* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
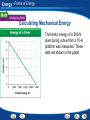
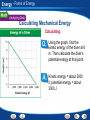
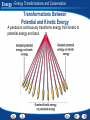
Energy - What Is Energy? Using Prior Knowledge Before you read, look at the section headings and visuals to see what this section is about. Then write what you know about energy in a graphic organizer like the one below. As you read, write what you learn. 1. 2. What You Know The joule is the unit of work. Energy has different forms. What You Learned Energy - What Is Energy? Kinetic Energy Kinetic energy increases as mass and velocity increases. Energy Kinetic Energy Definition The energy of motion Kinetic energy depends on… Mass and Velocity Calculating Kinetic Energy ½ mass times velocity2 Increase in Mass A similar increase in kinetic energy. Example doubling mass doubles kinetic energy. Increase in Velocity Increase in velocity changes kinetic energy differently due to the exponent. Example: doubling velocity, quadruples kinetic energy. Energy - What Is Energy? Exponents An exponent tells how many times a number is used as a factor. For example, 3 X 3 can be written as 32. You read this number as “three squared.” An exponent of 2 indicates that the number 3 is used as a factor two times. To find the value of a squared number, multiply the number by itself. 32 = 3 X 3 = 9 Practice Problem What is the value of the number 82? 64 Energy - What Is Energy? Potential Energy Gravitational potential energy increases as weight and height increase. Energy Potential Energy Definition Energy that is stored and held in readiness. Gravitational Potential Energy Based on Height and Weight Elastic Potential Energy Energy stored in objects that are stressed or compressed Potential Chemical Energy Energy stored in chemical bonds. Calculating Gravitational Potential Energy Gravitational Potential Energy = weight times height Energy Energy, Work, and Power Energy The ability to do work or cause change Transfer of Energy When an object or organism does work on another object or organism, some of the energy is transferred to the object or organism being acted on. Power The rate at which energy is being transferred Calculating Power The amount of energy transferred divided by the amount of time required for the transfer. This is described as a unit rate. The higher the unit rate, the more power. Energy End of Section: What Is Energy? Energy - Forms of Energy Calculating Mechanical Energy The kinetic energy of a 500-N diver during a dive from a 10-m platform was measured. These data are shown in the graph. Energy - Forms of Energy Calculating Mechanical Energy Reading Graphs: According to the graph, how much kinetic energy does the diver have at 8 m? About 1000 J Energy - Forms of Energy Calculating Mechanical Energy Calculating: Using the graph, find the kinetic energy of the diver at 6 m. Then calculate the diver’s potential energy at that point. Kinetic energy = about 2000 J; potential energy = about 3000 J Energy - Forms of Energy Calculating Mechanical Energy Inferring: The mechanical energy of the diver is the same at every height. What is the mechanical energy of the diver? About 5000 J Energy - Forms of Energy Building Vocabulary After you read the section, reread the paragraphs that contain definitions of Key Terms. Use the information you have learned to write a definition of each Key Term in your own words. Key Terms: Examples: mechanical nuclear energy energy A type The form of potential of energyenergy associated calledwith nuclear the position energyand is motion in stored ofthe an object nucleus is of called an atom. mechanical energy. electromagnetic thermal energy energy The sunlight that you eachenergy day is of a form of total potential andsee kinetic the particles in electromagnetic an object is calledenergy. thermal energy. electrical energy The energy of electric charges is electrical energy. chemical energy Chemical energy is potential energy stored in the chemical bonds that hold chemical compounds together. Energy Mechanical Energy Definition Mechanical energy is a result of the potential and kinetic energy associated with an object. Measurement Mechanical Energy is measured in Joules (J). Calculating Mechanical Energy Add together the potential and kinetic energy of an object. Energy Examples of Other Forms of Energy Thermal Energy Created by combustion or friction. The faster the particles move the more thermal energy produced. Electrical Energy Static Electricity Chemical Energy Energy stored in the food you eat. Nuclear Energy Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. Energy End of Section: Forms of Energy Energy - Energy Transformations and Conservation Energy Transformations Question Answer What is an energy transformation? An energy transformation is a change from one form of energy to another. What are some examples of transformations between potential and kinetic energy? Juggling and pendulums show transformations between potential and kinetic energy. What is conservation of energy? The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Energy - Energy Transformations and Conservation Energy Transformations Most forms of energy can be transformed into other forms. Energy Potential and Kinetic Transformation Kinetic to Potential As you throw something in the air, the kinetic energy decreases and the potential energy increases until the object reaches its maximum height. Potential to Kinetic Once an object reaches its maximum height after being thrown in the air and begins to fall, potential energy decreases as kinetic energy increases. What is conservation of energy? The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Energy - Energy Transformations and Conservation Transformations Between Potential and Kinetic Energy A pendulum continuously transforms energy from kinetic to potential energy and back. Energy Other Transformation Friction causes… •Mechanical energy to convert to thermal energy • Because of this no machine is 100% efficient Einstein’s Theory of Relativity Explains that energy can sometimes be created by destroying matter. Based on Einstein’s Theory… In some situations, energy alone is not conserved. However, since matter can be transformed to energy, scientists say matter and energy together are always conserved. Energy End of Section: Energy Transformations and Conservation Energy - Energy and Fossil Fuels Previewing Visuals When you preview, you look ahead at the material to be read. Preview Figure 18. Then write two questions that you have about the diagram in a graphic organizer like the one below. As you read, answer your questions. Using Fossil Fuel Energy Q. What energy transformation occurs in the sun? A. Nuclear energy to thermal energy and electromagnetic energy Q. What energy transformation takes place when coal is burned? A. Chemical energy to thermal energy Energy Fossil Fuels Examples: Coal, petroleum, and natural gas are all examples of fossil fuels. Stored as… Chemical Potential Energy Originated from… The sun Release of Release of potential energy is a result of potential chemical burning fossil fuels. Also know as combustion. energy Energy Energy Conversions On the Sun During nuclear fusion, nuclear energy is transformed into electromagnetic energy and thermal energy. During Photosynthesis Electromagnetic energy from the sun is transformed to chemical potential energy in the plant. During Combustion Potential chemical energy is transformed to thermal energy. Use of generators Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy Energy - Energy and Fossil Fuels Use of Fossil Fuels Fossil fuels can be burned to release the chemical energy stored millions of years ago. Energy End of Section: Energy and Fossil Fuels