Forms of Energy Energy Notes Forms of Energy All forms of Energy
... example of gravitational potential energy. When the water in the reservoir is released to spin the turbines, it becomes motion energy. ...
... example of gravitational potential energy. When the water in the reservoir is released to spin the turbines, it becomes motion energy. ...
Joules (J) are the units of energy
... 4. Dissipated – when energy is wasted & ‘lost’, usually as heat 5. Work – the transfer of energy 6. Power – the rate of doing work/transferring energy 7. Specific Heat Capacity – the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C 8. Energy Resource – a way of getting ...
... 4. Dissipated – when energy is wasted & ‘lost’, usually as heat 5. Work – the transfer of energy 6. Power – the rate of doing work/transferring energy 7. Specific Heat Capacity – the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C 8. Energy Resource – a way of getting ...
Energy and Design Process - Study Guide - Team 6
... 19. A old metal swing set left outside in the rain starts to rust. This is an example of a __irreversible chemical___ change. 20. Mr. Smith’s class was trying to determine if the height at which a paper helicopter is dropped affects that speed that it will fall. They made paper helicopters using the ...
... 19. A old metal swing set left outside in the rain starts to rust. This is an example of a __irreversible chemical___ change. 20. Mr. Smith’s class was trying to determine if the height at which a paper helicopter is dropped affects that speed that it will fall. They made paper helicopters using the ...
Reading: Different Forms of Energy
... Mechanical Energy The school bus you ride in, a frog leaping through the air, and even the sounds you hear all have mechanical energy. Mechanical energy is the energy associated with the motion or position of an object. Mechanical energy can occur as kinetic energy or potential energy. Thermal Energ ...
... Mechanical Energy The school bus you ride in, a frog leaping through the air, and even the sounds you hear all have mechanical energy. Mechanical energy is the energy associated with the motion or position of an object. Mechanical energy can occur as kinetic energy or potential energy. Thermal Energ ...
types of energy
... in the form of rays or waves or particles and Examples • -Heat from the sun warming your face • -Heat from a light bulb • -Heat from a fire ...
... in the form of rays or waves or particles and Examples • -Heat from the sun warming your face • -Heat from a light bulb • -Heat from a fire ...
Energy Review Worksheet - KEY
... Complete the following worksheet on a separate sheet of paper. Use your textbook to help you. 1. What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work 2. What are the different forms of energy? Potential, kinetic, electromagnetic, thermal, sound, nuclear, etc. 3. Compare kinetic and potential energy. Pot ...
... Complete the following worksheet on a separate sheet of paper. Use your textbook to help you. 1. What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work 2. What are the different forms of energy? Potential, kinetic, electromagnetic, thermal, sound, nuclear, etc. 3. Compare kinetic and potential energy. Pot ...
Thermal Energy Notes - Burnet Middle School
... Thermal Energy Often people mistakenly use thermal energy, temperature, and heat as interchangeable terms, however each has a very unique and specific scientific meaning. Matter is made up of particles or molecules. These molecules move (or vibrate) constantly. This is because the particles have kin ...
... Thermal Energy Often people mistakenly use thermal energy, temperature, and heat as interchangeable terms, however each has a very unique and specific scientific meaning. Matter is made up of particles or molecules. These molecules move (or vibrate) constantly. This is because the particles have kin ...
I. Forms of Energy - The Lesson Builder
... There are two basic types of energy, kinetic and potential. Kinetic energy is being used as an object is in motion. Potential energy is in storage just waiting to be used. Many things start out having potential energy, and then once they begin to move, the energy becomes kinetic. For example, a car ...
... There are two basic types of energy, kinetic and potential. Kinetic energy is being used as an object is in motion. Potential energy is in storage just waiting to be used. Many things start out having potential energy, and then once they begin to move, the energy becomes kinetic. For example, a car ...
Energy - murraysphysical
... 2. ______________ energy—the total amount of potential and kinetic energy in a system B. Law of Conservation of Energy—Energy may change from one form to another, but the ________________ of energy never changes. 1. Example—As a swing moves back and forth, its energy continually converts from ______ ...
... 2. ______________ energy—the total amount of potential and kinetic energy in a system B. Law of Conservation of Energy—Energy may change from one form to another, but the ________________ of energy never changes. 1. Example—As a swing moves back and forth, its energy continually converts from ______ ...
Energy
... P1. You do work when pushing a cart with a constant force. If you push the cart twice as far, how much is the work? P2. How much is the Kinetic Energy of a 2-kg object moving at 3.0 m/s? P3. You run a 100-W light bulb on for 1 hour. How much energy have you consumed? P4. What costs more to run: a 10 ...
... P1. You do work when pushing a cart with a constant force. If you push the cart twice as far, how much is the work? P2. How much is the Kinetic Energy of a 2-kg object moving at 3.0 m/s? P3. You run a 100-W light bulb on for 1 hour. How much energy have you consumed? P4. What costs more to run: a 10 ...
Energy Forms and Transformations
... • There are several other types of energy that are associated with the particles of objects. ...
... • There are several other types of energy that are associated with the particles of objects. ...
Chapter 2.3- Energy and Matter Notes CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS
... E=mc² (energy = mass x speed of light squared) In other words mass can be converted into LOTS of energy (This is how atomic bombs work!) Energy is the ability to do work or cause change Examples - Gasoline in a car makes it move - A spring in a pogo stick pushes a person upward - A tree falling can ...
... E=mc² (energy = mass x speed of light squared) In other words mass can be converted into LOTS of energy (This is how atomic bombs work!) Energy is the ability to do work or cause change Examples - Gasoline in a car makes it move - A spring in a pogo stick pushes a person upward - A tree falling can ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... types of energy involved in doing work (potential and kinetic, as well as other forms) and how work is done to transform that energy from one form to another. We will look at real life scenarios and calculate the amount of kinetic, gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy involved. ...
... types of energy involved in doing work (potential and kinetic, as well as other forms) and how work is done to transform that energy from one form to another. We will look at real life scenarios and calculate the amount of kinetic, gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy involved. ...
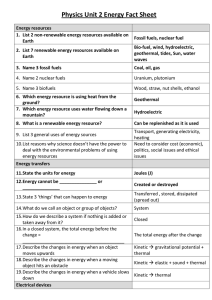
Physics Unit 2 Energy Fact Sheet
... 4. An electrical device uses 150J of energy in 3 seconds. Calculate the power of the appliance (4) 5. If 600J of work are done in 100 seconds, what is the power? (4) 6. A fish of 1kg mass is moving at 3m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the fish (4) 7. A person is 60kg and is lifted 2m up from the ...
... 4. An electrical device uses 150J of energy in 3 seconds. Calculate the power of the appliance (4) 5. If 600J of work are done in 100 seconds, what is the power? (4) 6. A fish of 1kg mass is moving at 3m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the fish (4) 7. A person is 60kg and is lifted 2m up from the ...
FXM Rev 2 Key - Grande Cache Community High School
... time This is a vector quantity that is a measure of the rate of change in displacement. It is measured in m/s. uniform motion An object with this type of motion is going a constant rate of velocity. It is not speeding up, slowing down or changing direction. All forces acting on this object are balan ...
... time This is a vector quantity that is a measure of the rate of change in displacement. It is measured in m/s. uniform motion An object with this type of motion is going a constant rate of velocity. It is not speeding up, slowing down or changing direction. All forces acting on this object are balan ...
The Science of Energy
... • Where does the body get the energy to shake a bottle? •How is energy stored in food? •What type of energy produced the radiant energy from the sun? •All energy can be traced back to what type? •If the source of energy must be burned, then how is it stored? ...
... • Where does the body get the energy to shake a bottle? •How is energy stored in food? •What type of energy produced the radiant energy from the sun? •All energy can be traced back to what type? •If the source of energy must be burned, then how is it stored? ...
Chemical Thermodynamics
... Energy can not be created nor destroyed, it can be converted from one form to another or transferred from a system to surroundings (or vice versa) ...
... Energy can not be created nor destroyed, it can be converted from one form to another or transferred from a system to surroundings (or vice versa) ...
Changing Energy Energy is the ability to do work. The many forms of
... You have learned that energy is the ability to do work or cause change. There are many different forms of energy. We may use one form of energy to run our cars, another to heat our homes, and still another to send TV pictures. People use large amounts of energy to help them perform work. Scientists ...
... You have learned that energy is the ability to do work or cause change. There are many different forms of energy. We may use one form of energy to run our cars, another to heat our homes, and still another to send TV pictures. People use large amounts of energy to help them perform work. Scientists ...
Energy Study Guide Part 1
... 9. What is electrical energy? Give 2 examples. The energy of moving electrons 1. TV/radio plugged in a socket 2. Charging a phone or tablet 10. What energy transformations must occur to make cars move up a hill? Chemical of gasoline changes into mechanical and thermal 11. When a light bulb is turned ...
... 9. What is electrical energy? Give 2 examples. The energy of moving electrons 1. TV/radio plugged in a socket 2. Charging a phone or tablet 10. What energy transformations must occur to make cars move up a hill? Chemical of gasoline changes into mechanical and thermal 11. When a light bulb is turned ...
Note-taking worksheet on Energy
... The law of conservation of energy states that energy may change from one form to another, but the _____________________ of energy does not change. a. Example – As a swing moves back and forth, its energy continually converts from __________________ to ________________ and back again. b. Example – If ...
... The law of conservation of energy states that energy may change from one form to another, but the _____________________ of energy does not change. a. Example – As a swing moves back and forth, its energy continually converts from __________________ to ________________ and back again. b. Example – If ...
Types of Energy Outline 6.1
... a. There is a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the mass of an object. The more mass an object has the greater the gravitational potential energy. b. There is also a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the height of an object. The higher that an object ...
... a. There is a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the mass of an object. The more mass an object has the greater the gravitational potential energy. b. There is also a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the height of an object. The higher that an object ...
Unit 6: Energy
... a. There is a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the mass of an object. The more mass an object has the greater the gravitational potential energy. b. There is also a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the height of an object. The higher that an object ...
... a. There is a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the mass of an object. The more mass an object has the greater the gravitational potential energy. b. There is also a direct relation between gravitational potential energy and the height of an object. The higher that an object ...
Planet Earth - Madeira City Schools
... the work done when a father lifts his daughter up into the air if he lifts her 1.5 m and uses a force of ...
... the work done when a father lifts his daughter up into the air if he lifts her 1.5 m and uses a force of ...