MiraCosta College Physics 152
... 1. Determine the electric force and potential energy between electric charges. 2. Calculate and sketch the electric field for various charge distributions using both the definition of the electric field and Gauss' Law. 3. Calculate the electric potential for various distributions of point and contin ...
... 1. Determine the electric force and potential energy between electric charges. 2. Calculate and sketch the electric field for various charge distributions using both the definition of the electric field and Gauss' Law. 3. Calculate the electric potential for various distributions of point and contin ...
PHYS 222 Exam 1 Study Guide
... PHYS 222 Exam 1 Study Guide Concepts covered: - Superposition: Electric and potential fields do not interact with one another, they only interact with the particles. - Rules for drawing and interpreting electric field diagrams: Lines cannot intersect, correct directions of arrows, perpendicular to c ...
... PHYS 222 Exam 1 Study Guide Concepts covered: - Superposition: Electric and potential fields do not interact with one another, they only interact with the particles. - Rules for drawing and interpreting electric field diagrams: Lines cannot intersect, correct directions of arrows, perpendicular to c ...
Divergence and Curl of the Magnetic Field
... their directions. But it is also convenient for the volume currents flowing through thick conductors or for current sheets flowing on surfaces. I shall give several examples of using the Ampere’s Law in a separate set of notes. As written in eqs. (4) or (7), the Ampere’s Law applies only to the mag ...
... their directions. But it is also convenient for the volume currents flowing through thick conductors or for current sheets flowing on surfaces. I shall give several examples of using the Ampere’s Law in a separate set of notes. As written in eqs. (4) or (7), the Ampere’s Law applies only to the mag ...
Course Title
... report will be used as bonus points (added to the participation) to help the students with their grade and must and discuss their results with the instructor in order to better understand the course. One report at least will be handed to the students. The report will ask the students to solve, deriv ...
... report will be used as bonus points (added to the participation) to help the students with their grade and must and discuss their results with the instructor in order to better understand the course. One report at least will be handed to the students. The report will ask the students to solve, deriv ...
Course Syllabus for PHY 424 – Electrodynamics I – Fall... I. Course Information
... of Arts & Sciences. See: http://academicintegrity.syr.edu for the complete Syracuse University Academic Integrity Policy. You may work together on HWs, but you are expected to write up your solutions on your own. You may not come up with a “common solution”, and then everyone in the group copies it. ...
... of Arts & Sciences. See: http://academicintegrity.syr.edu for the complete Syracuse University Academic Integrity Policy. You may work together on HWs, but you are expected to write up your solutions on your own. You may not come up with a “common solution”, and then everyone in the group copies it. ...
Physics with Mathematica Fall 2013 Exercise #4 17 Sep 2012
... density σ(x), and dq � = λ(x� )ds for a line charge density λ(x). Given an electrostatic potential function V (x), the electric field from that charge distribution is E(x) = −∇V (x). Consider a straight line segment of uniformly distributed charge Q and length L, lying along the x-axis and centered ...
... density σ(x), and dq � = λ(x� )ds for a line charge density λ(x). Given an electrostatic potential function V (x), the electric field from that charge distribution is E(x) = −∇V (x). Consider a straight line segment of uniformly distributed charge Q and length L, lying along the x-axis and centered ...
Chapter 22 Problem 66 † Given V (x)=3x - 2x 2
... Factor the potential function as much as possible. V (x) = x(3 − 2x − x2 ) V (x) = x(3 + x)(1 − x) The only places where the potential is equal to zero is when one of its factors is equal to zero. Therefore, Either x = 0, 3 + x = 0, or 1 − x = 0 From these 3 equations we get x = −3 m, 0 m, 1 m ...
... Factor the potential function as much as possible. V (x) = x(3 − 2x − x2 ) V (x) = x(3 + x)(1 − x) The only places where the potential is equal to zero is when one of its factors is equal to zero. Therefore, Either x = 0, 3 + x = 0, or 1 − x = 0 From these 3 equations we get x = −3 m, 0 m, 1 m ...
Electric Field
... • Specific charge for a specific value of force • Value needed for force magnitude ...
... • Specific charge for a specific value of force • Value needed for force magnitude ...
PLC Activity #2 Electric Fields & Potentials
... direction of the field? (b) Four other particles similarly travel through small holes in either plate A or plate B and then into the region between the plates. Three have charges +q1, +q2, and -q3. The fourth (labeled n) is a neutron, which is electrically neutral. Does the speed of each of those fo ...
... direction of the field? (b) Four other particles similarly travel through small holes in either plate A or plate B and then into the region between the plates. Three have charges +q1, +q2, and -q3. The fourth (labeled n) is a neutron, which is electrically neutral. Does the speed of each of those fo ...
PY4P05 Electromagnetic Interactions II 12 Lectures Dr. C. Patterson
... by one wavelength in the East-West direction. Calculate and sketch the horizontal polar diagram of the array when the dipoles are fed in phase with equal currents. 13) GP 13.4 Why is an antenna much shorter than a wavelength inefficient as a radiator of radio waves? If a commercial radio station tra ...
... by one wavelength in the East-West direction. Calculate and sketch the horizontal polar diagram of the array when the dipoles are fed in phase with equal currents. 13) GP 13.4 Why is an antenna much shorter than a wavelength inefficient as a radiator of radio waves? If a commercial radio station tra ...
Lecture18
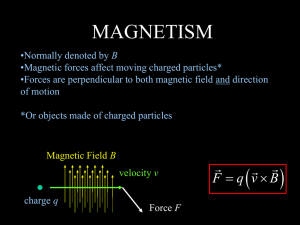
... •Force depends on charge just like electric fields •Force is maximum when the velocity and field are perpendicular, and zero when they are parallel •When the velocity and field are neither perpendicular nor parallel, the force still exists! ...
... •Force depends on charge just like electric fields •Force is maximum when the velocity and field are perpendicular, and zero when they are parallel •When the velocity and field are neither perpendicular nor parallel, the force still exists! ...