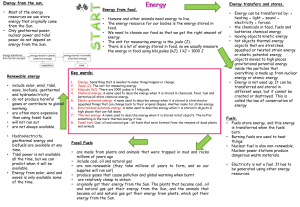
Types and Forms of Energy
... • The light given off by light bulbs and campfires are also forms of radiant energy ...
... • The light given off by light bulbs and campfires are also forms of radiant energy ...
ENERGY VOCABULARY REVIEW
... environment. Examples of these resources are solar energy, wind energy, and geothermal energy. 14. Inexhaustible resources can’t be used up by humans. The sun is an example. 15.Nonrenewable resources are used up much faster than they can be replaced. Fossil fuels and uranium are nonrenewable resour ...
... environment. Examples of these resources are solar energy, wind energy, and geothermal energy. 14. Inexhaustible resources can’t be used up by humans. The sun is an example. 15.Nonrenewable resources are used up much faster than they can be replaced. Fossil fuels and uranium are nonrenewable resour ...
Energy and Momentum
... Note that if the velocity of an object is doubled, its kinetic energy is quadrupled. Kinetic energy can also can be converted into other forms of energy. For example on mountain roads runaway lanes are often provided for trucks that lose their brakes while going down long hills. The runaway lane tak ...
... Note that if the velocity of an object is doubled, its kinetic energy is quadrupled. Kinetic energy can also can be converted into other forms of energy. For example on mountain roads runaway lanes are often provided for trucks that lose their brakes while going down long hills. The runaway lane tak ...
Section 1
... Section 1 1. B. Energy is the ability to do work or to cause change. Tip: We use energy to do work and make all movements. When we eat, our bodies transform the food into energy to do work. When we run or walk or do some work, we ‘burn’ energy in our bodies. 2. B. II and IV Tip: Energy comes in six ...
... Section 1 1. B. Energy is the ability to do work or to cause change. Tip: We use energy to do work and make all movements. When we eat, our bodies transform the food into energy to do work. When we run or walk or do some work, we ‘burn’ energy in our bodies. 2. B. II and IV Tip: Energy comes in six ...
JAN – PATHFINDER SCIENCE Section 1
... 1. B. Energy is the ability to do w ork or to cause change. Tip: We use energy to do work and make all movements. When we eat, our bodies transform the food into energy to do work. When we run or walk or do some work, we ‘burn’ energy in our bodies. 2. B. II and IV Tip: Energy comes in six forms: ch ...
... 1. B. Energy is the ability to do w ork or to cause change. Tip: We use energy to do work and make all movements. When we eat, our bodies transform the food into energy to do work. When we run or walk or do some work, we ‘burn’ energy in our bodies. 2. B. II and IV Tip: Energy comes in six forms: ch ...
Earth Science
... that is available for release from chemical reactions. The chemical bonds in a matchstick store energy that is transformed into thermal energy when the match is struck. Food is chemical energy that our bodies require. ...
... that is available for release from chemical reactions. The chemical bonds in a matchstick store energy that is transformed into thermal energy when the match is struck. Food is chemical energy that our bodies require. ...
ENERGY TANSFORMATION
... you design a heating system for a house, you need to specify how much heat energy you need. ...
... you design a heating system for a house, you need to specify how much heat energy you need. ...
Gravitational Potential Energy
... and the mass of an object. More massive objects have greater gravitational potential energy. ...
... and the mass of an object. More massive objects have greater gravitational potential energy. ...
Work, Power, and Energy
... velocity of 40 m/s. The mass of the baseball is 0.15 kg. The displacement of the baseball due to the deformation of the catcher’s glove and the movement of the catcher’s hand is 8 cm from the instant if first makes contact with the glove until it stops. a. How much kinetic energy dose the baseball p ...
... velocity of 40 m/s. The mass of the baseball is 0.15 kg. The displacement of the baseball due to the deformation of the catcher’s glove and the movement of the catcher’s hand is 8 cm from the instant if first makes contact with the glove until it stops. a. How much kinetic energy dose the baseball p ...
Types of Energy
... An example of mechanical energy is a wind up toy. When the toy is not moving it has potential energy. Work is done when you turn the crank the spring inside has elastic potential energy. When you let go of the springs it will spring back to its original shape. The toy has mechanical energy and then ...
... An example of mechanical energy is a wind up toy. When the toy is not moving it has potential energy. Work is done when you turn the crank the spring inside has elastic potential energy. When you let go of the springs it will spring back to its original shape. The toy has mechanical energy and then ...
Energy
... P1. You do work when pushing a cart with a constant force. If you push the cart twice as far, how much is the work? P2. How much is the Kinetic Energy of a 2-kg object moving at 3.0 m/s? P3. You run a 100-W light bulb on for 1 hour. How much energy have you consumed? P4. What costs more to run: a 10 ...
... P1. You do work when pushing a cart with a constant force. If you push the cart twice as far, how much is the work? P2. How much is the Kinetic Energy of a 2-kg object moving at 3.0 m/s? P3. You run a 100-W light bulb on for 1 hour. How much energy have you consumed? P4. What costs more to run: a 10 ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... For this unit, we will study the concepts of work and power, as well as the types of energy involved in doing work (potential and kinetic, as well as other forms) and how work is done to transform that energy from one form to another. We will look at real life scenarios and calculate the amount of k ...
... For this unit, we will study the concepts of work and power, as well as the types of energy involved in doing work (potential and kinetic, as well as other forms) and how work is done to transform that energy from one form to another. We will look at real life scenarios and calculate the amount of k ...
Section 1:Energy
... • Fossil fuels are non-renewable because they cannot be ______________ as quickly as they are ____________. ...
... • Fossil fuels are non-renewable because they cannot be ______________ as quickly as they are ____________. ...
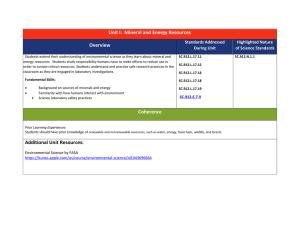
Unit I: Mineral and Energy Resources
... Political and economical pressures influences available data. Different forms of renewable energy are available ...
... Political and economical pressures influences available data. Different forms of renewable energy are available ...
Meters per second, south
... are moving energy. b. An earthquake is energy moving through the earth’s crust in the form of a seismic wave. c. A volcano is the pushing up of the earth’s surface by hot magma and/or gases. d. A glacier is a moving mountain of ice and soil. Waves are moving energy. Choices a, c, and d are moving Ma ...
... are moving energy. b. An earthquake is energy moving through the earth’s crust in the form of a seismic wave. c. A volcano is the pushing up of the earth’s surface by hot magma and/or gases. d. A glacier is a moving mountain of ice and soil. Waves are moving energy. Choices a, c, and d are moving Ma ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy
... • When the position of an object is altered it, creates Potential Energy. • A yo-yo on the table, doesn’t have energy, but when picked up, it alters its position and now it has the ability (or potential) to do work. • A bow doesn’t have the capacity to do work, unless it’s held at an elevated posit ...
... • When the position of an object is altered it, creates Potential Energy. • A yo-yo on the table, doesn’t have energy, but when picked up, it alters its position and now it has the ability (or potential) to do work. • A bow doesn’t have the capacity to do work, unless it’s held at an elevated posit ...
Energy Notes - Killeen ISD
... Work – Kinetic Energy Theorem Work done on an object causes it to MOVE! Thus, it has a change in kinetic energy! Actually, ANY energy form that can be converted to KE can be used to do work o an object! ...
... Work – Kinetic Energy Theorem Work done on an object causes it to MOVE! Thus, it has a change in kinetic energy! Actually, ANY energy form that can be converted to KE can be used to do work o an object! ...
Electrical Energy - niemiscyberclassroom
... Mechanical (Motion) Energy – movement of objects or substances from one place to another ...
... Mechanical (Motion) Energy – movement of objects or substances from one place to another ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy
... it falls, what happens to it’s potential energy? What happens to it’s kinetic energy? As it falls, its velocity goes up, so its kinetic energy goes up. It also looses height so its potential energy goes down. However, mechanical energy stays the same ME = KE + PE ...
... it falls, what happens to it’s potential energy? What happens to it’s kinetic energy? As it falls, its velocity goes up, so its kinetic energy goes up. It also looses height so its potential energy goes down. However, mechanical energy stays the same ME = KE + PE ...
Energy Statement PPT
... I can distinguish between kinetic and potential energies and describe how energy changes, is stored, or stays the same within a system. ...
... I can distinguish between kinetic and potential energies and describe how energy changes, is stored, or stays the same within a system. ...
energy & heat - Doral Academy Preparatory
... the position and motion of an object. Mechanical energy is matter in motion. An airplane soaring through the sky has mechanical energy just like the wind or a flowing river. • Thermal energy- The total potential and kinetic energy of the particles in an object. Thermal energy comes from the motion o ...
... the position and motion of an object. Mechanical energy is matter in motion. An airplane soaring through the sky has mechanical energy just like the wind or a flowing river. • Thermal energy- The total potential and kinetic energy of the particles in an object. Thermal energy comes from the motion o ...