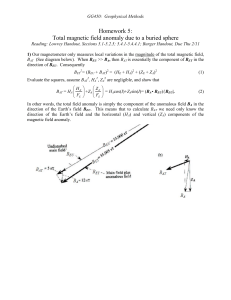
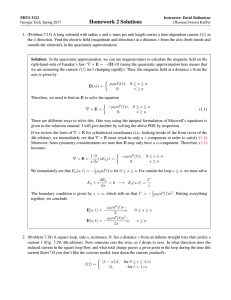
Total field anomaly over a sphere
... over the buried sphere (see diagram to the right). It turns out that the magnetic field due to a sphere with uniform magnetization M and radius a is identical to that of a magnetic dipole with a dipole moment m = (4/3a3)M. The Matlab function “dipole.m” takes m and I (for both the Earths field and ...
... over the buried sphere (see diagram to the right). It turns out that the magnetic field due to a sphere with uniform magnetization M and radius a is identical to that of a magnetic dipole with a dipole moment m = (4/3a3)M. The Matlab function “dipole.m” takes m and I (for both the Earths field and ...
Magnetic dipole moment of a moving electric dipole
... The transformation (3) of Fisher Rwas arrived at using the standard definition m = (1/2c) d3 r r × J. The origin of this definition is in a multipole expansion of the vector potential of a localized current distribution that is assumed to be divergenceless, i.e. ∇ · J = 0, so that the value of m is ...
... The transformation (3) of Fisher Rwas arrived at using the standard definition m = (1/2c) d3 r r × J. The origin of this definition is in a multipole expansion of the vector potential of a localized current distribution that is assumed to be divergenceless, i.e. ∇ · J = 0, so that the value of m is ...
Magnets Notes
... moving charges (Sects. 20.2-20.4). Charges moving perpendicularly to a magnetic field B go in circles whose radius R is proportional to their momentum over B; from this the mass of ions and charged molecules can be determined. Before getting to the magnets notes, here is a brief summary. 1. Magnets ...
... moving charges (Sects. 20.2-20.4). Charges moving perpendicularly to a magnetic field B go in circles whose radius R is proportional to their momentum over B; from this the mass of ions and charged molecules can be determined. Before getting to the magnets notes, here is a brief summary. 1. Magnets ...
Electric forces and electric fields
... • It is directing along a line joining the two particles and is inversely proportional to the square of the separation distance r, between them ...
... • It is directing along a line joining the two particles and is inversely proportional to the square of the separation distance r, between them ...
The Magnetosphere
... field, f is the azimuthal angle, r is the radial distance, wE is the angular frequency of the Earth, ...
... field, f is the azimuthal angle, r is the radial distance, wE is the angular frequency of the Earth, ...
NO CELL PHONES, TEXT MSG, etc. ALLOWED AT
... In path 1, the force on the charge is to the left and the displacement is to the right. The work done by the field is negative. In path 2, a component of the force is in the same direction as the displacement of the charge. The work done by the field is positive. In path 3, no work is done when the ...
... In path 1, the force on the charge is to the left and the displacement is to the right. The work done by the field is negative. In path 2, a component of the force is in the same direction as the displacement of the charge. The work done by the field is positive. In path 3, no work is done when the ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.