is energy
... • Nothing is lost when the reaction occurs • it is simply rearranged – Matter cannot be neither created or destroyed, but may be changed from one form to another ...
... • Nothing is lost when the reaction occurs • it is simply rearranged – Matter cannot be neither created or destroyed, but may be changed from one form to another ...
Forms Of Energy
... energy makes everything happen and can be divided into two types: stored energy is called potential energy. moving energy is called kinetic energy. CHAPTER 3 FORMS OF ENERGY - XPLORA Sat, 22 Apr 2017 12:28:00 GMT chapter 4 forms of energy activity 4.1: the story of energy study the picture showing t ...
... energy makes everything happen and can be divided into two types: stored energy is called potential energy. moving energy is called kinetic energy. CHAPTER 3 FORMS OF ENERGY - XPLORA Sat, 22 Apr 2017 12:28:00 GMT chapter 4 forms of energy activity 4.1: the story of energy study the picture showing t ...
Slide 1
... distance, it has done more work. You can use work to measure changes in energy. • Place two identical books on the table so there is a gap of about 8 cm between books. Place a sheet of notebook paper on the books so it covers the gap shown. Now drop a penny from a height of 10 cm onto the paper abov ...
... distance, it has done more work. You can use work to measure changes in energy. • Place two identical books on the table so there is a gap of about 8 cm between books. Place a sheet of notebook paper on the books so it covers the gap shown. Now drop a penny from a height of 10 cm onto the paper abov ...
Introduction to Energy
... In 2004, the United States used 30-35 percent more energy than it did in the 1970s. That might sound like a lot, but the population increased by over 30 percent and the nations gross national product (the total value of all the goods and services produced by a nation in one year) was more than 80 p ...
... In 2004, the United States used 30-35 percent more energy than it did in the 1970s. That might sound like a lot, but the population increased by over 30 percent and the nations gross national product (the total value of all the goods and services produced by a nation in one year) was more than 80 p ...
Introduction to Energy
... 1979 and 1980people used less energy. In 1985, when prices started to drop, energy use began to increase. We dont want to simplify energy demand too much. The price of energy is not the only factor in the equation. Other factors that affect how much energy we use include the publics concern for t ...
... 1979 and 1980people used less energy. In 1985, when prices started to drop, energy use began to increase. We dont want to simplify energy demand too much. The price of energy is not the only factor in the equation. Other factors that affect how much energy we use include the publics concern for t ...
Chapter 15 Notes
... ________ be replaced except over the course of _____________ of years. • Nonrenewable energy resources include oil, natural gas, coal, and uranium. Renewable Energy Resources • Renewable energy resources are resources that can be ____________ in a relatively _________ period of time. • Renewable ene ...
... ________ be replaced except over the course of _____________ of years. • Nonrenewable energy resources include oil, natural gas, coal, and uranium. Renewable Energy Resources • Renewable energy resources are resources that can be ____________ in a relatively _________ period of time. • Renewable ene ...
Test 3 Review
... The Nature of Energy. Energy is the ability to cause change or do work. Change occurs or work is done when energy is transferred from one object to another. There are two major categories of energy: Kinetic energy and potential energy. Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion. Th ...
... The Nature of Energy. Energy is the ability to cause change or do work. Change occurs or work is done when energy is transferred from one object to another. There are two major categories of energy: Kinetic energy and potential energy. Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion. Th ...
2.01 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
... Absorption: Sound can pass through or into a material; this is called absorption, because the material is absorbing the vibrations of the sound wave as it passes through it or into it. In __________ frequency waves more sound is absorbed. Refraction: When sound travels from one material to another i ...
... Absorption: Sound can pass through or into a material; this is called absorption, because the material is absorbing the vibrations of the sound wave as it passes through it or into it. In __________ frequency waves more sound is absorbed. Refraction: When sound travels from one material to another i ...
Work Energy Part 2
... Now the work done by friction is more than the initial potential energy. In this case, the child will not slide all the way down the slide. The 735 J of potential energy is not enough to overcome all the friction needed to reach the end of the slide. ...
... Now the work done by friction is more than the initial potential energy. In this case, the child will not slide all the way down the slide. The 735 J of potential energy is not enough to overcome all the friction needed to reach the end of the slide. ...
Energy Basics - the Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki!!
... Energy transfer In this model the energy is located in one place, and when something happens energy is transferred from that place to another by a process. Typical use of language: ‘The energy in the battery is transferred to the bulb by electricity and then from the bulb to the surroundings by l ...
... Energy transfer In this model the energy is located in one place, and when something happens energy is transferred from that place to another by a process. Typical use of language: ‘The energy in the battery is transferred to the bulb by electricity and then from the bulb to the surroundings by l ...
What Is Energy?
... difficult to generate large amounts of solar energy. 31. Answers will vary. Sample answer: The dams can affect the ecology of a river. ...
... difficult to generate large amounts of solar energy. 31. Answers will vary. Sample answer: The dams can affect the ecology of a river. ...
Chapter 12 Work and Energy
... position, shape, or condition of the object is called potential energy Potential energy is stored energy Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in any type of stretched or compressed elastic material, such as a spring or a ...
... position, shape, or condition of the object is called potential energy Potential energy is stored energy Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in any type of stretched or compressed elastic material, such as a spring or a ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy
... demonstrations (and short play time) • Please set up your science journals with the following data table (using a ruler is optional) Activity ...
... demonstrations (and short play time) • Please set up your science journals with the following data table (using a ruler is optional) Activity ...
Energy
... Mini Anchor Charts: Create your own graphic organizers with your group. First make a list of all of the energy words that you are confident that you can explain. Create an organizer for these words (take a picture). Then create a new organizer that is based on new criteria for example: the use, a tr ...
... Mini Anchor Charts: Create your own graphic organizers with your group. First make a list of all of the energy words that you are confident that you can explain. Create an organizer for these words (take a picture). Then create a new organizer that is based on new criteria for example: the use, a tr ...
1300 kg • (11m/s) 2 - Solon City Schools
... Trace the energy conversion of a coal- fired power plant. ...
... Trace the energy conversion of a coal- fired power plant. ...
15.1 Energy and Its Forms
... What is meant by kinetic energy? Applying a force to an object through some distance sets that object into motion An object in motion can apply a force to something and in turn do work to that object (it has energy– the ability to do work) Kinetic Energy – energy an object has because it is in motio ...
... What is meant by kinetic energy? Applying a force to an object through some distance sets that object into motion An object in motion can apply a force to something and in turn do work to that object (it has energy– the ability to do work) Kinetic Energy – energy an object has because it is in motio ...
CHAPTER 15 POWERPOINT
... What is meant by kinetic energy? Applying a force to an object through some distance sets that object into motion An object in motion can apply a force to something and in turn do work to that object (it has energy– the ability to do work) Kinetic Energy – energy an object has because it is in motio ...
... What is meant by kinetic energy? Applying a force to an object through some distance sets that object into motion An object in motion can apply a force to something and in turn do work to that object (it has energy– the ability to do work) Kinetic Energy – energy an object has because it is in motio ...
Different forms of energy have different uses.
... increases when the spring is compressed and decreases when it is released. Look at the bow that is being bent in the photograph below. When the bowstring is pulled, the bow bends and stores energy. When the string is released, both the string and the bow return to their normal shape. Stored energy i ...
... increases when the spring is compressed and decreases when it is released. Look at the bow that is being bent in the photograph below. When the bowstring is pulled, the bow bends and stores energy. When the string is released, both the string and the bow return to their normal shape. Stored energy i ...
ERT 455 - Portal UniMAP
... the product is the heat energy in the milk. Heat energy is added to the milk by the pump and by the hot water passing through the heat exchanger. Cooling water then removes part of the heat energy and some of the heat energy is also lost to the surroundings. ...
... the product is the heat energy in the milk. Heat energy is added to the milk by the pump and by the hot water passing through the heat exchanger. Cooling water then removes part of the heat energy and some of the heat energy is also lost to the surroundings. ...
Unit Three Assessment Study Guide
... ____ 21. Matter is needed to transfer thermal energy by a. conduction. c. radiation. b. convection. d. both a and b ____ 22. Disorder in the universe increases because a. spontaneous changes produce more order in a system. b. work produces disorder in a system. c. work produces waste heat, which lea ...
... ____ 21. Matter is needed to transfer thermal energy by a. conduction. c. radiation. b. convection. d. both a and b ____ 22. Disorder in the universe increases because a. spontaneous changes produce more order in a system. b. work produces disorder in a system. c. work produces waste heat, which lea ...
Energy Chapter 5
... changing the mass and velocity have the same affect on KE? NO – changing the velocity has a greater effect on KE than changing the mass by the same factor. WHY? – because velocity is squared. Therefore, doubling the mass will double the KE, but doubling the velocity will quadruple the KE. ...
... changing the mass and velocity have the same affect on KE? NO – changing the velocity has a greater effect on KE than changing the mass by the same factor. WHY? – because velocity is squared. Therefore, doubling the mass will double the KE, but doubling the velocity will quadruple the KE. ...
Energy Use - Effingham County Schools
... All power plants convert heat into electricity using steam. At nuclear power plants, the heat to make the steam is created when atoms split- fission. Fission takes place when the nucleus of a heavy atom like plutonium or uranium is split into two when struck by a neutron. This releases more neutron ...
... All power plants convert heat into electricity using steam. At nuclear power plants, the heat to make the steam is created when atoms split- fission. Fission takes place when the nucleus of a heavy atom like plutonium or uranium is split into two when struck by a neutron. This releases more neutron ...
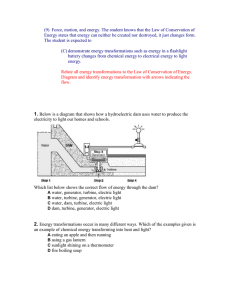
(9) Force, motion, and energy - 2010
... A. Energy is created. B. Energy is destroyed. C. The total amount of energy remains the same. D. One form of energy changes into more than one other form of energy. 19. Which form of energy is always generated whenever an energy transformation takes place? A. electrical energy B. light energy C. hea ...
... A. Energy is created. B. Energy is destroyed. C. The total amount of energy remains the same. D. One form of energy changes into more than one other form of energy. 19. Which form of energy is always generated whenever an energy transformation takes place? A. electrical energy B. light energy C. hea ...
World energy consumption
World energy consumption refers to the total energy used by all of human civilization. Typically measured per year, it involves all energy harnessed from every energy source applied towards humanity's endeavors across every single industrial and technological sector, across every country. Being the power source metric of civilization, World Energy Consumption has deep implications for humanity's social-economic-political sphere.Institutions such as the International Energy Agency (IEA), the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), and the European Environment Agency record and publish energy data periodically. Improved data and understanding of World Energy Consumption may reveal systemic trends and patterns, which could help frame current energy issues and encourage movement towards collectively useful solutions.In 2012, the IEA estimated that the world energy consumption was 155,505 terawatt-hour (TWh), or 5.598 × 1020 joules. This works out to 17.7 TW, or a bit less than the estimated 20 TW produced by radioactive decay on earth. From 2000–2012 coal was the source of energy with the largest growth. The use of oil and natural gas also had considerable growth, followed by hydro power and renewable energy. Renewable energy grew at a rate faster than any other time in history during this period, which can possibly be explained by an increase in international investment in renewable energy. The demand for nuclear energy decreased, possibly due to the accidents at Chernobyl and Three Mile Island.In 2011, expenditures on energy totaled over 6 trillion USD, or about 10% of the world gross domestic product (GDP). Europe spends close to one quarter of the world energy expenditures, Americans close to 20%, and Japan 6%.