Name:
... kinetic energy that was present before the collision is changed into kinetic energy again, the collision is said to be inelastic. Some of the energy is changed into _______ _____. In an elastic collision, momentum is ...
... kinetic energy that was present before the collision is changed into kinetic energy again, the collision is said to be inelastic. Some of the energy is changed into _______ _____. In an elastic collision, momentum is ...
Energy - Learning While Doing
... occur naturally. •Science hasn't found a way to use natural forms of electrical energy, like lightning. Instead, we use different energy sources to create electrical energy by using generators and turbines. ...
... occur naturally. •Science hasn't found a way to use natural forms of electrical energy, like lightning. Instead, we use different energy sources to create electrical energy by using generators and turbines. ...
Netscape: THE ENERGY STORY: Chapter 1
... light and heat energy. If it's nighttime, street lamps are using electrical energy to make light. A car drives by your school or house. It is being powered by gasoline, a type of stored energy. Our bodies eat food, which has energy in it. We use that food to play or study. Energy makes everything ha ...
... light and heat energy. If it's nighttime, street lamps are using electrical energy to make light. A car drives by your school or house. It is being powered by gasoline, a type of stored energy. Our bodies eat food, which has energy in it. We use that food to play or study. Energy makes everything ha ...
types of energy - Warren County Schools
... What is Kinetic Energy? • Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. • An object that has motion - whether it is vertical or horizontal motion has kinetic energy. ...
... What is Kinetic Energy? • Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. • An object that has motion - whether it is vertical or horizontal motion has kinetic energy. ...
Scott Lascelle Bill Davis Nanomaterials Workshop University of
... by submitting hydrogen gas to a high microwave electrical energy. Then methane is introduced into the chamber where the plasma strips the hydrogen from the methane molecule, leaving only the carbon atoms. This then allows the carbon to be deposited on the substrate in the form of carbon nanotubes. ...
... by submitting hydrogen gas to a high microwave electrical energy. Then methane is introduced into the chamber where the plasma strips the hydrogen from the methane molecule, leaving only the carbon atoms. This then allows the carbon to be deposited on the substrate in the form of carbon nanotubes. ...
Study Guide for Unit 2 Test, Energy KEY
... What is the energy stored in compounds that changes as the bonds are rearranged forming new compounds? ...
... What is the energy stored in compounds that changes as the bonds are rearranged forming new compounds? ...
lesson plan
... cable ties or even a tightly tied sling made from cut up plastic supermarket bags. The thin rope needs to be tied slightly down from the top on each side of each ball. For best effect and most fun you need a minimum of three balls. More is better! Start as Jiwi did by lifting one ball and releasing ...
... cable ties or even a tightly tied sling made from cut up plastic supermarket bags. The thin rope needs to be tied slightly down from the top on each side of each ball. For best effect and most fun you need a minimum of three balls. More is better! Start as Jiwi did by lifting one ball and releasing ...
PowerPoint Lecture
... • Different materials have different capacities for heat – Add the same energy to different materials, and you’ll get different temperature rises – Quantified as heat capacity – Water is exceptional, with 4,184 J/kg/ºC – Most materials are about 1,000 J/kg/ºC (including wood, air, metals) ...
... • Different materials have different capacities for heat – Add the same energy to different materials, and you’ll get different temperature rises – Quantified as heat capacity – Water is exceptional, with 4,184 J/kg/ºC – Most materials are about 1,000 J/kg/ºC (including wood, air, metals) ...
File
... are those types of energy that can be seen to change from one type to another, i.e. you see two types of energy. Examples include fireworks ...
... are those types of energy that can be seen to change from one type to another, i.e. you see two types of energy. Examples include fireworks ...
Lesson Plan
... from one form to another. Energy exists in daily life and one should know where it exists, in what form it exists, how it can be transferred and its impact on the world. Content: The concepts included are relevant to middle school or early secondary science students. This lesson introduces the conce ...
... from one form to another. Energy exists in daily life and one should know where it exists, in what form it exists, how it can be transferred and its impact on the world. Content: The concepts included are relevant to middle school or early secondary science students. This lesson introduces the conce ...
TYPES OF ENERGY
... source that we can use over and over again) and nonrenewable/conventional (an energy source that we are using up and cannot recreate in a short period of time). Renewable energy sources include solar energy (which comes from the sun and can be turned into electricity and heat), wind energy, geotherm ...
... source that we can use over and over again) and nonrenewable/conventional (an energy source that we are using up and cannot recreate in a short period of time). Renewable energy sources include solar energy (which comes from the sun and can be turned into electricity and heat), wind energy, geotherm ...
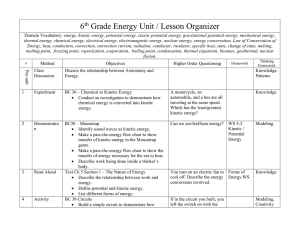
6th Grade Energy Unit / Lesson Organizer Domain Vocabulary
... Domain Vocabulary: energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, elastic potential energy, gravitational potential energy, mechanical energy, thermal energy, chemical energy, electrical energy, electromagnetic energy, nuclear energy, energy conservation, Law of Conservation of Energy, heat, conduction, ...
... Domain Vocabulary: energy, kinetic energy, potential energy, elastic potential energy, gravitational potential energy, mechanical energy, thermal energy, chemical energy, electrical energy, electromagnetic energy, nuclear energy, energy conservation, Law of Conservation of Energy, heat, conduction, ...
04_lecture_ppt - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • A measure of the internal energy that has been absorbed or transferred from another object • Two related processes – “Heating” = increasing internal energy – “Cooling” = decreasing internal energy ...
... • A measure of the internal energy that has been absorbed or transferred from another object • Two related processes – “Heating” = increasing internal energy – “Cooling” = decreasing internal energy ...
Let`s Convert Energy
... chemical energy, while hot objects contain thermal energy. A machine with moving parts or a moving fluid has mechanical energy. Charged objects are filled with electrical energy, and radioactive elements such as uranium contain nuclear energy. Another important concept of energy is that it may chang ...
... chemical energy, while hot objects contain thermal energy. A machine with moving parts or a moving fluid has mechanical energy. Charged objects are filled with electrical energy, and radioactive elements such as uranium contain nuclear energy. Another important concept of energy is that it may chang ...
Optically pumped solid
... return to a lower level. In ordinary light sources the many excited atoms or molecules emit light independently and in many different colours (wavelengths). If, however, during the brief instant that an atom is excited, light of a certain wavelength impinges on it, the atom can be stimulated to emit ...
... return to a lower level. In ordinary light sources the many excited atoms or molecules emit light independently and in many different colours (wavelengths). If, however, during the brief instant that an atom is excited, light of a certain wavelength impinges on it, the atom can be stimulated to emit ...
Energy Matters - Summary Notes.CWK (DR)
... being produced by other power stations, water is pumped back into the reservoir. This stores energy and during the day the water can be allowed to flow back down to produce electricity just like a normal power station. Such a system saves energy and also can be turned on quickly at times of peak dem ...
... being produced by other power stations, water is pumped back into the reservoir. This stores energy and during the day the water can be allowed to flow back down to produce electricity just like a normal power station. Such a system saves energy and also can be turned on quickly at times of peak dem ...
Roller Coaster Fun!
... friction plays a part in the ride. Therefore, they make each successive hill lower so that the coaster will be able to make it over each peak.7 Coaster designers also take advantage of friction to slow the coaster and bring it to a safe stop when breaks are applied at the end of the ride. Friction i ...
... friction plays a part in the ride. Therefore, they make each successive hill lower so that the coaster will be able to make it over each peak.7 Coaster designers also take advantage of friction to slow the coaster and bring it to a safe stop when breaks are applied at the end of the ride. Friction i ...
Answer Review Worksheet Day 9
... 4. When a pole-vaulter flexes the pole, the pole-vaulter increases the pole’s elastic potential energy and transforms it to increase the pole-vaulter’s gravitational potential energy. ...
... 4. When a pole-vaulter flexes the pole, the pole-vaulter increases the pole’s elastic potential energy and transforms it to increase the pole-vaulter’s gravitational potential energy. ...
Calculating potential and kinetic energy
... In the International System of Units (the SI system), the unit of energy is the joule. The specific heat capacity (or just specific heat) of a material is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram (g) of the material 1 degree Celsius (°C). It takes 4.18 joules to rais ...
... In the International System of Units (the SI system), the unit of energy is the joule. The specific heat capacity (or just specific heat) of a material is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram (g) of the material 1 degree Celsius (°C). It takes 4.18 joules to rais ...