Lect no.7 Classification of medicinal plants
... 4] Classification based on industrial uses of plants -Aromatic Plants: used in food, cosmetics and food industries. - Medicinal plants: plants that are used in medicine industry (extracts or herbal products). - Spices, condiments and Flavoring agents: plants used mainly in food and food industry and ...
... 4] Classification based on industrial uses of plants -Aromatic Plants: used in food, cosmetics and food industries. - Medicinal plants: plants that are used in medicine industry (extracts or herbal products). - Spices, condiments and Flavoring agents: plants used mainly in food and food industry and ...
Taxonomy and Binomial Nomenclature
... Uniqueness Every name has to be unique. If several names have been given to the same taxon, priority decides which name will be the valid name. ...
... Uniqueness Every name has to be unique. If several names have been given to the same taxon, priority decides which name will be the valid name. ...
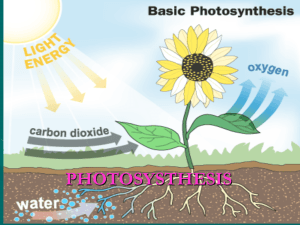
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... it to make food, which the stems conduct back to the roots for storage. • The law of cooperation can be seen in that if a particular part of the system does not fulfill its role the plant will not survive. ...
... it to make food, which the stems conduct back to the roots for storage. • The law of cooperation can be seen in that if a particular part of the system does not fulfill its role the plant will not survive. ...
File - Mrs. Rothenberg`s Science
... Your test will be on ____________________ Anything from the readings can be on the test. In addition, anything from our discussion in class can also be on the test. You should use your class notes, textbook, review homework that we corrected in class and this review sheet to help you prepare. When s ...
... Your test will be on ____________________ Anything from the readings can be on the test. In addition, anything from our discussion in class can also be on the test. You should use your class notes, textbook, review homework that we corrected in class and this review sheet to help you prepare. When s ...
Aim: How do scientists classify living organisms?
... Taxonomy is the branch of biology that involves the identification, naming, and classification of species. ...
... Taxonomy is the branch of biology that involves the identification, naming, and classification of species. ...
Plant Structural Adaptations
... Fill in the blanks with the following vocabulary words Non-Vascular ...
... Fill in the blanks with the following vocabulary words Non-Vascular ...
Alocasia cucullata
... the trip. It is not unusual for these plants to be quite wilted for a few days and some of the original leaves may even die, but new leaves will emerge from the base of the old ones. Don’t plant too deep, you should be able to see the original soil line by the color of the stalks – darker above the ...
... the trip. It is not unusual for these plants to be quite wilted for a few days and some of the original leaves may even die, but new leaves will emerge from the base of the old ones. Don’t plant too deep, you should be able to see the original soil line by the color of the stalks – darker above the ...
Chapter 21 * Plant evolution and adaptations
... Cuticle – Fatty coating on the outside of plant leaves that helps to protect the leaf from invading organisms and prevents unwanted water loss. STOMATA – Openings in the outer layer of leaves that allows for the exchange of gases in plants with a cuticle. Vascular Tissues – Specialized transport ti ...
... Cuticle – Fatty coating on the outside of plant leaves that helps to protect the leaf from invading organisms and prevents unwanted water loss. STOMATA – Openings in the outer layer of leaves that allows for the exchange of gases in plants with a cuticle. Vascular Tissues – Specialized transport ti ...
Plant nomenclature and taxonomy
... consequently is the basis for further pharmacological, phytochemical, analytical, and clinical study. By Dr. Youssef Ibrahim Ph.D. ...
... consequently is the basis for further pharmacological, phytochemical, analytical, and clinical study. By Dr. Youssef Ibrahim Ph.D. ...
pattys calathea care
... Patty’s Plants Calathea Calatheas are from eastern Brazil. They are a great colorful foliage plant for the home or office. Grow Calatheas in meduim to bright curtain filtered light. They can tolerate a little lower light too. An east or west window is perfect. To much light will burn their leaves. L ...
... Patty’s Plants Calathea Calatheas are from eastern Brazil. They are a great colorful foliage plant for the home or office. Grow Calatheas in meduim to bright curtain filtered light. They can tolerate a little lower light too. An east or west window is perfect. To much light will burn their leaves. L ...
Week 2 Study guide
... be able to explain why scientific names are used, the differences between genus, species, and cultivars, and give examples of common and scientific naming. We will also begin work on identification of flower types and components of flowers. 1. Identify the parts of the following flowers: ...
... be able to explain why scientific names are used, the differences between genus, species, and cultivars, and give examples of common and scientific naming. We will also begin work on identification of flower types and components of flowers. 1. Identify the parts of the following flowers: ...
Plants junior
... Plants junior Plants form the basis of the survival of all living things. In fact, they supply the majority of the oxygen that animals and men breathe and also the majority of the food that they consume. The plant kingdom includes about 350,000 very different species. In fact trees, shrubs, bushes, ...
... Plants junior Plants form the basis of the survival of all living things. In fact, they supply the majority of the oxygen that animals and men breathe and also the majority of the food that they consume. The plant kingdom includes about 350,000 very different species. In fact trees, shrubs, bushes, ...
Pharmacognosy
... It will be noted that in Pharmacopoeias & in research publications botanical names are followed by the names of the Scientists or botanists ( e.g. Linnaeus and Sole in the case of peppermint given above ) . These refer to the botanist who first described the species or variety . Botanical Systems of ...
... It will be noted that in Pharmacopoeias & in research publications botanical names are followed by the names of the Scientists or botanists ( e.g. Linnaeus and Sole in the case of peppermint given above ) . These refer to the botanist who first described the species or variety . Botanical Systems of ...
Plants
... ………………………….. are plants with a thick, hard stem called trunk. …………………………. are plants with a lot of stems and leaves. ...
... ………………………….. are plants with a thick, hard stem called trunk. …………………………. are plants with a lot of stems and leaves. ...
Plant adaptations - Parkland School District
... leaves that only grow after it rains. Plant adaptations.com ...
... leaves that only grow after it rains. Plant adaptations.com ...
Plant Classification.pub
... The conservatory’s permanent collection has a large number of the plants from the Arecaceae (palm), Bromeliaceae (bromeliad), and Orchidaceae (orchid) families. ...
... The conservatory’s permanent collection has a large number of the plants from the Arecaceae (palm), Bromeliaceae (bromeliad), and Orchidaceae (orchid) families. ...
Plant growth - WordPress.com
... The sugars can be broken down and used for energy (cellular respiration) ...
... The sugars can be broken down and used for energy (cellular respiration) ...
Control Systems In Plants
... The study of plants began when early humans began to distinguish edible plants from poisonous ones. Then began to make things from wood and other plant products. ...
... The study of plants began when early humans began to distinguish edible plants from poisonous ones. Then began to make things from wood and other plant products. ...
Megan Tierney Virginia Cooperative Extension
... 2000 BC - Indian (Ayurvedic) texts described medicinal plants 1000-1700 AD - “Age of Herbals” in Europe ...
... 2000 BC - Indian (Ayurvedic) texts described medicinal plants 1000-1700 AD - “Age of Herbals” in Europe ...
Plants Can be Dangerous
... Plants Can be Dangerous! Most plants make their food during photosynthesis and normally get necessary water and nutrients from the soil. However, some plants have evolved other methods of surviving. These plants are called parasitic, epiphytic, or carnivorous plants. Parasitic Plants: attach themsel ...
... Plants Can be Dangerous! Most plants make their food during photosynthesis and normally get necessary water and nutrients from the soil. However, some plants have evolved other methods of surviving. These plants are called parasitic, epiphytic, or carnivorous plants. Parasitic Plants: attach themsel ...
AMARYLLIS
... clay in the bottom of the pot for drainage. Then they added a nutritious composted soilmix and water. They placed the bulb in the soil up to its neck. They were careful not to damage the roots. After planting they firmly pressed the soil down so that the bulb was set securely in place. Next they wil ...
... clay in the bottom of the pot for drainage. Then they added a nutritious composted soilmix and water. They placed the bulb in the soil up to its neck. They were careful not to damage the roots. After planting they firmly pressed the soil down so that the bulb was set securely in place. Next they wil ...
Cultivated plant taxonomy

Cultivated plant taxonomy is the study of the theory and practice of the science that identifies, describes, classifies, and names cultigens—those plants whose origin or selection is primarily due to intentional human activity. Cultivated plant taxonomists do, however, work with all kinds of plants in cultivation.Cultivated plant taxonomy is one part of the study of horticultural botany which is mostly carried out in botanical gardens, large nurseries, universities, or government departments. Areas of special interest for the cultivated plant taxonomist include: searching for and recording new plants suitable for cultivation (plant hunting); communicating with and advising the general public on matters concerning the classification and nomenclature of cultivated plants and carrying out original research on these topics; describing the cultivated plants of particular regions (horticultural floras); maintaining databases, herbaria and other information about cultivated plants.Much of the work of the cultivated plant taxonomist is concerned with the naming of plants as prescribed by two plant nomenclatural Codes. The provisions of the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (Botanical Code) serve primarily scientific ends and the objectives of the scientific community, while those of the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (Cultivated Plant Code) are designed to serve both scientific and utilitarian ends by making provision for the names of plants used in commerce — the cultigens that have arisen in agriculture, forestry and horticulture. These names, sometimes called variety names, are not in Latin but are added onto the scientific Latin names, and they assist communication among the community of foresters, farmers and horticulturists.The history of cultivated plant taxonomy can be traced from the first plant selections that occurred during the agrarian Neolithic Revolution to the first recorded naming of human plant selections by the Romans. The naming and classification of cultigens followed a similar path to that of all plants until the establishment of the first Cultivated Plant Code in 1953 which formally established the cultigen classification category of cultivar. Since that time the classification and naming of cultigens has followed its own path.