Forms of Energy * Day 4
... Thermal Energy The total potential energy and kinetic energy of all the microscopic particles in an object make up its thermal energy. When an object’s atoms move faster, its thermal energy increases, and the object ...
... Thermal Energy The total potential energy and kinetic energy of all the microscopic particles in an object make up its thermal energy. When an object’s atoms move faster, its thermal energy increases, and the object ...
Pifer.weebly.com – Physical Science page Types of Energy Chapter
... called ____________________________that are constantly moving. We generate electrical energy when we succeed to cause the these electrons to move from one atom to the other, with the use of _______________________ forces . Video: Electrical energy is transferred to _____________ energy and _________ ...
... called ____________________________that are constantly moving. We generate electrical energy when we succeed to cause the these electrons to move from one atom to the other, with the use of _______________________ forces . Video: Electrical energy is transferred to _____________ energy and _________ ...
Energy: - Weebly
... The internal motion of the atoms is called heat energy, because moving particles produce heat. Heat energy can be produced by friction. Heat energy causes changes in temperature and phase of any form of matter. ...
... The internal motion of the atoms is called heat energy, because moving particles produce heat. Heat energy can be produced by friction. Heat energy causes changes in temperature and phase of any form of matter. ...
energy
... doing nothing much but "sitting" in the battery being potential, suddenly starts turning into electrical energy. The new electrical energy, formerly known as chemical, zips through some wires to the electric motor that spins the disc. Now the energy that used to be electrical has become the mechanic ...
... doing nothing much but "sitting" in the battery being potential, suddenly starts turning into electrical energy. The new electrical energy, formerly known as chemical, zips through some wires to the electric motor that spins the disc. Now the energy that used to be electrical has become the mechanic ...
Chapter_Superconductivity
... Energy Gap : The energy gap of superconductors is of entirely different nature than the energy gap in insulators. In superconductor the energy gap is due to electron-electron interaction in fermi gas whereas in insulator or semiconductor the energy gap is caused by electron lattice interaction. In i ...
... Energy Gap : The energy gap of superconductors is of entirely different nature than the energy gap in insulators. In superconductor the energy gap is due to electron-electron interaction in fermi gas whereas in insulator or semiconductor the energy gap is caused by electron lattice interaction. In i ...
STATION ONE: What is Potential Energy? Potential energy is the
... is energy from interactions between charged particles; thermal energy, which relates to heat energy of molecules; and nuclear energy, which is energy that’s stored between the particles within atomic nuclei. Light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as gamma rays or X-rays are also tho ...
... is energy from interactions between charged particles; thermal energy, which relates to heat energy of molecules; and nuclear energy, which is energy that’s stored between the particles within atomic nuclei. Light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as gamma rays or X-rays are also tho ...
What is Piezo Electricity
... crystals are mechanically stressed and the converse piezo electric effect is the stress or strain in the crystals when an electric potential is applied. The most common crystals used is lead zirconate titanate crystals. The Piezo effect finds many applications such as the production and detection of ...
... crystals are mechanically stressed and the converse piezo electric effect is the stress or strain in the crystals when an electric potential is applied. The most common crystals used is lead zirconate titanate crystals. The Piezo effect finds many applications such as the production and detection of ...
Chapter 15 overview
... efficiently. Finding ways to use less energy or to use energy more efficiently is known as energy conservation. Examples of energy conservation include • turning off lights when they are not being used • carpooling or using mass transportation such as buses and subways • using energy-efficient appli ...
... efficiently. Finding ways to use less energy or to use energy more efficiently is known as energy conservation. Examples of energy conservation include • turning off lights when they are not being used • carpooling or using mass transportation such as buses and subways • using energy-efficient appli ...
I2 Medical imaging
... • X-rays pass through human (or dog) flesh very easy, but do not pass through bone as easily. ...
... • X-rays pass through human (or dog) flesh very easy, but do not pass through bone as easily. ...
Forms of Energy Web Practice
... ____ 13. After an energy conversion, you end up with the same total amount of energy as the original amount of potential energy. Which of the following laws explains this rule? a. law of energy changes c. law of power and energy b. law of conservation of energy d. law of potential energy ____ 14. Wh ...
... ____ 13. After an energy conversion, you end up with the same total amount of energy as the original amount of potential energy. Which of the following laws explains this rule? a. law of energy changes c. law of power and energy b. law of conservation of energy d. law of potential energy ____ 14. Wh ...
Forces Motion and Energy
... *Fossil fuels are the most important ____nonrenewable______resource. Nonrenewable resources include oil, natural gas, and coal. A. ...
... *Fossil fuels are the most important ____nonrenewable______resource. Nonrenewable resources include oil, natural gas, and coal. A. ...
Extreme Events in Resonant Radiation from Three
... both in the input energy and in the profile of the spatial phase curvature. The extent of the spatial phase variation in the incident plane of the nonlinear crystal considered in the simulations is very weak, of the order of tens of meters at the laser output (i.e. before the actual experimental set ...
... both in the input energy and in the profile of the spatial phase curvature. The extent of the spatial phase variation in the incident plane of the nonlinear crystal considered in the simulations is very weak, of the order of tens of meters at the laser output (i.e. before the actual experimental set ...
File
... You may not know it, but energy is all around us. In fact you are made of energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. In order to do any work you need energy. Electronics use energy, cars use energy and even your body uses energy. The Bulldozer uses energy to move the dirt. ...
... You may not know it, but energy is all around us. In fact you are made of energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. In order to do any work you need energy. Electronics use energy, cars use energy and even your body uses energy. The Bulldozer uses energy to move the dirt. ...
Name: Date: Subject: Energy Objectives Objective 1: ASWBAT to
... You may not know it, but energy is all around us. In fact you are made of energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. In order to do any work you need energy. Electronics use energy, cars use energy and even your body uses energy. The Bulldozer uses energy to move the dirt. ...
... You may not know it, but energy is all around us. In fact you are made of energy. Energy is defined as the ability to do work. In order to do any work you need energy. Electronics use energy, cars use energy and even your body uses energy. The Bulldozer uses energy to move the dirt. ...
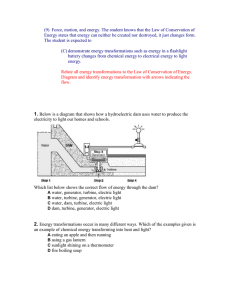
(9) Force, motion, and energy - 2010
... converted to light energy. What happened to the remaining 3 volts? A It is converted to heat energy. B It is converted to chemical energy. C It is converted to kinetic energy. D It is converted to potential energy. 17. Which energy transformation occurs when wood logs are burning in a fireplace? A. ...
... converted to light energy. What happened to the remaining 3 volts? A It is converted to heat energy. B It is converted to chemical energy. C It is converted to kinetic energy. D It is converted to potential energy. 17. Which energy transformation occurs when wood logs are burning in a fireplace? A. ...
energy_forms_and_changes
... Each color of light (Roy G Biv) represents a different amount of electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic Energy is also carried by X-rays, radio waves, and laser ...
... Each color of light (Roy G Biv) represents a different amount of electromagnetic energy. Electromagnetic Energy is also carried by X-rays, radio waves, and laser ...
energy
... – The ability for energy to be transformed automates, lights, entertains, and warms the world in an astounding multitude of ways. ...
... – The ability for energy to be transformed automates, lights, entertains, and warms the world in an astounding multitude of ways. ...
Unit Three Assessment Study Guide
... ____ 21. Matter is needed to transfer thermal energy by a. conduction. c. radiation. b. convection. d. both a and b ____ 22. Disorder in the universe increases because a. spontaneous changes produce more order in a system. b. work produces disorder in a system. c. work produces waste heat, which lea ...
... ____ 21. Matter is needed to transfer thermal energy by a. conduction. c. radiation. b. convection. d. both a and b ____ 22. Disorder in the universe increases because a. spontaneous changes produce more order in a system. b. work produces disorder in a system. c. work produces waste heat, which lea ...
Document
... There are two TYPES of energy: potential and kinetic. Energy can’t be created or destroyed so we need to convert energy we have into what we need. The energy we use comes from many sources: Fossil fuel (coal, oil, natural gas), nuclear power, sun, wind, geothermal, hydropower. Most of this we conver ...
... There are two TYPES of energy: potential and kinetic. Energy can’t be created or destroyed so we need to convert energy we have into what we need. The energy we use comes from many sources: Fossil fuel (coal, oil, natural gas), nuclear power, sun, wind, geothermal, hydropower. Most of this we conver ...
Energy Flow Introduction
... travels in transverse waves. Radiant energy includes visible light, x-rays, gamma rays and radio waves. Light is one type of radiant energy. Sunshine is radiant energy, which provides the fuel and warmth that make life on Earth possible. Thermal Energy, or heat, is the vibration and movement of the ...
... travels in transverse waves. Radiant energy includes visible light, x-rays, gamma rays and radio waves. Light is one type of radiant energy. Sunshine is radiant energy, which provides the fuel and warmth that make life on Earth possible. Thermal Energy, or heat, is the vibration and movement of the ...
Energy Notes
... The energy needed to strike a match is transformed first to thermal energy. The thermal energy causes particles in the match to release the stored chemical energy, which is transferred into thermal energy and the electromagnetic energy you see as light ...
... The energy needed to strike a match is transformed first to thermal energy. The thermal energy causes particles in the match to release the stored chemical energy, which is transferred into thermal energy and the electromagnetic energy you see as light ...
Energy
... • Examples are: light energy, heat energy, mechanical energy, gravitational energy, electrical energy, sound energy, chemical energy, nuclear (atomic) energy. • These forms of energy can be transferred and transformed between one another. This is of immense benefit to us. ...
... • Examples are: light energy, heat energy, mechanical energy, gravitational energy, electrical energy, sound energy, chemical energy, nuclear (atomic) energy. • These forms of energy can be transferred and transformed between one another. This is of immense benefit to us. ...
Energy
... • Examples are: light energy, heat energy, mechanical energy, gravitational energy, electrical energy, sound energy, chemical energy, nuclear (atomic) energy. • These forms of energy can be transferred and transformed between one another. This is of immense benefit to us. ...
... • Examples are: light energy, heat energy, mechanical energy, gravitational energy, electrical energy, sound energy, chemical energy, nuclear (atomic) energy. • These forms of energy can be transferred and transformed between one another. This is of immense benefit to us. ...