Biochemistry 6: Model Organisms
... principles, they sometimes fail to display the clear-cut dominant/recessive relationship observed by Mendel. In many cases, in contrast to Mendelian genetics, two or more genes are known to influence the phenotype of a single characteristic. Another exception to Mendelian inheritance is the presence ...
... principles, they sometimes fail to display the clear-cut dominant/recessive relationship observed by Mendel. In many cases, in contrast to Mendelian genetics, two or more genes are known to influence the phenotype of a single characteristic. Another exception to Mendelian inheritance is the presence ...
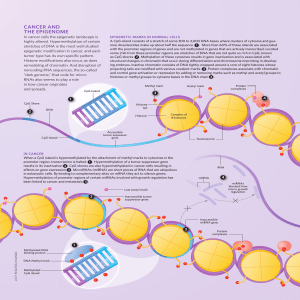
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
STUDY GUIDE-5Mendelian Genetics
... c. the pattern of inheritance (monohybrid, dihybrid, sex-linked, and linked genes) can be predicted from genotype/phenotype data 14.3 I can use an example to describe how environmental factors may influence many traits both directly and indirectly. Illustrative examples: a. Flower color based on soi ...
... c. the pattern of inheritance (monohybrid, dihybrid, sex-linked, and linked genes) can be predicted from genotype/phenotype data 14.3 I can use an example to describe how environmental factors may influence many traits both directly and indirectly. Illustrative examples: a. Flower color based on soi ...
pdffile - UCI Math
... (1810–1882) put forth their theories—Schleiden in 1838 and Schwann in 1839—that all plants and animals are composed of cells, there has been continuous refinement of cell theory. Cells are the basic units and building blocks of nearly every organism. (One exception is viruses, which are simple organ ...
... (1810–1882) put forth their theories—Schleiden in 1838 and Schwann in 1839—that all plants and animals are composed of cells, there has been continuous refinement of cell theory. Cells are the basic units and building blocks of nearly every organism. (One exception is viruses, which are simple organ ...
Appendix Genomic
... A group of propagating organisms, either single cell or multicellular, derived from a single progenitor cell. Such organisms should be genetically identical, although this can be invalidated due to mutation events. CODOMINANCE Two dominant alleles within a single gene that equally affect the phenoty ...
... A group of propagating organisms, either single cell or multicellular, derived from a single progenitor cell. Such organisms should be genetically identical, although this can be invalidated due to mutation events. CODOMINANCE Two dominant alleles within a single gene that equally affect the phenoty ...
Mutation and DNA
... Can be caused due to abnormal synapsis event at Meiosis I by incorrect chromosomes coming together. Associated with 2 forms of leukemia – oncogenes translocated to incorrect regions within chromosomes of leukocytes (white blood cells) ...
... Can be caused due to abnormal synapsis event at Meiosis I by incorrect chromosomes coming together. Associated with 2 forms of leukemia – oncogenes translocated to incorrect regions within chromosomes of leukocytes (white blood cells) ...
Std.8 Genetics Study Guide
... Sex chromosome disorders – result from nondisjunction of sex chromosomes o Turners Syndrome – XO in females o Kleinfelter’s Syndrome – XXY in males Sex-Linked Genes – o Genes located on the X or Y chromosome o Many genes are located on the X-chromosome ...
... Sex chromosome disorders – result from nondisjunction of sex chromosomes o Turners Syndrome – XO in females o Kleinfelter’s Syndrome – XXY in males Sex-Linked Genes – o Genes located on the X or Y chromosome o Many genes are located on the X-chromosome ...
The Fugates Inheritance
... Dominant vs recessive Dominant - a genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of that gene (example: BB or Bb) Recessive - the recessive form is overpowered by its counterpart, or dominant, form located on the other of a pair of chromosomes (example: bb ...
... Dominant vs recessive Dominant - a genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of that gene (example: BB or Bb) Recessive - the recessive form is overpowered by its counterpart, or dominant, form located on the other of a pair of chromosomes (example: bb ...
Lack of expression of XIST from a small ring X chromosome
... with the variant sequence being on the paternally inherited ring chromosome that is not present in all of her cells. The patient's paternal grandmother was heterozygous for the variant (Figure 4C). Over 100 X chromosomes from male and female controls were examined for this variant using the BanI ass ...
... with the variant sequence being on the paternally inherited ring chromosome that is not present in all of her cells. The patient's paternal grandmother was heterozygous for the variant (Figure 4C). Over 100 X chromosomes from male and female controls were examined for this variant using the BanI ass ...
ChromoSock Mitosis Instructor Protocol
... 2. Direct students to remove the ChromoSocks and arrange in pairs. Chromosomes, like socks, occur in pairs. These pairs are called homologs. Students will draw the cell and label the chromosome ploidy and number. Students are to use an “I” shape to represent a single chromosome; later in the activ ...
... 2. Direct students to remove the ChromoSocks and arrange in pairs. Chromosomes, like socks, occur in pairs. These pairs are called homologs. Students will draw the cell and label the chromosome ploidy and number. Students are to use an “I” shape to represent a single chromosome; later in the activ ...
Unit 5: Genetics
... tumor to develop. Women who inherit a mutated copy of either the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have an increased chance of developing breast cancer. In addition, there may be an increased risk for other cancers. ...
... tumor to develop. Women who inherit a mutated copy of either the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have an increased chance of developing breast cancer. In addition, there may be an increased risk for other cancers. ...
Body Cells
... • What’s a sex chromosome & how’s it different from an autosome? • In a human DIPLOID cell, how many chromosomes are there? • In a human HAPLOID cell, how many chromosomes? • After fertilization takes place (sperm meets egg), the resulting cell (zygote) is .... Diploid or haploid? • Do you think the ...
... • What’s a sex chromosome & how’s it different from an autosome? • In a human DIPLOID cell, how many chromosomes are there? • In a human HAPLOID cell, how many chromosomes? • After fertilization takes place (sperm meets egg), the resulting cell (zygote) is .... Diploid or haploid? • Do you think the ...
Repair of Broken Chromosomes and Maintenance of Chromosome
... What is the mutation rate and the spectrum of mutations for the DNA sequences that are copied during DSB repair? What is the role of mismatch repair? What’s an “old” strand? What are the roles of different DNA polymerases? ...
... What is the mutation rate and the spectrum of mutations for the DNA sequences that are copied during DSB repair? What is the role of mismatch repair? What’s an “old” strand? What are the roles of different DNA polymerases? ...
Radiation.ppt - 123seminarsonly.com
... call it back into a division cycle. Usually, however, cells pass on to irreversible differentiation with their chromosomes unduplicated. S-phase is a discrete period of interphase of a few hours duration during which the chromosomal DNA and protein is duplicated, and the new chromatin segregated in ...
... call it back into a division cycle. Usually, however, cells pass on to irreversible differentiation with their chromosomes unduplicated. S-phase is a discrete period of interphase of a few hours duration during which the chromosomal DNA and protein is duplicated, and the new chromatin segregated in ...
The Science of Genetics
... factors make certain recessive traits disappear. Allele – matched pair of genes that control a trait Law of Segregation – alleles responsible for trait separate and then combine with other parent at fertilization – each parent provides one of two genes for the trait ...
... factors make certain recessive traits disappear. Allele – matched pair of genes that control a trait Law of Segregation – alleles responsible for trait separate and then combine with other parent at fertilization – each parent provides one of two genes for the trait ...
xx, y:y: j
... Complete the two Punnett squares below to compare autosomal recessive disorders with autosomal dominant disorders, Fill in the possible genotypes for offspring, and write in the phenotype (no disorder.icarrier, or disorder) for each, ...
... Complete the two Punnett squares below to compare autosomal recessive disorders with autosomal dominant disorders, Fill in the possible genotypes for offspring, and write in the phenotype (no disorder.icarrier, or disorder) for each, ...
Rita Levi Montalcini was born on April 22nd, 1909
... individuals that are heterozygous for two genes generates four possible phenotypes. Mendel also found that a gene is a sequence of DNA located on a locus on a chromosome. Organisms are determined by a pair of sex chromosomes – XX for female and XY for male- women produce only gametes with X chromos ...
... individuals that are heterozygous for two genes generates four possible phenotypes. Mendel also found that a gene is a sequence of DNA located on a locus on a chromosome. Organisms are determined by a pair of sex chromosomes – XX for female and XY for male- women produce only gametes with X chromos ...
EVOLUTIONARY PERSPECTIVE
... FRAGILE X SYNDROME • More common in boys than girls • Boys 1 in 4,000 and girls 1 in 8,000 • Similar physical features across different ethnicities • Cognitive features like hyperventilation and hypersensitivity ...
... FRAGILE X SYNDROME • More common in boys than girls • Boys 1 in 4,000 and girls 1 in 8,000 • Similar physical features across different ethnicities • Cognitive features like hyperventilation and hypersensitivity ...
What unites these phenomena?
... Dnmt1 and associated proteins scan newly replicated DNA for hemimethylated sites and methylate the CpG’s on the newly synthesized strands ...
... Dnmt1 and associated proteins scan newly replicated DNA for hemimethylated sites and methylate the CpG’s on the newly synthesized strands ...
Genetics Exam 2
... A. DNA recombines B. Sister chromatids move to opposite poles C. The nuclear membrane disappears D. RNA replicates E. DNA content essentially doubles _____During prophase of mitosis ___. A. DNA recombines B. Sister chromatids move to opposite poles C. The nuclear membrane disappears D. RNA replicate ...
... A. DNA recombines B. Sister chromatids move to opposite poles C. The nuclear membrane disappears D. RNA replicates E. DNA content essentially doubles _____During prophase of mitosis ___. A. DNA recombines B. Sister chromatids move to opposite poles C. The nuclear membrane disappears D. RNA replicate ...
Unit 8 - Ace The Race
... Epigenetic inheritance Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene activity that are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence. Epigenetic inheritance is a pattern in which a nuclear gene or chromosome gets modified itself that changes the gene expression. This phenomenon is not permanent ...
... Epigenetic inheritance Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene activity that are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence. Epigenetic inheritance is a pattern in which a nuclear gene or chromosome gets modified itself that changes the gene expression. This phenomenon is not permanent ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... One of the first genetic disorders studied caused by recessive alleles was PKU. What are the symptoms of PKU? Tay-sachs is also caused by recessive alleles found on the autosomes. What are the symptoms of Tay-Sachs? There is no cure but the gene can be detected. Cystic Fibrosis (autosomal recessive) ...
... One of the first genetic disorders studied caused by recessive alleles was PKU. What are the symptoms of PKU? Tay-sachs is also caused by recessive alleles found on the autosomes. What are the symptoms of Tay-Sachs? There is no cure but the gene can be detected. Cystic Fibrosis (autosomal recessive) ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.