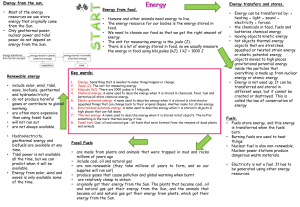
Chapter 5 Study Guide “Energy and Power”
... minutes a night, for at least up to 5 nights, and have your parents sign off on this form, I will give you 5 extra credit points on the test. You must bring this signed study guide on the day of the test, not before, not after, in order to receive credit (this is non-negotiable). ...
... minutes a night, for at least up to 5 nights, and have your parents sign off on this form, I will give you 5 extra credit points on the test. You must bring this signed study guide on the day of the test, not before, not after, in order to receive credit (this is non-negotiable). ...
Science Year 7 Learn Sheet DC4 – Energy
... Chemical energy: A name used to describe energy when it is stored in chemicals. Food, fuel and batteries all store chemical energy. Elastic potential energy: A name used to describe energy when it is stored in stretched or squashed things that can change back to their original shapes. Another name f ...
... Chemical energy: A name used to describe energy when it is stored in chemicals. Food, fuel and batteries all store chemical energy. Elastic potential energy: A name used to describe energy when it is stored in stretched or squashed things that can change back to their original shapes. Another name f ...
Conservation of Energy
... Energy is the ability to do work. When work is done energy is transferred . Energy can only be turned from one form to another. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. Consider a car running down a slope : At the top of the slope the car has potential energy. As it runs down the slope the potential e ...
... Energy is the ability to do work. When work is done energy is transferred . Energy can only be turned from one form to another. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. Consider a car running down a slope : At the top of the slope the car has potential energy. As it runs down the slope the potential e ...
REvison Sheet -TEX2
... D. Chemical Energy E. Electrical Energy 3. The energy that a body has due to its motion. A. Potential energy B. Kinetic energy √ C. Electrical Energy D. Mechanical Energy E. Chemical Energy 4. Energy generated using natural sources that are easily available on earth, always there and will never run ...
... D. Chemical Energy E. Electrical Energy 3. The energy that a body has due to its motion. A. Potential energy B. Kinetic energy √ C. Electrical Energy D. Mechanical Energy E. Chemical Energy 4. Energy generated using natural sources that are easily available on earth, always there and will never run ...
potential energy.
... – Agricultural waste – Forestry waste – Biofuel These sources have not been traditionally used as Energy source However, these sources will always be available in nature and are renewable Hence it is best to use nonconventional sources Example Hydro-electric power project located at Koyna dam in Mah ...
... – Agricultural waste – Forestry waste – Biofuel These sources have not been traditionally used as Energy source However, these sources will always be available in nature and are renewable Hence it is best to use nonconventional sources Example Hydro-electric power project located at Koyna dam in Mah ...
Unit 4: Energy
... Solve kinetic and potential energy using conservation of energy. • What is the potential energy of a 2 kg potted plant that is on a 1 m high plant stand? Ep = mgh 2kg x 9.8m/s 2 x 1m = 19.6 J • What is the kinetic energy of a 3 kg ball that is rolling at 2 m/s? ...
... Solve kinetic and potential energy using conservation of energy. • What is the potential energy of a 2 kg potted plant that is on a 1 m high plant stand? Ep = mgh 2kg x 9.8m/s 2 x 1m = 19.6 J • What is the kinetic energy of a 3 kg ball that is rolling at 2 m/s? ...
Sunnyside_gr_6_botrac
... - Connections will be reinforced throughout the unit by me through communications with them as the students work through each of the activities included in the unit. Lesson builds on existing curriculum: - “Bottle Racers” builds on the information imparted to the students in Ch. 2 of our Glencoe sci ...
... - Connections will be reinforced throughout the unit by me through communications with them as the students work through each of the activities included in the unit. Lesson builds on existing curriculum: - “Bottle Racers” builds on the information imparted to the students in Ch. 2 of our Glencoe sci ...
Energy Conversion and Rural Electrification
... • Nuclear Energy: is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom- the energy that holds the nucleus together. The nucleus of a uranium atom is an example of nuclear energy. • Stored Mechanical Energy: is energy stored in objects by the application of a force. Compressed springs and stretched rubber ...
... • Nuclear Energy: is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom- the energy that holds the nucleus together. The nucleus of a uranium atom is an example of nuclear energy. • Stored Mechanical Energy: is energy stored in objects by the application of a force. Compressed springs and stretched rubber ...
Introduction - WordPress.com
... • Nuclear Energy: is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom- the energy that holds the nucleus together. The nucleus of a uranium atom is an example of nuclear energy. • Stored Mechanical Energy: is energy stored in objects by the application of a force. Compressed springs and stretched rubber ...
... • Nuclear Energy: is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom- the energy that holds the nucleus together. The nucleus of a uranium atom is an example of nuclear energy. • Stored Mechanical Energy: is energy stored in objects by the application of a force. Compressed springs and stretched rubber ...
Integrated Science Energy Test
... a) Work input is equal to work output. b) Work input is greater than work output. c) Work input is less than work output. d) The IMA is always equal to one. 29. Do ideal machines exist? Why or why not? (2 pts) Ideal machines do not exist because some work is always lost due to friction. ...
... a) Work input is equal to work output. b) Work input is greater than work output. c) Work input is less than work output. d) The IMA is always equal to one. 29. Do ideal machines exist? Why or why not? (2 pts) Ideal machines do not exist because some work is always lost due to friction. ...
Energy - Catawba County Schools
... * Chemical energy is the energy stored in chemical bond. * When bonds are broken, the released energy can do work. * Ex. Coal, gasoline * Electrical energy is energy associated with electrical charges. * Batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy. * Ex. Lightning * Electromagnetic energy ...
... * Chemical energy is the energy stored in chemical bond. * When bonds are broken, the released energy can do work. * Ex. Coal, gasoline * Electrical energy is energy associated with electrical charges. * Batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy. * Ex. Lightning * Electromagnetic energy ...
Physics Demonstration
... A boulder is sitting on the top of a mountain. The boulder has a mass of 500 kg. The mountain is 1500 meters high. What is the boulder’s potential energy before it released? ...
... A boulder is sitting on the top of a mountain. The boulder has a mass of 500 kg. The mountain is 1500 meters high. What is the boulder’s potential energy before it released? ...
Energy and its importance script
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. Energy is found in many sources in nature, including sunlight, wind, water, plants, and animals. All activities of living things need energy. Appliances and machines need energy to work too. Therefore, energy is very important to mankind. The Differe ...
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. Energy is found in many sources in nature, including sunlight, wind, water, plants, and animals. All activities of living things need energy. Appliances and machines need energy to work too. Therefore, energy is very important to mankind. The Differe ...
Physical Science Plans Week 15
... SC.7.P.11.2 (AA) – Investigate and describe the transformation of energy from one form to another. SC.6.P.11.1 – Explore the Law of Conservation of Energy by differentiating between potential and kinetic energy. SC.7.P.11.3 – Cite evidence to explain that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only ...
... SC.7.P.11.2 (AA) – Investigate and describe the transformation of energy from one form to another. SC.6.P.11.1 – Explore the Law of Conservation of Energy by differentiating between potential and kinetic energy. SC.7.P.11.3 – Cite evidence to explain that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only ...
Energy
... Solar Energy, radiant energy produced in the Sun as a result of nuclear fusion reactions. Flat plate collectors utilize the sun’s energy to warm a carrier fluid, which in turn provides usable heat to a household solar energy contributes to the growth of plant life (biomass) . SOLAR CELL, SOLAR COOKE ...
... Solar Energy, radiant energy produced in the Sun as a result of nuclear fusion reactions. Flat plate collectors utilize the sun’s energy to warm a carrier fluid, which in turn provides usable heat to a household solar energy contributes to the growth of plant life (biomass) . SOLAR CELL, SOLAR COOKE ...
Chapter 9 Motion Notes
... • Mechanical Energy can be all potential energy, all kinetic energy or part potential and part kinetic energy ...
... • Mechanical Energy can be all potential energy, all kinetic energy or part potential and part kinetic energy ...
File
... Test Prep Questions: Answer the following questions in order to review for this Thursday’s test questions. (1) A car uses chemical energy in gasoline to move. What form does the gasoline change into that helps the car to move? a. thermal energy c. mechanical energy b. sound energy d. nuclear energy ...
... Test Prep Questions: Answer the following questions in order to review for this Thursday’s test questions. (1) A car uses chemical energy in gasoline to move. What form does the gasoline change into that helps the car to move? a. thermal energy c. mechanical energy b. sound energy d. nuclear energy ...
Energy and Work - AP Physics 2 Homework Page
... Give the SI units for energy Use and rearrange the equations for potential energy, kinetic energy to solve problems Analyse real world situations in terms of energy and work (e.g. rollercoasters) ...
... Give the SI units for energy Use and rearrange the equations for potential energy, kinetic energy to solve problems Analyse real world situations in terms of energy and work (e.g. rollercoasters) ...
Energy PowerPoint #1
... • Nuclear energy can be used to create electricity, but it must first be released from the atom. • A nuclear reactor, or power plant, is a series of machines that can control nuclear fission to produce electricity. • About 15 percent of the worlds electricity is generated by nuclear ...
... • Nuclear energy can be used to create electricity, but it must first be released from the atom. • A nuclear reactor, or power plant, is a series of machines that can control nuclear fission to produce electricity. • About 15 percent of the worlds electricity is generated by nuclear ...
S8P2 Energy Transformations - Mrs. Carnes
... The Law of Conservation of Energy • No matter how energy is transformed, energy itself is not made or destroyed. • Law of Conservation of Energy states while energy may change from one form to another, energy is neither created nor destroyed ...
... The Law of Conservation of Energy • No matter how energy is transformed, energy itself is not made or destroyed. • Law of Conservation of Energy states while energy may change from one form to another, energy is neither created nor destroyed ...
energy around us
... c. Show your card when instructed to. (The back of your card should have clues.) ...
... c. Show your card when instructed to. (The back of your card should have clues.) ...
What is a wave?
... CONDENSATION is defined as the conversion of a substance (like water) from the vapor state to a denser liquid state that is initiated by a reduction in temperature of the vapor. This process is responsible for the formation of clouds. Condensation is also a vital component of the water cycle for cl ...
... CONDENSATION is defined as the conversion of a substance (like water) from the vapor state to a denser liquid state that is initiated by a reduction in temperature of the vapor. This process is responsible for the formation of clouds. Condensation is also a vital component of the water cycle for cl ...