with the genes in both parent fish. ...
... cells in the reproduction of the bacteria and the fish shown in the chart. Part C Explain one advantage for the type of reproduction used by bacteria. Part D Compare the genes in the fist offspring with the genes in both parent fish. ...
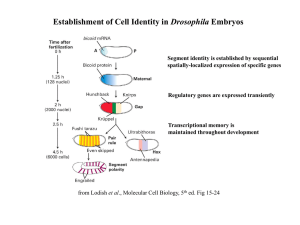
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Prions template conformational conversion of other molecules of the same protein ...
... Prions template conformational conversion of other molecules of the same protein ...
Leukaemia Section t(14;19)(q32;q13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... A: where the survival is not reduced compared to age matched population, to staging C: with a median survival of 2 years. t(14;19) is often associated with rapidly progressive disease, and overall prognosis is poor compared to the expected survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and low-grade B-cel ...
... A: where the survival is not reduced compared to age matched population, to staging C: with a median survival of 2 years. t(14;19) is often associated with rapidly progressive disease, and overall prognosis is poor compared to the expected survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and low-grade B-cel ...
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea - Biology E
... 2. Which two domains include prokaryotes? Prokaryotes are found in the domains Archaea and Bacteria. 3. What are prokaryotes? ! Most prokaryotes are unicellular. Prokaryotic cells typically have diameters of 0.5–5 µm, much smaller than the 10–100 µm diameter of many eukaryotic cells. The three most ...
... 2. Which two domains include prokaryotes? Prokaryotes are found in the domains Archaea and Bacteria. 3. What are prokaryotes? ! Most prokaryotes are unicellular. Prokaryotic cells typically have diameters of 0.5–5 µm, much smaller than the 10–100 µm diameter of many eukaryotic cells. The three most ...
Final Worksheet
... 2) Chromosomes are lined up in the middle of the cell. 3) Sister chromatids separate. 4) Chromosomes continue to condense, centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell. 5) Nuclear membranes reform completely around the chromosomes. 6) Sister chromatids form. 7) Cleavage furrow or the cell wall for ...
... 2) Chromosomes are lined up in the middle of the cell. 3) Sister chromatids separate. 4) Chromosomes continue to condense, centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell. 5) Nuclear membranes reform completely around the chromosomes. 6) Sister chromatids form. 7) Cleavage furrow or the cell wall for ...
Patterns of Heredity
... their X chromosome. o X-linked traits most likely will be _______________to the normal condition and the Y chromosome lacks the gene for a trait, so males have a higher chance of having the disorder. • These traits generally do NOT show up in ______________ since females have genes on both their X c ...
... their X chromosome. o X-linked traits most likely will be _______________to the normal condition and the Y chromosome lacks the gene for a trait, so males have a higher chance of having the disorder. • These traits generally do NOT show up in ______________ since females have genes on both their X c ...
My Biology SOL Review Packet - 2014 2015
... Fill in the blanks below with the correct mitosis vocabulary terms. Some terms will be used more than once. Vocabulary: nucleus, replicated, interphase (S phase), prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase,cytokinesis, centromere, sister chromatids, chromatin, centrioles, spindle fibers, cell plate, c ...
... Fill in the blanks below with the correct mitosis vocabulary terms. Some terms will be used more than once. Vocabulary: nucleus, replicated, interphase (S phase), prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase,cytokinesis, centromere, sister chromatids, chromatin, centrioles, spindle fibers, cell plate, c ...
Chapter 24: Genes and Chromosomes
... Page: 952 Difficulty: 2 What are introns? Ans: Introns are regions of genes (primarily eukaryotic) that in mRNA are transcribed but are not translated. They do not code for amino acid sequences within the protein that is coded by the gene. Thus they interrupt the colinearity between the nucleotide s ...
... Page: 952 Difficulty: 2 What are introns? Ans: Introns are regions of genes (primarily eukaryotic) that in mRNA are transcribed but are not translated. They do not code for amino acid sequences within the protein that is coded by the gene. Thus they interrupt the colinearity between the nucleotide s ...
Past History of the Retson Family based on DNA evidence Written
... together, form a complement of 23 individual chromosomes (haploid) in the resultant sperm or the egg and represent a random mix of the ancestral paternal and maternal genetic information. Fertilization of the egg by the sperm restores the full compliment. In a further mixing of information, a segmen ...
... together, form a complement of 23 individual chromosomes (haploid) in the resultant sperm or the egg and represent a random mix of the ancestral paternal and maternal genetic information. Fertilization of the egg by the sperm restores the full compliment. In a further mixing of information, a segmen ...
Gene Mutations - WordPress.com
... father. • Each organism also has a pair of sex chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. ...
... father. • Each organism also has a pair of sex chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. ...
View/Open - Gadarif University Repository
... single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. • In eukaryotes, nuclear chromosomes are packaged by proteins into a condensed structure called chromatin. This allows the very long DNA molecules to fit into the cell nucleus. ...
... single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. • In eukaryotes, nuclear chromosomes are packaged by proteins into a condensed structure called chromatin. This allows the very long DNA molecules to fit into the cell nucleus. ...
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
... Cells that have only one of each homologous pair are said to be haploid, a condition that is represented by n. Cells that have two of each homologous pair are said to be diploid or 2n. For each of the following, is the cell haploid or diploid? ...
... Cells that have only one of each homologous pair are said to be haploid, a condition that is represented by n. Cells that have two of each homologous pair are said to be diploid or 2n. For each of the following, is the cell haploid or diploid? ...
Biology 3 Study Guide
... NATURAL SELECTION – What is the biological meaning of “evolution”? Can an individual evolve? How is natural selection different from evolution? What are the four basic tenets of natural selection? What is directional selection and what impact does it have on a population? What is stabilizing select ...
... NATURAL SELECTION – What is the biological meaning of “evolution”? Can an individual evolve? How is natural selection different from evolution? What are the four basic tenets of natural selection? What is directional selection and what impact does it have on a population? What is stabilizing select ...
Genetics, II
... • If female is heterozygous for a gene located on the X chromosome, she is a mosaic Two cell populations in adult cat: Active X Early embryo: X chromosomes ...
... • If female is heterozygous for a gene located on the X chromosome, she is a mosaic Two cell populations in adult cat: Active X Early embryo: X chromosomes ...
PPT Version - OMICS International
... one population are selected according to their fitness, and form new solutions (offspring) by using genetic operators (crossover, mutation). This is motivated by a hope, that the new population will be better than the old one. • This is repeated until some condition (for example number of generation ...
... one population are selected according to their fitness, and form new solutions (offspring) by using genetic operators (crossover, mutation). This is motivated by a hope, that the new population will be better than the old one. • This is repeated until some condition (for example number of generation ...
level one science: biology
... I can show that I understand the role of DNA by explaining that it contains the instructions for how an organism looks and lives and how it enables instructions to be passed on to the next generation. I can use the term double helix to describe the shape of DNA. I know the four letters used for the ...
... I can show that I understand the role of DNA by explaining that it contains the instructions for how an organism looks and lives and how it enables instructions to be passed on to the next generation. I can use the term double helix to describe the shape of DNA. I know the four letters used for the ...
lesson plan - Achievement First
... 3. Identify the whether the process relates to asexual or sexual reproduction: ________ A diploid prokaryote divides to produce two new diploid cells ________ Dead skin cells are replaced by new identical cells ________ Sperm and egg cells fuse ________ An amoeba, a eukaryotic single-celled organism ...
... 3. Identify the whether the process relates to asexual or sexual reproduction: ________ A diploid prokaryote divides to produce two new diploid cells ________ Dead skin cells are replaced by new identical cells ________ Sperm and egg cells fuse ________ An amoeba, a eukaryotic single-celled organism ...
Chapter 11
... Information • Genetic information in DNA molecule resides in sequence of nucleotides. • Gene - Segment of DNA that directs protein ...
... Information • Genetic information in DNA molecule resides in sequence of nucleotides. • Gene - Segment of DNA that directs protein ...
Chromosome
A chromosome (chromo- + -some) is a packaged and organized structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. It is not usually found on its own, but rather is complexed with many structural proteins called histones as well as associated transcription (copying of genetic sequences) factors and several other macromolecules. Two ""sister"" chromatids (half a chromosome) join together at a protein junction called a centromere. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only when the cell is undergoing mitosis. Even then, the full chromosome containing both joined sister chromatids becomes visible only during a sequence of mitosis known as metaphase (when chromosomes align together, attached to the mitotic spindle and prepare to divide). This DNA and its associated proteins and macromolecules is collectively known as chromatin, which is further packaged along with its associated molecules into a discrete structure called a nucleosome. Chromatin is present in most cells, with a few exceptions - erythrocytes for example. Occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, chromatin composes the vast majority of all DNA, except for a small amount inherited maternally which is found in mitochondria. In prokaryotic cells, chromatin occurs free-floating in cytoplasm, as these cells lack organelles and a defined nucleus. The main information-carrying macromolecule is a single piece of coiled double-stranded DNA, containing many genes, regulatory elements and other noncoding DNA. The DNA-bound macromolecules are proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions. Chromosomes vary widely between different organisms. Some species such as certain bacteria also contain plasmids or other extrachromosomal DNA. These are circular structures in the cytoplasm which contain cellular DNA and play a role in horizontal gene transfer.Compaction of the duplicated chromosomes during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) results either in a four-arm structure (pictured to the right) if the centromere is located in the middle of the chromosome or a two-arm structure if the centromere is located near one of the ends. Chromosomal recombination during meiosis and subsequent sexual reproduction plays a vital role in genetic diversity. If these structures are manipulated incorrectly, through processes known as chromosomal instability and translocation, the cell may undergo mitotic catastrophe and die, or it may unexpectedly evade apoptosis leading to the progression of cancer.In prokaryotes (see nucleoids) and viruses, the DNA is often densely packed and organized. In the case of archaea by homologs to eukaryotic histones, in the case of bacteria by histone-like proteins. Small circular genomes called plasmids are often found in bacteria and also in mitochondria and chloroplasts, reflecting their bacterial origins.