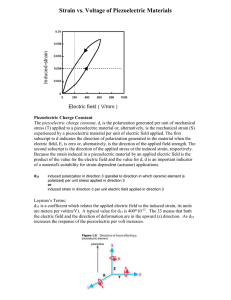
Electrostatics
... orientation or positions of the charges within the atoms and molecules themselves ...
... orientation or positions of the charges within the atoms and molecules themselves ...
PHYS 241 Exam Review
... Gauss’s Law • What does it tell me? – The electric flux (flow) through a closed surface is proportional to the enclosed charge ...
... Gauss’s Law • What does it tell me? – The electric flux (flow) through a closed surface is proportional to the enclosed charge ...
The Millikan Oil Drop Experiment
... pinhole. If the droplet was charged, it could be brought to a halt and held stationary by applying a voltage across the metal plates. When the droplet was stationary, the force exerted by the electrostatic field, EQ (where E is the field and Q is the charge on the droplet), was equal to the weight ...
... pinhole. If the droplet was charged, it could be brought to a halt and held stationary by applying a voltage across the metal plates. When the droplet was stationary, the force exerted by the electrostatic field, EQ (where E is the field and Q is the charge on the droplet), was equal to the weight ...
9/6/16 1 Continuous Charge Distributions: Electric
... Two long, charged concentric cylinders have radii of r1=3.0 cm and r2=6.0 cm. The charge per unit length is 5.0 x 10-6 C/m on the inner cylinder and -7.0 x 10-6 C/m on the outer cylinder. Find the electric field at (a) r = 4.0 cm and (b) r = 8.0 cm, where r is the radial distance from the common axi ...
... Two long, charged concentric cylinders have radii of r1=3.0 cm and r2=6.0 cm. The charge per unit length is 5.0 x 10-6 C/m on the inner cylinder and -7.0 x 10-6 C/m on the outer cylinder. Find the electric field at (a) r = 4.0 cm and (b) r = 8.0 cm, where r is the radial distance from the common axi ...
4 Minute Drill - MrStapleton.com
... • Explain what happens to an electric force as you move farther from the source. • Define polarization. 18.3. Coulomb’s Law • State Coulomb’s law in terms of how the electrostatic force changes with the distance between two objects. • Calculate the electrostatic force between two charged point force ...
... • Explain what happens to an electric force as you move farther from the source. • Define polarization. 18.3. Coulomb’s Law • State Coulomb’s law in terms of how the electrostatic force changes with the distance between two objects. • Calculate the electrostatic force between two charged point force ...
PHY481: Electrostatics Introductory E&M review (2) Lecture 2
... Field of a line of charge - use Gauss’s Law Consider an infinitely long line of charge with linear charge density λ , and a cylindrical gaussian surface. – The electric field is parallel to the surface at the top and bottom of the cylinder, E•dA is zero. – The electric field is perpendicular to t ...
... Field of a line of charge - use Gauss’s Law Consider an infinitely long line of charge with linear charge density λ , and a cylindrical gaussian surface. – The electric field is parallel to the surface at the top and bottom of the cylinder, E•dA is zero. – The electric field is perpendicular to t ...
Voltage and Electric Potential
... conservative vector field. Therefore, we can write any electric field as the gradient of a specific scalar field V ( r ) : ...
... conservative vector field. Therefore, we can write any electric field as the gradient of a specific scalar field V ( r ) : ...
Q1. A hot object and a cold object are placed in thermal contact and
... isolated. They transfer energy until they reach a final equilibrium temperature. The change in the entropy of the hot object (∆Sh), the change in the entropy of the cold object (∆Sc), and the change in the entropy of the combination (∆Stotal) are: A) B) C) D) E) ...
... isolated. They transfer energy until they reach a final equilibrium temperature. The change in the entropy of the hot object (∆Sh), the change in the entropy of the cold object (∆Sc), and the change in the entropy of the combination (∆Stotal) are: A) B) C) D) E) ...
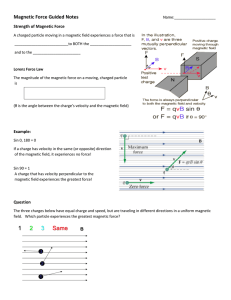
Magnetic Force Guided Notes
... What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on a proton moving at 2.5 X 105 m/s in a magnetic field of 0.5 T … (a) …if the velocity and magnetic field are at right angles? (b) … if the velocity and magnetic field are at 30°? (c) … if the velocity is parallel to a magnetic field? ...
... What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on a proton moving at 2.5 X 105 m/s in a magnetic field of 0.5 T … (a) …if the velocity and magnetic field are at right angles? (b) … if the velocity and magnetic field are at 30°? (c) … if the velocity is parallel to a magnetic field? ...
Field (physics)
In physics, a field is a physical quantity that has a value for each point in space and time. For example, on a weather map, the surface wind velocity is described by assigning a vector to each point on a map. Each vector represents the speed and direction of the movement of air at that point. As another example, an electric field can be thought of as a ""condition in space"" emanating from an electric charge and extending throughout the whole of space. When a test electric charge is placed in this electric field, the particle accelerates due to a force. Physicists have found the notion of a field to be of such practical utility for the analysis of forces that they have come to think of a force as due to a field.In the modern framework of the quantum theory of fields, even without referring to a test particle, a field occupies space, contains energy, and its presence eliminates a true vacuum. This lead physicists to consider electromagnetic fields to be a physical entity, making the field concept a supporting paradigm of the edifice of modern physics. ""The fact that the electromagnetic field can possess momentum and energy makes it very real... a particle makes a field, and a field acts on another particle, and the field has such familiar properties as energy content and momentum, just as particles can have"". In practice, the strength of most fields has been found to diminish with distance to the point of being undetectable. For instance the strength of many relevant classical fields, such as the gravitational field in Newton's theory of gravity or the electrostatic field in classical electromagnetism, is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source (i.e. they follow the Gauss's law). One consequence is that the Earth's gravitational field quickly becomes undetectable on cosmic scales.A field can be classified as a scalar field, a vector field, a spinor field or a tensor field according to whether the represented physical quantity is a scalar, a vector, a spinor or a tensor, respectively. A field has a unique tensorial character in every point where it is defined: i.e. a field cannot be a scalar field somewhere and a vector field somewhere else. For example, the Newtonian gravitational field is a vector field: specifying its value at a point in spacetime requires three numbers, the components of the gravitational field vector at that point. Moreover, within each category (scalar, vector, tensor), a field can be either a classical field or a quantum field, depending on whether it is characterized by numbers or quantum operators respectively. In fact in this theory an equivalent representation of field is a field particle, namely a boson.