Energy and Energy Resources Practice Test
... ____ 13. As a baseball flies through the air after being hit, which of the following types of energy does it have? a. potential energy c. mechanical energy b. kinetic energy d. chemical energy ____ 14. What is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching called? a. friction c. ...
... ____ 13. As a baseball flies through the air after being hit, which of the following types of energy does it have? a. potential energy c. mechanical energy b. kinetic energy d. chemical energy ____ 14. What is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching called? a. friction c. ...
Chapter 15 Power Point Notes
... 3. Describe the energy conversions that take place when a flashlight is turned on. 4. Identify the conversions: An object is raised and then allowed to fall. As it hits the ground it stops, produces a sound, and becomes warmer. ...
... 3. Describe the energy conversions that take place when a flashlight is turned on. 4. Identify the conversions: An object is raised and then allowed to fall. As it hits the ground it stops, produces a sound, and becomes warmer. ...
Energy - GZ @ Science Class Online
... renewable as long as the same amount of trees are planted to replace those cut down. The carbon dioxide released when burning the fuels will also be reabsorbed by the plants as they grow. ...
... renewable as long as the same amount of trees are planted to replace those cut down. The carbon dioxide released when burning the fuels will also be reabsorbed by the plants as they grow. ...
Energy - Cobb Learning
... work (exerts a force over a distance to move an object) the object or organism uses energy. ...
... work (exerts a force over a distance to move an object) the object or organism uses energy. ...
Potential Energy Kinetic Energy
... water boils producing steam. The steam is then used to drive turbines which turn electrical generators. Solar cells produce electricity directly from the sun’s radiation. Fossil Fuels are an energy resource formed from the remains of organisms that lived long ago, includes coal, oil, and natural gas ...
... water boils producing steam. The steam is then used to drive turbines which turn electrical generators. Solar cells produce electricity directly from the sun’s radiation. Fossil Fuels are an energy resource formed from the remains of organisms that lived long ago, includes coal, oil, and natural gas ...
Energy:
... Information on Research Project Homework Energy Jigsaw Homework Begin Project Research ...
... Information on Research Project Homework Energy Jigsaw Homework Begin Project Research ...
Energy - GZ @ Science Class Online
... renewable as long as the same amount of trees are planted to replace those cut down. The carbon dioxide released when burning the fuels will also be reabsorbed by the plants as they grow. ...
... renewable as long as the same amount of trees are planted to replace those cut down. The carbon dioxide released when burning the fuels will also be reabsorbed by the plants as they grow. ...
Energy density - pssurvival.com
... which will be available for billions of years (in the form of sunlight) but so far (2016), sustained fusion power production continues to be elusive. Power from fission of uranium and thorium in nuclear power plants will be available for many decades or even centuries because of the plentiful supply ...
... which will be available for billions of years (in the form of sunlight) but so far (2016), sustained fusion power production continues to be elusive. Power from fission of uranium and thorium in nuclear power plants will be available for many decades or even centuries because of the plentiful supply ...
6-5.2 - S2TEM Centers SC
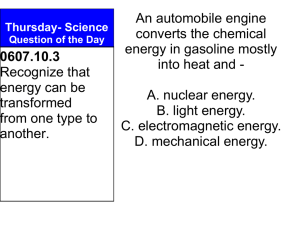
... types of energy such as mechanical, sound, light, and heat. (See Indicator 65.4) All of the energy from the electric circuit eventually changes to another form, much of it heat energy. The energy from all of these transformations still exists. The total amount of energy is conserved. It is not ess ...
... types of energy such as mechanical, sound, light, and heat. (See Indicator 65.4) All of the energy from the electric circuit eventually changes to another form, much of it heat energy. The energy from all of these transformations still exists. The total amount of energy is conserved. It is not ess ...
Energy: Forms and Changes
... work (exerts a force over a distance to move an object) the object or organism uses energy. ...
... work (exerts a force over a distance to move an object) the object or organism uses energy. ...
STUDENT GUIDE
... That energy can be demonstrated, observed and measured in a system can be stated because of the Law of Conservation of Energy. Contributions of many scientists over time and new discoveries about different forms of energy have all supported the current acceptance of the Law of Conservation of Energy ...
... That energy can be demonstrated, observed and measured in a system can be stated because of the Law of Conservation of Energy. Contributions of many scientists over time and new discoveries about different forms of energy have all supported the current acceptance of the Law of Conservation of Energy ...
Energy
... •The ability to do work or cause change is called energy. •When an object or living thing does work on another object, some of its energy is transferred to that object. •You can think of work then, as the transfer of energy. •Power is the rate at which energy is transferred, or the amount of energy ...
... •The ability to do work or cause change is called energy. •When an object or living thing does work on another object, some of its energy is transferred to that object. •You can think of work then, as the transfer of energy. •Power is the rate at which energy is transferred, or the amount of energy ...
Chemical Energy
... • If we took that same 3 kilograms of gasoline and broke open every single atom in it we would release 2.7 x 1017 Joules of energy! • This is almost 2 billion times the energy we obtained from the "ordinary" burning of one gallon of gasoline! ...
... • If we took that same 3 kilograms of gasoline and broke open every single atom in it we would release 2.7 x 1017 Joules of energy! • This is almost 2 billion times the energy we obtained from the "ordinary" burning of one gallon of gasoline! ...
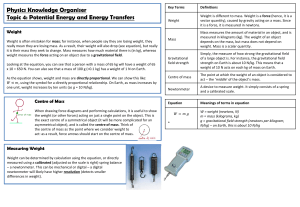
4 Potential energy and elasticity
... When boiling water in kettle, electrical potential energy is transferred to thermal energy When using your phone, chemical potential energy is transferred to electrical energy, which is transferred to the surroundings, where it is stored as thermal energy. The amount of energy that a moving obje ...
... When boiling water in kettle, electrical potential energy is transferred to thermal energy When using your phone, chemical potential energy is transferred to electrical energy, which is transferred to the surroundings, where it is stored as thermal energy. The amount of energy that a moving obje ...
Energy: Forms and Changes
... The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The greater the mass of a moving object, the more kinetic energy it ...
... The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The greater the mass of a moving object, the more kinetic energy it ...
Energy, Work, and Power
... M = mass in kg of the object being lifted G = strength of gravity, 10N kg-1 h = change in height, in metres ...
... M = mass in kg of the object being lifted G = strength of gravity, 10N kg-1 h = change in height, in metres ...
Energy:
... a form of kinetic energy due to the random motion of the particles in an object; the faster the particles move, the greater the thermal energy. also depends on the number of particles (for example, even though steam particles from a hot bath move faster than the liquid water particles in the bath, t ...
... a form of kinetic energy due to the random motion of the particles in an object; the faster the particles move, the greater the thermal energy. also depends on the number of particles (for example, even though steam particles from a hot bath move faster than the liquid water particles in the bath, t ...
Grade 12 Unit 3 - Amazon Web Services
... If the metric (SI) system is used, force is measured in Newtons (N); displacement is in meters (m); velocity is in meters/second (m/s); mass is in kilograms (kg); and work and energy are both measured in joules (J). A Newton or force is equal to mass x acceleration; therefore, a Newton is actually a ...
... If the metric (SI) system is used, force is measured in Newtons (N); displacement is in meters (m); velocity is in meters/second (m/s); mass is in kilograms (kg); and work and energy are both measured in joules (J). A Newton or force is equal to mass x acceleration; therefore, a Newton is actually a ...
Work and Energy Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the
... ____ 19. The kinetic energy of the pendulum bob in Figure 15-1 increases the most between locations a. A and B. c. B and D. b. A and C. d. C and D. ____ 20. The equation E = mc2 relates energy and a. force. c. mass. b. gravity. d. work. ____ 21. In which of the following does Einstein’s famous equat ...
... ____ 19. The kinetic energy of the pendulum bob in Figure 15-1 increases the most between locations a. A and B. c. B and D. b. A and C. d. C and D. ____ 20. The equation E = mc2 relates energy and a. force. c. mass. b. gravity. d. work. ____ 21. In which of the following does Einstein’s famous equat ...
Class Notes
... gas. These substances are called fossil fuels. In Ireland we mainly use peat, gas, coal and oil to make electricity. ...
... gas. These substances are called fossil fuels. In Ireland we mainly use peat, gas, coal and oil to make electricity. ...
Forms of Energy Sources
... Scientifically, energy is defined as the ability to do work. While there are many forms of energy, they can be grouped into two categories: potential energy, or stored energy; and kinetic energy, or energy of motion. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy and it is possessed by things such as ...
... Scientifically, energy is defined as the ability to do work. While there are many forms of energy, they can be grouped into two categories: potential energy, or stored energy; and kinetic energy, or energy of motion. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy and it is possessed by things such as ...
energy - Ms. McGuirk`s 6th Grade Science Class
... Light Energy • Produced by vibrations of electrically charged particles. ...
... Light Energy • Produced by vibrations of electrically charged particles. ...
Energy policy of Australia
The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of Government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal.Federal energy policies continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production as the exports by those industries contribute significantly to the earnings of foreign exchange and government revenues. Australia is one of the most coal-dependent countries in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage, despite the fact that the coal industry produces approximately 38% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. Federal policy has reverted to a pro-coal economy with drastic cuts to alternate and renewable energy government offices, targets and subsidies ""With proposals to repeal the carbon price, dismantle the Climate Change Authority and the Clean Energy Finance Corporation, and the dilution of the Renewable Energy Target already in train, the budget measures, which include the closure of the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, the dumping of the million solar roofs program (both contrary to election promises) and the research funding cuts at the CSIRO, Bureau of Meteorology and elsewhere,...the obliteration of the Clean Energy Future package] is complete"". The Conservative government has implemented many of the 75-point wish list drawn up by the influential Institute of Public Affairs. The Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) is a right-wing, corporate funded think tank based in Melbourne. It has close links to the Liberal Party of Australia. The IPA's key policy positions include: advocacy for privatisation and deregulation; attacks on the positions of unions and non-government organisations; support of assimilationist indigenous policy (cf. the Bennelong Society) and refutation of the science involved with environmental issues such as climate change. Federal policy was beginning to change during the previous Liberal government with the publication of the Garnaut report and Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper, the announcement of an Emissions Trading Scheme to commence in 2010, and the announcement of a national mandatory renewable energy target of 20% of electricity supply in Australia by 2020.State energy policies such as Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets ensure that renewable energy contributes a greater percentage of the country's energy supply.Due to Australia's reliance on coal and gas for energy, in 2000 the country was the highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the developed world, irrespective of whether or not emissions from land clearing were included. It is also one of the countries most at risk from climate change according to the Stern report.Renewable energy commercialisation in Australia is an area of relatively minor activity compared to the fossil fuels industry. Australia's renewable energy industries are diverse, covering numerous energy sources and scales of operation, and currently contribute about 8–10% of Australia's total energy supply. The major area where renewable energy is growing is in electricity generation following the introduction of government Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets. The two most populous states, New South Wales and Victoria have renewable energy targets of 20% and 25% respectively by 2020.