Ok so we are going to focus on a set of chromosomes coming down
... here. We'll see a few more. As a result of all the inversions, the x and the y no longer nicely align. UGH if they can't swap parts, what's going to happen? The fruits and veggies on the Y rot, the ultimate?? form of rotting is just plain getting lost, or deleted. So the Y is getting shorter, and ...
... here. We'll see a few more. As a result of all the inversions, the x and the y no longer nicely align. UGH if they can't swap parts, what's going to happen? The fruits and veggies on the Y rot, the ultimate?? form of rotting is just plain getting lost, or deleted. So the Y is getting shorter, and ...
B2.7 Topic outcome sheet
... g) A gene is a small section of DNA. h) Each gene codes for a particular combination of amino acids which make a specific protein. i) Each person (apart from identical twins) has unique DNA. This can be used to identify individuals in a process known as DNA fingerprinting. B2.7.3 Genetic disorders a ...
... g) A gene is a small section of DNA. h) Each gene codes for a particular combination of amino acids which make a specific protein. i) Each person (apart from identical twins) has unique DNA. This can be used to identify individuals in a process known as DNA fingerprinting. B2.7.3 Genetic disorders a ...
Bacterial Conjugation
... Chromosome Transfer – 3rd Step • The F(-) cell removes an equal amount of its DNA and inserts the new Hfr DNA strand into its chromosome • F(-) is now known as a recombinant F(-) cell ...
... Chromosome Transfer – 3rd Step • The F(-) cell removes an equal amount of its DNA and inserts the new Hfr DNA strand into its chromosome • F(-) is now known as a recombinant F(-) cell ...
Mosaicism - Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust
... to an altered cell or cells that contain too few or too many chromosomes. Alternatively, a ‘spelling mistake’ may happen in a gene which stops it working properly in that cell. Altered cells may continue to be copied, resulting in an embryo which has ‘mosaicism’ (also called a mosaic embryo). This s ...
... to an altered cell or cells that contain too few or too many chromosomes. Alternatively, a ‘spelling mistake’ may happen in a gene which stops it working properly in that cell. Altered cells may continue to be copied, resulting in an embryo which has ‘mosaicism’ (also called a mosaic embryo). This s ...
Discuss how living things need to adapt to changing
... Purpose is to produce sex cells with half the usual chromosome number. Mention the mixing of genes (crossing over), but there is no need to go into great detail. Discuss role of DNA from both parents in carrying instructions to next generation of animal/plant and how this results in genetic va ...
... Purpose is to produce sex cells with half the usual chromosome number. Mention the mixing of genes (crossing over), but there is no need to go into great detail. Discuss role of DNA from both parents in carrying instructions to next generation of animal/plant and how this results in genetic va ...
DNA Typing
... • Proving paternity is more difficult, and relies on statistical arguments of the probability that the child and the alleged father are related. Multiple loci (different VNTR’s) must be examined to provide convincing evidence that the alleged father is the true father. The same statements (exclusion ...
... • Proving paternity is more difficult, and relies on statistical arguments of the probability that the child and the alleged father are related. Multiple loci (different VNTR’s) must be examined to provide convincing evidence that the alleged father is the true father. The same statements (exclusion ...
Using Gene Ontology - Center for Genomic Sciences
... for members of known function Problem: moderate changes in many genes simultaneously will escape detection New approach: start with a vocabulary of known GO categories or pathways, and look for coherent changes Variations: look for chromosome locations, or protein domains, that are common among many ...
... for members of known function Problem: moderate changes in many genes simultaneously will escape detection New approach: start with a vocabulary of known GO categories or pathways, and look for coherent changes Variations: look for chromosome locations, or protein domains, that are common among many ...
Lab 11: Simple genomic data analysis using R 1. UCSC genome
... specify chromosome and location to get part of the data. Go down a little bit to select “all fields from selected table.” Then specify output file name in the textbox by “hg38genes.txt”, and select file type return as “gzip compressed”, then click “get output.” This will take a little time. Or you c ...
... specify chromosome and location to get part of the data. Go down a little bit to select “all fields from selected table.” Then specify output file name in the textbox by “hg38genes.txt”, and select file type return as “gzip compressed”, then click “get output.” This will take a little time. Or you c ...
in non sex cells
... trait of an individual can be determined by one genes, but is usually determined by the interaction of many different genes. A single gene can influence more than one trait. A human cell contains many thousands of different genes coding for many different traits. ...
... trait of an individual can be determined by one genes, but is usually determined by the interaction of many different genes. A single gene can influence more than one trait. A human cell contains many thousands of different genes coding for many different traits. ...
11.4 Meiosis
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
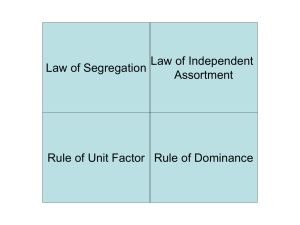
Genetics The father of genetics is Gregor Mendel (1822
... rather to the transmission of specific units of inheritance (genes) Modern Principles of Inheritance 1) Inherited traits are transmitted by genes, which occur in pairs called alleles Alleles are inherited as parts of chromosomes 2) The Principle of dominance: -When two alternate forms of the same ge ...
... rather to the transmission of specific units of inheritance (genes) Modern Principles of Inheritance 1) Inherited traits are transmitted by genes, which occur in pairs called alleles Alleles are inherited as parts of chromosomes 2) The Principle of dominance: -When two alternate forms of the same ge ...
170-175
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
File
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
... 1. The offspring of two parents obtains a single copy of every gene from each parent. 2. A gamete must contain one complete set of genes. 3. Genes are located at specific positions on spindles. 4. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 5. One member of each homologous chromosome pair com ...
history of genetics
... which cause pneumonia. Of the two strains he studied, one had a sugar coat and one did not. The coated strain causes pneumonia and is called the smooth (S) strain. The noncoated strain does not cause pneumonia and is called rough (R) strain because, without the coat, the bacteria colonies have rough ...
... which cause pneumonia. Of the two strains he studied, one had a sugar coat and one did not. The coated strain causes pneumonia and is called the smooth (S) strain. The noncoated strain does not cause pneumonia and is called rough (R) strain because, without the coat, the bacteria colonies have rough ...
Proteins and Genes
... Proteins are used by cells to build structures and are used in chemical activities. Enzymes are proteins that aid in chemical reactions such as digestion and cellular respiration. Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They also contain nitrogen and some sulphur. They help build cell ...
... Proteins are used by cells to build structures and are used in chemical activities. Enzymes are proteins that aid in chemical reactions such as digestion and cellular respiration. Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They also contain nitrogen and some sulphur. They help build cell ...
Inheritance – question hunt Teaching notes
... molecules and proteins, a gene is a section of a chromosome that codes for one characteristic (protein). 17. DNA fingerprinting. DNA code is unique to each individual. 18. Phenotype is the expression of a characteristic that can be observed. Genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism. 19. Crossin ...
... molecules and proteins, a gene is a section of a chromosome that codes for one characteristic (protein). 17. DNA fingerprinting. DNA code is unique to each individual. 18. Phenotype is the expression of a characteristic that can be observed. Genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism. 19. Crossin ...
Genes that are located on the same
... Genes that are located on the same chromosome are called linked genes. Alleles for these genes tend to segregate together during meiosis, unless they are separated by crossing-over. Crossing-over occurs when two homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis I. **The closer together ...
... Genes that are located on the same chromosome are called linked genes. Alleles for these genes tend to segregate together during meiosis, unless they are separated by crossing-over. Crossing-over occurs when two homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis I. **The closer together ...
Gene Mutation
... species become available for widespread use? If you were a state employee in charge of a specific waterway, what questions would you ask before you approved the introduction of a laboratory-produced, polyploid species into your ...
... species become available for widespread use? If you were a state employee in charge of a specific waterway, what questions would you ask before you approved the introduction of a laboratory-produced, polyploid species into your ...
Genetics - Standish
... easy to take care of. Difficult: These babies cry and fuss a lot. They don’t have regular, predictable sleep patterns; they awaken more than other infants do, and they aren’t easy to soothe when they’re upset. Parents know when they have a baby with a difficult temperament, because the infant is s ...
... easy to take care of. Difficult: These babies cry and fuss a lot. They don’t have regular, predictable sleep patterns; they awaken more than other infants do, and they aren’t easy to soothe when they’re upset. Parents know when they have a baby with a difficult temperament, because the infant is s ...
Complex Patterns of inheritance
... 3. Predict the possible offspring of a colorblind male and a normal female. 4. Predict the possible offspring of a mom with blood type IAi and a dad with Ibi. 5. What is a possible explanation for a ...
... 3. Predict the possible offspring of a colorblind male and a normal female. 4. Predict the possible offspring of a mom with blood type IAi and a dad with Ibi. 5. What is a possible explanation for a ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.