Genetics Exam 3
... ________________________________ Traits that show up in both sexes but are expressed differently. ______________________ __________An organism composed of two or more genetically different cell types. ________________________________ A chromosomal mutation in which there is a change in position of c ...
... ________________________________ Traits that show up in both sexes but are expressed differently. ______________________ __________An organism composed of two or more genetically different cell types. ________________________________ A chromosomal mutation in which there is a change in position of c ...
Lecture 17 Functional Genetics III Basic Approaches
... Functional genomics: Identify the function of each and every gene in the genome. Since the characterization of the function of a protein domain in one organism generally provides hint to its function in another organism, the first goal of functional genomics is to identify as many genes as possible ...
... Functional genomics: Identify the function of each and every gene in the genome. Since the characterization of the function of a protein domain in one organism generally provides hint to its function in another organism, the first goal of functional genomics is to identify as many genes as possible ...
Genetics - Faculty Web Sites
... don't start life as very short individuals - they become short over time, growing more slowly than their sisters and friends with each passing year. Studies have shown that a medicine called recombinant human growth hormone, or GH, can improve the height of girls with Turner syndrome. However, these ...
... don't start life as very short individuals - they become short over time, growing more slowly than their sisters and friends with each passing year. Studies have shown that a medicine called recombinant human growth hormone, or GH, can improve the height of girls with Turner syndrome. However, these ...
Edvotek Kit #116: Genetically Inherited Disease Detection Using Pre
... Sickle Cell results from a Point Mutation on the short arm of chromosome 11. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) between an A to T results in a new amino acid in the sixth position of the beta chain of hemoglobin in red blood cells. In normal hemoglobin (Hb A), glutamic acid (Glu) is present. In ...
... Sickle Cell results from a Point Mutation on the short arm of chromosome 11. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) between an A to T results in a new amino acid in the sixth position of the beta chain of hemoglobin in red blood cells. In normal hemoglobin (Hb A), glutamic acid (Glu) is present. In ...
Genetics & Prenatal Development
... Sex Linked Traits • The sex chromosomes, the 23rd pair of chromosomes, determine biological sex • In females, the 23rd pair of chromosomes is made up of two large X chromosomes. XX • In males, a large X chromosome and a smaller Y chromosome make up the 23rd pair. XY • For males, the smaller Y chrom ...
... Sex Linked Traits • The sex chromosomes, the 23rd pair of chromosomes, determine biological sex • In females, the 23rd pair of chromosomes is made up of two large X chromosomes. XX • In males, a large X chromosome and a smaller Y chromosome make up the 23rd pair. XY • For males, the smaller Y chrom ...
Cell Structure & Function
... remains constant within a certain species , yet the number varies from one species to another. For example in Man number of chromosomes in somatic cell is 46 chromosomes ,in pea plant, the number of chromosomes is 14 ,in maize number of chromosomes is 20.The cells of the maize plant that have twenty ...
... remains constant within a certain species , yet the number varies from one species to another. For example in Man number of chromosomes in somatic cell is 46 chromosomes ,in pea plant, the number of chromosomes is 14 ,in maize number of chromosomes is 20.The cells of the maize plant that have twenty ...
11-4 Meiosis - Laurel County Schools
... Gregor Mendel did not know where the _____________ he had discovered were _________________. However, his _____________________ of how genes should behave were so ____________ that it was not long before biologists were certain they had found them—____________ are located on ______________________ i ...
... Gregor Mendel did not know where the _____________ he had discovered were _________________. However, his _____________________ of how genes should behave were so ____________ that it was not long before biologists were certain they had found them—____________ are located on ______________________ i ...
MENDEL AND MEIOSIS NOTES
... Two organisms can look alike (tall pea plants) but have different underlying allele combinations. Phenotype – the way an organism looks and behaves ...
... Two organisms can look alike (tall pea plants) but have different underlying allele combinations. Phenotype – the way an organism looks and behaves ...
Genetics - Dr Magrann
... and mental retardation. One day it might be possible to control the expression of that gene even before birth so that at least this symptom of Down syndrome does not appear. ...
... and mental retardation. One day it might be possible to control the expression of that gene even before birth so that at least this symptom of Down syndrome does not appear. ...
why care
... Meiosis – A Source of Distinction Meiosis does two things 1) Meiosis takes a cell with two copies of every gene (a diploid; 2n) and makes cells with a single copy of every gene (a haploid; 1n). This is a good idea if you’re going to combine two cells to make a new organism. This trick is accomplish ...
... Meiosis – A Source of Distinction Meiosis does two things 1) Meiosis takes a cell with two copies of every gene (a diploid; 2n) and makes cells with a single copy of every gene (a haploid; 1n). This is a good idea if you’re going to combine two cells to make a new organism. This trick is accomplish ...
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
... carry genetic information; located in the nucleus of every human cell ...
... carry genetic information; located in the nucleus of every human cell ...
Keystone Practice Questions #2 Cell Division, DNA
... A. It was a silent mutation that caused a change in the DNA of the organism. B. It was a silent mutation that caused a change in the phenotype of the organism. C. It was a nonsense mutation tha ...
... A. It was a silent mutation that caused a change in the DNA of the organism. B. It was a silent mutation that caused a change in the phenotype of the organism. C. It was a nonsense mutation tha ...
Sample File
... terms of clines, or the continuous gradation over space in the form or frequency of a trait. Clinal analysis of a continuous trait, such as body shape, allows anthropologists to interpret human variation in body build as an adaptation to climate. People native to cold climates tend to have great ...
... terms of clines, or the continuous gradation over space in the form or frequency of a trait. Clinal analysis of a continuous trait, such as body shape, allows anthropologists to interpret human variation in body build as an adaptation to climate. People native to cold climates tend to have great ...
CHAPTER 21
... recessive visible apricot is employed for the same reason. Any cross-over that did occur would immediately be apparent because it would result in Bar, not apricot, male progeny. If there was no crossing-over (and there should be very little because of the inversion), there were four types of F1 prog ...
... recessive visible apricot is employed for the same reason. Any cross-over that did occur would immediately be apparent because it would result in Bar, not apricot, male progeny. If there was no crossing-over (and there should be very little because of the inversion), there were four types of F1 prog ...
Chapter 4 study game
... that have a certain trait b. Picture of chromosomes c. Geneticist studying traits ...
... that have a certain trait b. Picture of chromosomes c. Geneticist studying traits ...
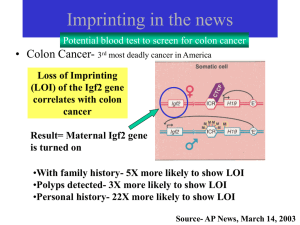
Imprinting
... MechanismMethylation serves two purposes 1. Inactivate a gene (e.g. H19) 2. Prevent binding of epigenetic marker so that Igf2 is activated ...
... MechanismMethylation serves two purposes 1. Inactivate a gene (e.g. H19) 2. Prevent binding of epigenetic marker so that Igf2 is activated ...
Transcription Control in Eukaryotes
... Transcription control in eukaryotes is more complex than in prokaryotes, with more gene-gene interactions, presumably required to produce more different cell types in more complex organisms. We will consider some examples and models to illustrate some general principles. ...
... Transcription control in eukaryotes is more complex than in prokaryotes, with more gene-gene interactions, presumably required to produce more different cell types in more complex organisms. We will consider some examples and models to illustrate some general principles. ...
Human Heredity
... True or False: Barr bodies are found only in males. If you saw a white cat with orange and black spots, is it most likely a male or a female? ...
... True or False: Barr bodies are found only in males. If you saw a white cat with orange and black spots, is it most likely a male or a female? ...
Chapter 2
... 5. “Cross-fostering” studies show that a. life-long expression of genes in individuals can be regulated by their early environment. b. life-long expression of genes in individuals is immune to early environmental influence. c. simple chemicals can modulate neural activity and development. d. epigene ...
... 5. “Cross-fostering” studies show that a. life-long expression of genes in individuals can be regulated by their early environment. b. life-long expression of genes in individuals is immune to early environmental influence. c. simple chemicals can modulate neural activity and development. d. epigene ...
to learn more
... X-‐linked recessive inheritance (Sex-‐linked inheritance) Human cells contain 22 pairs of chromosomes, called autosomes, and one pair of sex chromosomes: X and Y for men and X and X for women. A g ...
... X-‐linked recessive inheritance (Sex-‐linked inheritance) Human cells contain 22 pairs of chromosomes, called autosomes, and one pair of sex chromosomes: X and Y for men and X and X for women. A g ...
14-1, 2 - greinerudsd
... • Just like physical traits, some diseases can be inherited on our chromosomes. • And, just like physical traits, some are X-linked, some are recessive, some are dominant or ...
... • Just like physical traits, some diseases can be inherited on our chromosomes. • And, just like physical traits, some are X-linked, some are recessive, some are dominant or ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.