Satiable Curiosity - Journal of Genetic Genealogy
... The human Y chromosome has long stretches of duplicated segments, with multiple copies of some genes and genetic markers. These segments differ only slightly over most of their length, but microsatellites (Short Tandem Repeats or STRs) contained within these segments tend to be more variable, due to ...
... The human Y chromosome has long stretches of duplicated segments, with multiple copies of some genes and genetic markers. These segments differ only slightly over most of their length, but microsatellites (Short Tandem Repeats or STRs) contained within these segments tend to be more variable, due to ...
Laboratory Projects
... Centromeres on the same chromatid attach to opposite poles: Chromosome Breakage ...
... Centromeres on the same chromatid attach to opposite poles: Chromosome Breakage ...
HRW BIO CRF Ch 06_p01-58
... ______ 5. The two exact copies of DNA that make up each chromosome are called a. homologous chromosomes. c. chromatids. b. centromeres. d. autosomes. ______ 6. The two chromatids of a chromosome are attached at a point called the a. diploid. c. spindle. b. centriole. d. centromere. ______ 7. Chromos ...
... ______ 5. The two exact copies of DNA that make up each chromosome are called a. homologous chromosomes. c. chromatids. b. centromeres. d. autosomes. ______ 6. The two chromatids of a chromosome are attached at a point called the a. diploid. c. spindle. b. centriole. d. centromere. ______ 7. Chromos ...
PowerPoint
... chromosomes double Cell divides once Chromatid divides once Leaves 2n in each daughter cell ...
... chromosomes double Cell divides once Chromatid divides once Leaves 2n in each daughter cell ...
Crossing Over and Independent Assortment Notes
... http://highered.mcgraw‐hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter3/animation__random_orientation_of_chromosomes_during_meiosis.html ...
... http://highered.mcgraw‐hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter3/animation__random_orientation_of_chromosomes_during_meiosis.html ...
Unit 3- Section 2
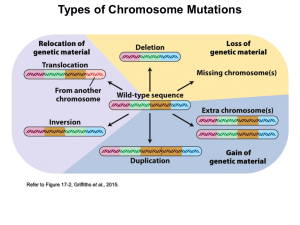
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
... Deletion-A portion of the chromosome is lost and the information is lost with it. Duplication-A portion from the homologous chromosome is added Inversion- A portion is added but it attaches in the ...
Chromosome Rearrangements Concepts: Chromosome
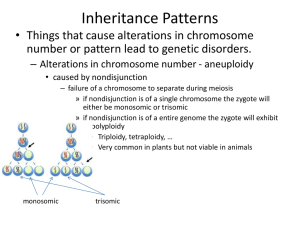
... 1. Chromosomes can undergo physical rearrangements of their DNA, which include deletions, duplications, inversions, and/or translocations of DNA segments. 2. Rearranged chromosomes may pair improperly at meiosis and alter the distribution of chromosomes thereby affecting fertility. 3. Rearrangements ...
... 1. Chromosomes can undergo physical rearrangements of their DNA, which include deletions, duplications, inversions, and/or translocations of DNA segments. 2. Rearranged chromosomes may pair improperly at meiosis and alter the distribution of chromosomes thereby affecting fertility. 3. Rearrangements ...
Genetics Vocabulary Week 3
... chromosomes is reduced in HALF; four daughter cells are created each having half of the number of chromosomes (Ex: Humans have 46 chromosomes. An egg cell only has 23 chromosomes.) Asexual Reproduction – one parent producing offspring identical to parent and to other offspring. Buzz words are one, i ...
... chromosomes is reduced in HALF; four daughter cells are created each having half of the number of chromosomes (Ex: Humans have 46 chromosomes. An egg cell only has 23 chromosomes.) Asexual Reproduction – one parent producing offspring identical to parent and to other offspring. Buzz words are one, i ...
Chromosomal Genetics and Pathology (Dr
... classify according to location of centromere: metacentric = centromere in the middle, submetacentric = centromere closer to one end, acrocentric = centromere very close to one end (only satellites and telomeres, no important genes, on short arm) acrocentric chromosomes: 13, 14, 15, 21, 22 FISH ...
... classify according to location of centromere: metacentric = centromere in the middle, submetacentric = centromere closer to one end, acrocentric = centromere very close to one end (only satellites and telomeres, no important genes, on short arm) acrocentric chromosomes: 13, 14, 15, 21, 22 FISH ...
Pedigree and Karyotype Power point
... half shaded circle or square. They are heterozygous- they have a recessive gene but it does not show. ...
... half shaded circle or square. They are heterozygous- they have a recessive gene but it does not show. ...
BDOL Interactive Chalkboard
... meiosis I (reductional) & meiosis II (equational). 1. Meiosis I begins with one diploid (2N) cell. 2. Meiosis II is simply mitotic process. 3. End of meiosis II = 4 haploid(N) daughter cells ...
... meiosis I (reductional) & meiosis II (equational). 1. Meiosis I begins with one diploid (2N) cell. 2. Meiosis II is simply mitotic process. 3. End of meiosis II = 4 haploid(N) daughter cells ...
Meiosis and Sex
... 2. Understand genetic linkage 3. Explain sex-linked genes and why more common in males ...
... 2. Understand genetic linkage 3. Explain sex-linked genes and why more common in males ...
Related Document
... When red and white snapdragons are crossed their offspring are pink. This is an example of ______________. The term that is used when both alleles contribute to the phenotype (such as in chickens with both black and white feathers). ...
... When red and white snapdragons are crossed their offspring are pink. This is an example of ______________. The term that is used when both alleles contribute to the phenotype (such as in chickens with both black and white feathers). ...
MITOSIS THE HEREDITARY MATERIAL OF ORGANISMS (PLANTS
... MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS? WHAT STAGE IS THE BEST TO DETERMINE KARYOTYPIC TRAITS? II. CHROMOSOME NUMBER A. CHROMOSOMES ARE PRESENT IN PAIRS IN SEXUALLY REPRODUCING ORGANISMS (PLANTS) 1. THE TWO MEMBERS OF EACH PAIR ARE ESSENTIALLY IDENTICAL (KARYOTYPE) AND ARE CALLED HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES a. ONE HOMOLOGU ...
... MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS? WHAT STAGE IS THE BEST TO DETERMINE KARYOTYPIC TRAITS? II. CHROMOSOME NUMBER A. CHROMOSOMES ARE PRESENT IN PAIRS IN SEXUALLY REPRODUCING ORGANISMS (PLANTS) 1. THE TWO MEMBERS OF EACH PAIR ARE ESSENTIALLY IDENTICAL (KARYOTYPE) AND ARE CALLED HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES a. ONE HOMOLOGU ...
7th Grade Science Notes
... Genes that are on these chromosomes are called “sex-linked” genes. Each male carries an X and a Y chromosome. Each female carries two X chromosomes. If a disease or abnormality occurs on the X chromosome, it will always be expressed in the male because they have only one X. It may not be expressed i ...
... Genes that are on these chromosomes are called “sex-linked” genes. Each male carries an X and a Y chromosome. Each female carries two X chromosomes. If a disease or abnormality occurs on the X chromosome, it will always be expressed in the male because they have only one X. It may not be expressed i ...
Mitosis and Cell Cycle Test Review Sheet
... 9. What are the 3 stages of Interphase and what happens in each of these stages? ...
... 9. What are the 3 stages of Interphase and what happens in each of these stages? ...
Mammalian X Chromosome Inactivation
... 4. Telomeric and centromeric regions Features of Facultative Heterochromatin 1. Referred to as silent chromatin 2. Potential to become heterochromatic (Barr body) ...
... 4. Telomeric and centromeric regions Features of Facultative Heterochromatin 1. Referred to as silent chromatin 2. Potential to become heterochromatic (Barr body) ...
Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21
... Position-effect variegation is exhibited by this w+/w heterozygote. Wild-type allele is no longer wild-type in its expression in some of the eye facets. Any chromosomal change that places a locus next to heterochromatin can result in inactivation of that gene. ...
... Position-effect variegation is exhibited by this w+/w heterozygote. Wild-type allele is no longer wild-type in its expression in some of the eye facets. Any chromosomal change that places a locus next to heterochromatin can result in inactivation of that gene. ...
Genetic Disorders Class Notes
... uncontrolled movements, emotional disturbances, mental deterioration, fatal (8:100,000) ...
... uncontrolled movements, emotional disturbances, mental deterioration, fatal (8:100,000) ...